* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 210B
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
History of phycology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
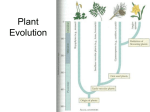
BIOLOGY 210B Diversity of Plants – An Overview Agenda • Plant Diversity Overview • What are green plants? • Terrestrial adaptations • The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • Green Algae • Bryophytes • Tracheophytes Green Plants (Viridiplantae) non-vascular plants Green algae vascular plants (tracheophytes) Bryophytes seedless plants chlorphytes Mosses lycophytes charophytes Hornworts ferns (pteridophytes) Liverworts seed plants gymnosperms (coniferophytes) angiosperms (anthophytes) monocots dicots/eudicots Plant Diversity Overview Agenda • Plant Diversity Overview • What are green plants? • Terrestrial adaptations • The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • Green Algae • Bryophytes • Tracheophytes What are green plants? • Green Plants (Viridiplantae) all share: • Rigid cell walls containing cellulose • Are generally photoautotrophs • Exhibit Alternation of generation • Multicellular gametophyte (n) stage & multicellular sporophyte (2n) stage • Reproduce sexually • But still able to reproduce asexually All terrestrial plants are derived from the green algae - charophyta Agenda • Plant Diversity Overview • What are green plants? • Terrestrial adaptations • The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • Green Algae • Bryophytes • Tracheophytes Terrestrial Adaptations 1. Protection from desiccation • Waxy cuticle and stomata Terrestrial Adaptations 2. Moving water using tracheids • Tracheophytes have tracheids • Xylem – vascular tissue used to conduct mainly water • Usually adaxial • • • In a stem it is more central In a leaf it is toward the upper side Phloem – vascular tissue used to conduct products of photosynthesis • Usually abaxial • • In a stem it is more peripheral In a leaf it is toward the underside Agenda • Plant Diversity Overview • What are green plants? • Terrestrial adaptations • The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • Green Algae • Bryophytes • Tracheophytes The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • All land plants are haplodiplontic • It is an alternation of generation between • The diploid sporophyte and the haploid gametophyte • Mulitcellular haploid and diploid life stages • We are diplontic The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • There are differences between the major groups • Mosses • Dominant is the gametophyte • Sporophyte is reduced and dependent on the gametophyte • Angiosperms • Dominant is the sporophyte • Gametophyte is reduced and dependent on the sporophyte The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • There are differences between the major groups • Mosses • Dominant is the gametophyte • Sporophyte is reduced • Angiosperms • Dominant is the sporophyte • Gametophyte is reduced and dependent on the sporophyte Agenda • Plant Diversity Overview • What are green plants? • Terrestrial adaptations • The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • Green Algae • Bryophytes • Tracheophytes Green Algae algae • Streptophytes – Gave rise to land plants • Modern chlorophytes closely resemble land plants • Chloroplasts are biochemically similar to those of the plants Liverworts • Chlorophytes – Gave rise to aquatic Charophytes lineages Chlorophytes • Green algae have two distinct Green Algae - Chlorphytes • Early green algae probably resembled Chlamydomonas reinhardtiii • Individuals are microscopic • 2 anterior flagella • Most individuals are haploid • Reproduces asexually and sexually • Not haplodiplontic (but still have alternation of generation) • Always unicellular Green Algae - Chlorophyta • Volvox • Colonial chlorophyte • Hollow sphere of a single layer of 500–60,000 cells • Individual cells each have two flagella • Few cells are specialized for reproduction • Asexual or sexual Green Algae - Chlorophyta • Ulva • Multicellular chlorophyte • Haplodiplontic life cycle • Gametophyte and sporophyte have identical appearance • No ancestral chlorophytes gave rise to land plants Green Algae - Charophytes • Gave rise to land plants • Charophytes have haplontic life cycles • Evolution of diplontic embryo and haplodiplontic life cycle occurred after move to land • 2 candidate Charophyta clades • Charales • Coleochaetales • Both charophyte clades form green mats around the edges of freshwater ponds and marshes • One species must have successfully inched its way onto land through adaptations to drying Chara Coleochaete Agenda • Plant Diversity Overview • What are green plants? • Terrestrial adaptations • The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • Green Algae • Bryophytes • Tracheophytes • Do have other conducting cells • but lack lignin in cell walls & therefore are not like the tracheids in vascular plants • Simple, but highly adapted to diverse terrestrial environments • 24,700 species in 3 clades • Liverworts • Mosses • Hornworts • Gametophyte – conspicuous and photosynthetic • Sporophytes – small and dependent & unbranched with a single sporangium • Require water for sexual reproduction Tracheophytes Hornworts Mosses first land plants • Called nontracheophytes because they lack tracheids Liverworts • Closest living descendants of the Charophytes The Bryophytes Bryophytes • Some confusion exists due to presence of vascular tissue (even though it does not have lignin) • To call them “non-vascular” then is slightly misleading, as extinct groups had vessels and mosses have vessels • Bryophytes however have a sporophyte that is unbranched and produces only one sporangium • All other land plants have branched sporophytes and carries multiple sporangia (polysporangiophytes) Byrophytes - Liverworts • Have flattened gametophytes with liverlike lobes • The majority look like mosses • Form gametangia in umbrella-shaped structures • Contain apical pores for gas exchange • Can’t close like stomata! • Also undergo asexual reproduction Bryophytes – the Mosses • Gametophytes consist of small, leaflike structures around a stemlike axis • Not true leaves – no true vascular tissue (lignins are absent) • Anchored to substrate by rhizoids • Rhizoids also contains cells that absorb water! • Some mosses also have cells to transport nutrients • Multicellular gametangia form at the tips of gametophytes • Archegonia – Female gametangia • Antheridia – Male gametangia • Flagellated sperm must swim in water Bryophytes – the Mosses Bryophytes - Hornworts • Sporophyte is photosynthetic (only one in the bryophytes) • Cells have a single large chloroplast • Has a stomata • Sporophyte embedded in gametophyte tissue The Tracheophytes • Cooksonia, the first vascular land plant • Appeared about 420 MYA • Phylum Rhyniophyta • Only a few centimeters tall • No roots or leaves • Homosporous – only 1 type of spore • Contain vascular tissue • Xylem • Conducts water and minerals • Phloem • Conducts products of photosynthesis • Location of these? • What did true vascular tissues allow for? • Cuticle and stomata also present in the tracheophytes Agenda • Plant Diversity Overview • What are green plants? • Terrestrial adaptations • The Haplodiplontic Life Cycle • Green Algae • Bryophytes • Tracheophytes Tracheophytes • Vascular plants include seven extant phyla grouped in three clades Lycophytes (club mosses) 2. Pterophytes (ferns, whisk ferns, and horsetails) 3. Seed plants • Structures/adaptations to land 1. • Roots • Increased stability • Increased transport of water/nutrients • Leaves • Increase surface area… for? • Evolved twice • Lycophylls – found in seed plants only • Euphylls – (true leaves) are found in ferns and seed plands • Only took ~400 MY between vascular tissue and first true leaves • Seeds • Resistant • Built in food supply • Only in gymnosperms & angiosperms Tracheophytes Chlorophytes Charophytes Liverworts Mosses Hornworts Lycophytes Ferns + Allies Gymnosperms Angiosperms Flowers Fruits Seeds Euphylls Stems, roots, leaves Dominant sporophyte Vascular tissue Stomata Multicellular embryo Antheridia and archegonia Cuticle Plasmodesmata Chlorophyll a and b Ancestral alga • Fruits in the flowering plants (angiosperms) • add a layer of protection to seeds • also provided for? Tracheophytes • Continued next time….