* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Physiology Notes for students
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
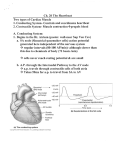
Heart Physiology: Electrical Events Intrinsic cardiac conduction system Composed of _________________________ found nowhere else in the body Causes _____________________________ in only one direction--from ________________________________________ Sets the heart's basic ________________ Heart Physiology: Sequence of Excitation Sinoatrial (SA) node (____________________) Generates impulses about ____ times/minute (sinus rhythm) Depolarizes ___________ than any other part of the myocardium From SA node, impulse spreads through atria to AV node and then atria ____________ Atrioventricular (AV) node Delays impulses to give atria time to finish _________________ Impulse then passes rapidly through __________________________ Atrioventricular (AV) bundle (bundle of His) Only ____________ connection between the atria and ventricles Right and left bundle _________________________ Two pathways in the interventricular septum that carry the impulses toward the __________ of the heart Purkinje fibers Complete the pathway into the apex and ___________________ Contraction ejects blood _________________ into the large ____________________ leaving the heart Homeostatic Imbalances Defects in the intrinsic conduction system may result in _________________________: irregular heart rhythms Uncoordinated atrial and ventricular ___________________ ___________________: rapid, irregular contractions; useless for pumping blood ________________________: rapid heart rate (over 100 beats per minute) _________________________: heart rate substantially slower than normal (less than 60 beats per minute) Electrocardiography Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): a composite of all the _________________________ generated by nodal and contractile cells at a given time Three waves _________________: depolarization of SA node _________________: ventricular depolarization _________________: ventricular repolarization Heart Sounds Two sounds (lub-dup) associated with _________________________ First sound occurs as AV valves close and signifies beginning of __________________________ Second sound occurs when SL valves close at the beginning of _____________________________________ Heart murmurs: abnormal heart sounds most often indicative of __________________ problems Mechanical Events: The Cardiac Cycle Cardiac cycle: all events associated with blood flow through the heart during _______________________________________ Systole—____________________________ Diastole—____________________________ Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Mid-to-late diastole heart in complete _________________________ pressure in heart is ____________ blood is flowing passively into and through atria into ventricles from pulmonary and systemic circulations semilunar valves are _____________ AV valves are _____________ atria ____________________ forcing blood remaining in their chambers into the ventricles Ventricular systole Atria ________________ and ventricles begin to _____________ Rising ventricular pressure results in ___________ of AV valves Isovolumetric contraction phase (all valves are ____________) In ejection phase, ventricular pressure _________________ pressure in the large arteries, forcing the SL valves open and blood rushes out of ventricles during ventricular systole, atria are _______________ and filling up with blood Early diastole Ventricles ______________ semilunar valves snap shut (preventing ________________) intraventricular pressure ___________ below pressure in atria AV valves ____________ causing ventricles to refill with blood, completing the cycle Blood Vessels _____________________: carry blood away from the heart walls usually ________________ than those of veins ________________________: extend and branch through tissues and directly serve the needs of the body cells ___________________: drain the tissues and return the blood to the heart have ______________ that prevent backflow of blood Physiology of Circulation __________________: rhythmic expansion and recoil of arteries resulting from heart contraction normal resting pulse is _____________________ beats per minute _______________________________: pressure the blood exerts against the inner walls of the blood vessels force that keeps blood _________________ continuously even between heartbeats Measuring Blood Pressure systolic pressure: pressure in the arteries at the peak of _________________________ in normal adults __________ mmHg diastolic pressure: pressure when the ________________________________________ in normal adults _________ mmHg The Lymphatic System The primary function is to _________________________, a clear, colorless fluid containing _____________________ that helps rid the body of toxins, waste and other unwanted materials subset of the ______________________ system ______________________________ serve as multiplication sites for agranular WBCs (lymphocytes) The tonsils, adenoids, ______________ and thymus are all part of the lymphatic system