* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - U of M Physics
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
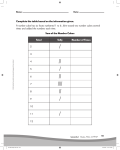
Physics 1102 Week 8 Discussion Spring 2014 Coulomb: F = kqr12q2 , where k = 9 ⇥ 109 N m2 /C2 . e = 1.6 ⇥ 10 19 C F = Gmr12m2 , where G = 6.67 ⇥ 10 11 N m2 /kg2 (Gravitational Force Law) ~ F~on q = q E MC1. The diagram shows two pairs of heavily charged plastic cubes. Cubes 1 and 2 attract each other and cubes 1 and 3 repel each other. Which of the following illustrates the forces of cube 2 on cube 3 and cube 3 on cube 2? MC2. Two particles have charges Q and Q (equal magnitude and opposite sign). For a net force of zero to be exerted on a third charge it must be placed: (A) midway between Q and -Q (B) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining Q and -Q, but not on that line itself (C) on the line joining Q and -Q, to the side of Q opposite -Q (D) on the line joining Q and -Q, to the side of -Q opposite Q (E) at none of these places (there is no place) MC3. The figure shows three electric charges labeled Q1 , Q2 , Q3 , and some electric field lines in the region surrounding the charges. What are the signs of the three charges? (A) Q1 is positive, Q2 is negative, Q3 is positive. (B) Q1 is negative, Q2 is positive, Q3 is negative. (C) Q1 is positive, Q2 is positive, Q3 is negative. (D) All three charges are negative. (E) All three charges are positive. MC4. An electron is initially moving to the right when it enters a uniform electric field directed upwards. Which trajectory shown below will the electron follow? (A) trajectory W (B) trajectory X (C) trajectory Y (D) trajectory Z (E) the electron will be deflected out of the page Physics 1102 Week 8 Discussion Spring 2014 Coulomb: F = kqr12q2 , where k = 9 ⇥ 109 N m2 /C2 . e = 1.6 ⇥ 10 19 C F = Gmr12m2 , where G = 6.67 ⇥ 10 11 N m2 /kg2 (Gravitational Force Law) ~ F~on q = q E MC1. The diagram shows two pairs of heavily charged plastic cubes. Cubes 1 and 2 attract each other and cubes 1 and 3 repel each other. Which of the following illustrates the forces of cube 2 on cube 3 and cube 3 on cube 2? MC2. Two particles have charges Q and Q (equal magnitude and opposite sign). For a net force of zero to be exerted on a third charge it must be placed: (A) midway between Q and -Q (B) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining Q and -Q, but not on that line itself (C) on the line joining Q and -Q, to the side of Q opposite -Q (D) on the line joining Q and -Q, to the side of -Q opposite Q (E) at none of these places (there is no place) MC3. The figure shows three electric charges labeled Q1 , Q2 , Q3 , and some electric field lines in the region surrounding the charges. What are the signs of the three charges? (A) Q1 is positive, Q2 is negative, Q3 is positive. (B) Q1 is negative, Q2 is positive, Q3 is negative. (C) Q1 is positive, Q2 is positive, Q3 is negative. (D) All three charges are negative. (E) All three charges are positive. MC4. An electron is initially moving to the right when it enters a uniform electric field directed upwards. Which trajectory shown below will the electron follow? (A) trajectory W (B) trajectory X (C) trajectory Y (D) trajectory Z (E) the electron will be deflected out of the page Electric vs Gravitic What is the electric force between a proton and an electron separated by one angstrom? The angstrom is a unit of measurment used somethimes in optics: 1Å= 10 10 m. (b) What is the gravitational force between a proton and an electron at the same separation? (The mass of a proton is about 1.67 ⇥ 10 27 kg and the electron mass is roughly 9.11 ⇥ 10 31 kg. (c) Reflecting on your answers for parts (a) and (b), do we need to consider gravity when studying atomic forces? Your Dryer is an Electrostatics Discussion Inducing Machine You and a friend are doing the laundry when you unload the dryer and, being inquisitive 1102 students, you begin discussing static electricity. Your friend wants to get some idea of the amount of charge that causes static cling. You immediately dive into the recycling bin and rescue two empty soda cans, each with mass 120 grams, and perfect conductors! You tie the cans to the two ends of a (non conducting) string (one to each end) and hang the center of the string over a nail sticking out of the wall. Each can now hangs straight down 30 cm from the nail. Luckily, your nonconducting robotic arm is also in the laundry room, so you program the robot to take your maroon and gold flannel shirt from the dryer and touch it to the cans, which are initially in contact. The cans move apart until they each hang stationary at an angle of 10 from the vertical. (a) Assuming that there are equal amounts of charge on each can, calculate the amount of charge transferred from your shirt to each can. (b) How many electrons are transferred between the shirt and each can? (c) Sketch the electric field of these cans. Phys 1102 March 13, 2014 Solution from Prof. Wynveen. Thanks!