* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
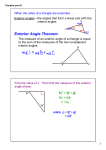
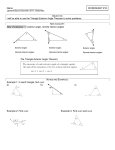
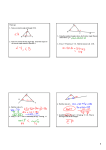
Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems CK12 Editor Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based collaborative model termed the FlexBook®, CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning, powered through the FlexBook Platform®. Copyright © 2012 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution/NonCommercial/Share Alike 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-SA) License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/terms. Printed: September 26, 2012 AUTHOR CK12 Editor www.ck12.org C ONCEPT Concept 1. Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems 1 Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems Learning Objectives • • • • Identify interior and exterior angles in a triangle. Understand and apply the Triangle Sum Theorem. Utilize the complementary relationship of acute angles in a right triangle. Identify the relationship of the exterior angles in a triangle. Interior and Exterior Angles The terms interior and exterior help when you need to identify the different angles in triangles. The three angles inside the triangles are called interior angles. On the outside, exterior angles are the angles formed by extending the sides of the triangle. The exterior angle is the angle formed by one side of the triangle and the extension of the other. The angles on the inside of a triangle are called __________________ angles. The angles on the outside of a triangle are called _________________ angles. You can see that the words “interior” and “exterior” share the same 6 letters at the end “-terior.” However, they have different prefixes: 1 www.ck12.org “in-” means “inside” and “ex-” means “outside.” Can you think of some other pairs of words that share an ending but have opposite prefixes “in” and “ex”? internal and external include and exclude ... ? Note: In triangles and other polygons there are TWO sets of exterior angles, one “going” clockwise, and the other “going” counterclockwise. Clockwise goes around a circle in the same direction as a clock tells time: Counterclockwise goes around a circle in the opposite direction as a clock tells time: The following diagram helps you see the difference between counterclockwise exterior angles and clockwise exterior angles on the same triangle: 2 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems Exterior angles can be measured in two directions, ______________ and ________________ - __________________. Linear Pair Postulate If you look at one vertex of the triangle, you will see that the interior angle and an exterior angle form a linear pair. Based on the Linear Pair Postulate, we can conclude that interior and exterior angles at the same vertex will always be supplementary. This tells us that the two exterior angles at the same vertex are congruent. 3 www.ck12.org The two exterior angles at the same vertex are _____________________. Example 1 What is m6 RQS in the triangle below? interior angle + exterior angle = 180◦ m6 RQS + 115 = 180 −115 − 115 m6 RQS = 65 Thus, m6 RQS = 65◦ Reading Check: 1. What is m6 ABC in the triangle below? 4 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems 2. What other angle in the triangle above would be congruent to 6 ABC? Why? Triangle Sum Theorem The sum of the measures of the interior angles in a triangle is 180◦ . • All three angles in a triangle add up to ___________________. Regardless of whether the triangle is right, obtuse, acute, scalene, isosceles, or equilateral, the interior angles will always add up to 180◦ . Examine each of the triangles shown below. Notice that each of the triangles has an angle that sums to 180◦ . 100◦ + 40◦ + 40◦ = 180◦ 90◦ + 30◦ + 60◦ = 180◦ 45◦ + 75◦ + 60◦ = 180◦ Reading Check: 1. True or false: The interior angles of only right triangles sum to 180◦ . 2. True or false: The interior angles of scalene triangles are equiangular and sum to 180◦ . 3. Draw a triangle below and label each of the three interior angles. Show your work to make sure your angles add up to 180◦ . + + = 180◦ You can also use the Triangle Sum Theorem to find a missing angle in a triangle. Set the sum of the angles equal to 180◦ and solve for the missing value. Example 2 What is m6 T in the triangle below? 5 www.ck12.org Set up an equation where the three angle measures sum to 180◦ . Then, solve for m6 T . 82◦ + 43◦ + m6 T = 180◦ 125 + m6 T = 180 −125 − 125 m6 T = 55 Thus, m6 T = 55◦ Reading Check: What is m6 Y in the triangle below? Acute Angles in a Right Triangle Expanding on the Triangle Sum Theorem, you can find more specific relationships. For example, in any right triangle, by definition, one of the angles will measure 90◦ . This means that the sum of the other two angles will always be 90◦ , resulting in a total sum of 180◦ (since 90 + 90 = 180). Therefore, the two acute angles in a right triangle will always be complementary. • In a right triangle, the two acute angles will add up to _______________. 