* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cardiac impulse
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
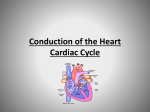
12/10/11 Miss Radford Control of the cardiac cycle WAL: about how the cardiac cycle is regulated and controlled. Some Most All • How are the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node and bundle of His involved in controlling the cardiac cycle? • What is myogenic stimulation of the heart? • What are “cardiac output” and “stroke volume” and how can these be calculated? Your progress test on Cells will be on: • Tuesday 3rd March • Homework – revision and heart and lungs sections of unit 1 booklets (due in the following week) plus any left over disease sections from the first part of the booklet (due 10th March)!! Today we are covering from the specification: Starter – refresh your mind • Complete the heart structure worksheet to recap how blood flows through the heart. • Use the information sheet attached to help you. 2. Which chambers of the heart have thicker walls? 3. Relate the thickness of the chambers to their functions. 4. What is the function of the valves? Label the valves on the diagram above. 5. What is the type of muscle that makes up the walls of the heart? Why is it so special, and how does it maintain a constant blood supply? 6. Trance the pathway a drop of blood would take from the time it leaves the aorta, to the time it returns to the left ventricle ready to leave the aorta again, describing the chambers and vessels. Challenge: can you write these as numeric equations? Definitions Heart rate = # beats • Heart rate: number of heartbeats per minute minute • Stroke volume: volume of blood (cm3) pumped by heart in 1 beat Stroke Volume = blood cm3 beat • Cardiac output: stroke volume multiplied by the 3 Xblood heart rateOutput gives the amount (cm=3)blood pumped Cardiac = blood cmof # beats minute minute by heart in 1 minute beats Get out your calculators! Heart rate (beats/min) Stroke Volume (cm3/beat) At rest 75 75 During exercise 180 120 Cardiac Output (cm3/min) 5,625 21,600 The Cardiac Cycle • • • • • Cardiac Cycle - The events of one heart beat One cycle – 0.8 second (72 cycles a minute) 2 main processes – contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle; Diastole – lasts 0.5 seconds, represents the relaxation phase, chambers fill with blood Systole – lasts 0.3 seconds, represents the contraction phase, blood pushed out of chambers/heart The Heart’s Conduction System • The heart is myogenic • This means it generates its own electrical impulse • The impulse that it generates is spread throughout the heart and causes it to contract • This is known as the cardiac impulse The Spread of the Electrical Impulse • The impulse starts in the SA Node (located at the top of the right atrium) • Called the pacemaker • The impulse travels through the atria walls • This causes both atria to contract • The cardiac impulse then reaches the AV node • Also located in the right atrium • The AV node helps delay the impulse to allow the atria to finish their contraction • It then spreads the impulse down the bundle of His • This is located in the Septum of the heart • The bundle of His splits into left and right branches • The impulse spreads around the ventricle walls through a network of purkinje fibres • This causes both ventricles to contract • The ventricles then relax • The cycle is repeated with the next cardiac impulse Cardiac Impulse • http://video.about.com/heartdisease/Conduc tion-System.htm Q. Describe how the sinoatrial node (SAN) and the atrioventricular node (AVN) control the increase in heart rate during exercise • • • • • • • • • • SAN initiates heart beat/sends impulses; intrinsic/myogenic/pacemaker; spread of impulses through atria; atria contracts/systole; impulse reaches AV Node; Reduced delay of spread of impulses; Bundle of His; Purkinje fibres conducting impulses; ventricular systole/contraction; period of diastole/relaxation for filling; Task – demonstrate your understanding • Read pages 92 & 93 of your textbook. • Answer questions 1 to 5.