* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s Laws 1.The First Law: Force and Inertia 2.The Second Law
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
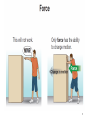
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton’s Laws 1.The First Law: Force and Inertia 2.The Second Law: Force = Mass x Acceleration 3.The Third Law: Action and Reaction 1 Objectives – today & tomorrow 1)Describe how the law of inertia affects the motion of an object. 2)Describe balanced and unbalanced forces. Calculate the net force for two or more forces acting on an object. Review examples. 3)Measure and describe force in terms of newtons (N). Explain where the unit of force a newton (N) comes from. 2 The First Law: Inertia states that a body at rest will stay at rest and a body in motion will stay in motion, unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Newton’s First Law Video http://my.hrw.com/sh2/sh07_10/student/flash/visual_concepts/70587.htm 3 Force: is an action that can change motion. A force is what we call a push or a pull, or any action that has the ability to change an object’s motion. Forces can be used to increase or decrease the speed of an object, or change the direction of motion. 4 5 Inertia: is the term used to describe an object’s ability to resist any change in its state of motion. An object with a lot of inertia takes a lot of force to start or stop it. Meanwhile an object with less inertia requires a small amount of force to start or stop. Inertia is a property of matter. A body will keep moving at a constant speed and in the same direction until an unbalanced force acts on it. 6 Which systems in a car overcome the law of inertia and how? “Take a moment to fill in blanks.” The _________ supplies force that allows you to change motion by pressing the gas pedal. The _________are designed to help you change your motion by slowing down. The ___________is designed to help you change your motion by changing your direction. 7 What happens in a crash? Inertia can explain what happens in a car crash. When a car traveling about 40mph collides head-on with something solid, the car crumples, slows down, and stops within approximately 0.1 s. Any passenger not wearing a safety belt continues to move forward at the same speed the car was traveling. 8 Q1 A force is a ___________. A force is a push or pull. Forces, such as the force of the atmosphere against a person’s body, are not always noticeable. 9 Q 2 - When are forces on an object balanced? When forces are equal in size and opposite in direction, they are balanced forces, and the net force is zero. The object is at rest. 10 Q3 - Inertia is …… A. the tendency of an object to have a positive acceleration B. the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion C. The tendency of an object to have a net force of zero. D. The tendency of an object to change in speed or direction. 11 NEXT Complete / see Mental Map of Force = mass x acceleration Where does the SI Unit of Force (N) for newton named after Sir Isaac Newton come from and how is it built? 12