* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Valvular Heart Disease Aortic Stenosis
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Marfan syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Common Clinical Scenarios
*Younger people
_Functional murmur vs
_ MVP vs
_ AS
*Older people
_Aortic sclerosis vs
_Aortic stenosis
Aetiology
Young patient
_Thick congenital bicuspid
valve
*2% population
*3:1 male:female
*Co-existing COA 6%
patients
_Rarely
*Unicuspid valve
*supravalvular AS
*Subaortic stenosis
_Discrete
_Diffuse { Tunnel}
Middle age {40- 50y }
_Thick bicuspid valve
_Rheumatic disease
Old age {60- 80y}
_Thick degenerative
valve
_Calcification of
bicuspid valve
_Rheumatic AS
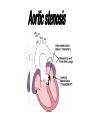
Aortic Stenosis
Subvalvular
Valvular
(HCM; IHSS
Supravalvular
COP maintained normal for years by progressive LVH
_ Coronary blood flow becomes inadequate
Exertional Angina
_LV outflow obstruction limits COP after exercise
Exertional syncope
_LVEDP raise
Pulmonary congestion
Dyspnoea ,Pulmonary
oedema
_Patients asymptomatic for long time once symptoms appear deteriorate
rapidly
Clinical features:
*Cardinal Symptoms
_Mild or moderate AS usually asymptomatic
_Chest pain (angina)
Rreduced coronary flow reserve
Increased demand-high afterload
_Syncope/Dizziness (exertional pre-syncope)
Fixed cardiac output
Vasodepressor response
_Dyspnoea on exertion & rest
Impaired exercise tolerance
_Episodes of acute pulmonary oedema
_Sudden death
*Other signs of LV failure
Diastolic & systolic dysfunction
Clinical features cont..
*Signs
_Ejection systolic murmer
_Slaw rising carotid pulse
_Narrow pulse pressure
_Thrusting apex beat { LV pressure overload }
_Signs of pulmonary congestion { basal crepitation }
Auscultation :
S1
S2
Mild-Moderate
S1
S2
Severe
Some points about physical signs :
_Intensity DOES NOT predict severity
_Presence of thrill DOES NOT predict severity
Conditions indicating severity:
_”Diamond” shaped, harsh, systolic crescendodecrescendo {Long murmer}
_Decreased, delay & prolongation of pulse
amplitude {Anacrotic pulse }
_Paradoxical S2
_S4 (with left ventricular hypertrophy)
_S3 (with left ventricular failure)
* ECG
_ LVH
_ LBBB
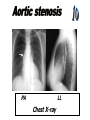
* Chest XR
_Enlarged LV
_Dilated Ascending aorta
_May be normal
_Calcified AV
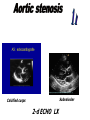
* ECHO
_May be normal
_Calcified AV with restricted opening
_Thickened LV walls
*Dopler
_ Estimates gradient
_detects AR
*Cardiac Catheterization :
_Systolic gradient between LV and Aorta
_Post-stenotic dilatation of aorta
_Detects AR if present
_To detect presence of CAD
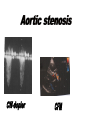
ECG
PA
LL
Chest X-ray
Subvalvuler
Calcified cusps
2-d ECHO LX
Natural history
_Heart failure reduces life
expectancy to less than 2
years
_Angina and syncope reduce life
expectancy between 2 and 5
years
_Rate of progression @ 0.1
cm2/year
ECHO (cont.)
Criteria for determining severity of AS
G (mmHg)
AVA (cm2)
Mild
< 25
> 1.5
Moderate
25-50
1-1.5
Severe
50-80
0.7-1
Critical
>80
<0.7
*Medical
_ Prophylaxis against IE
_ Anticoagulants if in AF
_Diuretics cautiously for pulmonary congestion
_Vasodilators are CONTRAINDICATED
* Surgical
_ Patients with symptoms and valve gradient >50 and normal
COP should have AV replacement { Mechanical }
_ Symptomatic Elderly patients need AV replacement with
{Bioprosthesis}
_ Aortic Balloon valvoplasty for congenital AS
Disc Valve
Bio-prosthetic Valve
Caged-Ball Valve
Comparison between Mechanical and Prosthetic Valves
* MECHANICAL
_Durable
_Large orifice
_High thromboembolic
potential
_Best in Left Side
_Chronic warfarin
therapy
BIO-PROSTHETIC
_Not durable
_Smaller
orifice/functional
stenosis
_Low thromboembolic
potential
_Consider in elderly
_Best in tricuspid
position
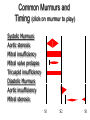
Common Murmurs and
Timing (click on murmur to play)
Systolic Murmurs
Aortic stenosis
Mitral insufficiency
Mitral valve prolapse
Tricuspid insufficiency
Diastolic Murmurs
Aortic insufficiency
Mitral stenosis
S1
S2
S1