6 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems Example 3 What is the measure of the missing angle g in the triangle below? Since the triangle above is a right triangle, the two acute angles must be complementary, which means their sum will be 90◦ . We will represent the missing angle with the variable g and write an equation. The two acute angles are __________________ and __________________ so: 38◦ + g = 90◦ Now we can use inverse operations to isolate the variable, and then we will have the measure of the missing angle. 38 + g = 90 − 38 − 38 g = 52 The measure of the missing angle g is 52◦ Reading Check: 1. True or false: In a right triangle, the right angle is 90◦ and the other two angles are equiangular. 2. Why are the two acute angles in a right triangle complementary but not supplementary? Explain. 3. What is the measure of the missing angle a in the triangle below? 7 www.ck12.org Exterior Angles in a Triangle Recall that the exterior and interior angles around a single vertex create a linear pair, so they add up to 180◦ as shown below. 120◦ + 60◦ = 180◦ A linear pair describes two angles that add up to ________________. Imagine an equilateral triangle and the exterior angles it forms, like in the diagram below. Since each interior angle measures 60◦ in an equilateral triangle, each exterior angle will measure 120◦ . 8 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems • Every interior angle in an equilateral (or equiangular) triangle equals ______________. • Every exterior angle in an equilateral (or equiangular) triangle equals ______________. What is the sum of the three exterior angles? Add them to find out: 120◦ + 120◦ + 120◦ = 360◦ The sum of these three exterior angles is 360◦ . The sum of the exterior angles in any triangle will always be equal to 360◦ . • For any triangle, all exterior angles will add up to ________________. You can use this information just as you did the Triangle Sum Theorem to find missing angles and measurements. As a review, The Triangle Sum Theorem says that all _________________ angles in a triangle add up to 180◦ . We just discovered that all __________________________ angles in a triangle add up to 360◦ . Example 4 What is the value of the angle P in the triangle below? 9 www.ck12.org You can set up an equation relating the three exterior angles to 360◦ . Notice that p is an interior angle in the triangle, not an exterior angle, so be careful with how you set up this equation! Solve for the value of the exterior angle. Let’s call the measure of the exterior angle e. Label e in the diagram above. Now, set up an equation with the sum of the exterior angles equal to 360◦ : 130◦ + 110◦ + e = 360◦ 240◦ + e − 240◦ = 360◦ − 240◦ e = 120◦ The missing exterior angle measures 120◦ . However, this is not your final answer! You have one more step to find the value of p. You can use e (that you found above) to find p because the interior and exterior angles (angle e and angle p) form a linear pair. Linear pairs add up to _______________ so: 120◦ + p = 180◦ − 120◦ − 120◦ p = 60◦ Your final answer for the measure of angle p is 60◦ ! Exterior Angles in a Triangle Theorem In a triangle, the measure of an exterior angle is equal to the sum of the remote interior angles. Look at the diagram from the previous example for a moment. If we focus on the exterior angle at angle D, then the interior angles at angles A and B are called remote interior angles. Every exterior angle has 2 remote interior angles that correspond to it: 10 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Triangle Sum and Exterior Angle Theorems The 120◦ exterior angle at 6 D above has 2 remote ____________________________ angles, one at angle __________ and the other at angle __________. Notice that the exterior angle at point D measured 120◦ . At the same time, the interior angle at point A measured 70◦ and the interior angle at point B measured 50◦ . The sum of interior angles m6 A + m6 B = 70◦ + 50◦ = 120◦ Notice the measures of the remote interior angles sum to the measure of the exterior angle at point D. This relationship is always true, and it is a result of the Linear Pair Postulate and the Triangle Sum Theorem. • The measure of an exterior angle is equal to the ______________ of the measures of its ______________________ interior angles. Reading Check: 1. To what angle measure do all three interior angles in a triangle sum? 2. To what angle measure do all three exterior angles in a triangle sum? 3. Name the two remote interior angles to the exterior angle at point H in the diagram below. 4. Find the measure of the exterior angle at point H in the diagram above. 5. When used as an adjective, the word “remote” means “removed in space, time, or relation.” Based on this definition, why do you think that word is used to identify a particular set of interior angles in a triangle? 6. Can you think of another way to find the measure of the exterior angle at point H? Describe your step-by-step method: 11 www.ck12.org Graphic Organizer for Lesson 2 TABLE 1.1: Angle Sums in a Triangle Angles All three interior angles in a triangle All three clockwise exterior angles of a triangle All three counter clockwise exterior angles of a triangle The two acute angles in a right triangle One interior angle in a triangle and the exterior angle at the same vertex Two remote interior angles in a triangle 12 Draw a picture of the angles What do these angles add up to?