* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ElectromagnetismPresentation
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
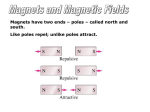
Electromagnetism What is a Magnet? A magnet is a body which attracts iron and other combinations of metals with iron. The magnet can "magnetize" other objects which in turn act like magnets. Magnetic Poles • Every magnet has two poles, a south pole and a north pole. • Similar to electric charges, opposite poles attract and like poles repel each other. Magnetic Poles • North poles and south poles always exist in pairs. You can never have two south poles or two north poles on the same magnet. Even if you cut the magnet in half. Earth’s Magnetic Field • Earth’s molten iron core creates a magnetic field. Earth’s Magnetic Field Protects Us • Earth’s magnetic field deflects the sun’s dangerous solar wind around the planet. Solar Wind Magnetic Fields • Magnetism is very much related to electricity. • Just as an electric charge is surrounded by an electric field, the same charge is also surrounded by a magnetic field if it is moving. • Charged particles in motion create both electric fields and magnetic fields. How is a magnetic field created? • If moving charged particles create magnetic fields, then what creates the magnetic field in a bar magnet? How is a magnetic field created? • Electrons orbiting in iron atoms create the magnetic fields of magnets. Electric Currents and Magnetic Fields • Current carrying wires produce magnetic fields that are circular and perpendicular to the direction of the current. Electric Currents and Magnetic Fields • We know the direction of the magnetic field by using the Right-Hand-Rule. Magnetic Field in a Coil Magnetic Field in a Coil • By putting a current through looped wire, a strong magnet can be created. Electric Motors • By passing a current through a loop that is between two magnets, a simple motor can be made.