* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8th grade science materials - A Teacher`s Portfolio by Layne C. Smith
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Milankovitch cycles wikipedia , lookup
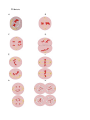
December 9, 2008 8th grade Science: Mrs. Bryant Sections 2.1 & 2.2 Vocabulary Quiz Modified Name: ___________________________ Date:____________________ Period____ 1. A fracture in the Earth's lithosphere is called: a. stress b. fault 2. The force applied by an object pressing on, pulling on, or pushing against another object is called: a. stress b. focus 3. A shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault is called: a. seismic wave b. earthquake December 11, 2008 8th grade Science: Mrs. Bryant Sections 2.1 & 2.2 Vocabulary Quiz Modified Name: ___________________________ Date:____________________ Period____ Identify: A. Pyroclastic flow C. Magma B. Lava D.____ a mountain that forms as continental crust crumbles and bends into folds. a. folded mountain b. fault-block mountain E.____are mountains that form as blocks of rock move up or down along normal faults. a. folded mountain b. fault-block mountain A. ____I am a ball of hot, solid metals at Earth's center. B. ____I'm the name that Alfred Wegener gave to the huge supercontinent that he proposed had once existed. C. _____I'm the thin layer of rock that surround Earth. D. _____I'm Earth's thickest layer, measuring nearly 2900 kilometers. E. _____I occur in a deep valley formed as tectonic plates move apart. Word 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Bank Inner Core Pangea Crust Mantle Rift Valley Circle the word that correctly matches the definition. 6. Definition: I am one plate sinking beneath another. Continental Drift A. Deduction B. Subduction 7. Definition: I'm the hypothesis that proposed that Earth's continents were once joined in a single landmass and then gradually moved apart. A. Continental Drift B. Continental Joining 8. Definition: I'm the layer of liquid metals that surrounds the inner core. A. Outer Core B. Mid Core 9. Definition: I'm the transfer of heat within a material. A. Condensation B. Convection 10. Definition: I'm Earth's crust and the very top of the mantle combined. A. Lithosphere B. Troposphere When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! By Joey Biega December 2008 Title When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! Click to add text When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! Title When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! Title When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! It show location on an interactive map 46°12′00.17″N 122°11′21.13″W And 4,605 feet (1,404 m) in the air This is the age of rock 40,000 years Mount St. Helens erupted on May 18, 1980, at 08:32 a.m. Pacific Daylight Time First ascent 1853 by Thomas J. Dryer When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! Between 1980 and 1986, activity continued at Mount St. Helens, with a new lava dome forming in the crater. Numerous small explosions and dome-building eruptions occurred. From December 7, 1989 to January 6, 1990, and from November 5, 1990 to February 14, 1991, the mountain erupted with sometimes huge clouds of ash. People Who Got Hurt The removal of the north side of the mountain reduced St. Helens' height by about 1,300 feet (400 m) and left a crater one to 2 miles (3.2 km) wide and 0.5 miles (800 m) deep, with its north end open in a huge breach. The eruption killed 57 people, nearly 7,000 big game animals (deer, elk, and bear), and an estimated 12 million fish from a hatchery.[6] It destroyed or extensively damaged over 200 homes, 185 miles (298 km) of highway and 15 miles (24 km) of railways The next steps Define the next steps Analyze the ideas developed? Continue with a larger group? Develop tasks to follow up on Turning ideas to reality When Mount St. Helens Blew Its Top! thermal energy;it ejected more than 0.67 cubic miles (2.8 cubic km) of material. The removal of the north side of the mountain reduced St. Helens' height by about 1,300 feet (400 m) and left a crater one to 2 miles (3.2 km) wide and 0.5 miles (800 m) Chapter 2 Test Science: Mrs. Bryant MODIFIED Name________________________________ Date_______________________ Period______ Match the term with the word in the bank A.______ An imaginary line about which a turning body, such as Earth rotates. B.______ The motion of one body around another, such as Earth in its orbit around the sun; the time it takes an object to go around once. C.______ One part of a pattern of temperature changes and other weather trends over the course of a year. D._____ In an orbit, a position and time in which sunlight shines equally on the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere; a time of year when daylight and darkness are nearly equal for most of Earth. E.______ In an orbit, a position and time during which one hemisphere gets the maximum area of sunlight, while the other hemisphere gets its minimum amount. F.______ A large, dark plain of solidified lava on the Moon. G._____ An event during which one object in space casts a shadow onto another. H._____ This occurs because the Moon's gravity changes the shape of Earth's oceans. I._____ A round pit left behind on the surface of a planet or other body in space after a smaller object strikes the surface. K.____ The sun seems to darken because the Moon's shadow falls onto part of Earth. Word Bank 1. axis of rotation 2. revolution 3. season 4. equinox 5. solstice 6. mare 7. eclipse 8. tides 9. solar eclipse 10. impact craters Earth's Surface Quiz November 11, 2008 Science: Mrs. Bryant MODIFIED Name________________________________ Date_______________________ Period______ Circle the correct answer 1. Represents Earth's curved surface on a flat map. (P.20) a. Map Scale b. Projection 2. Divides Earth in the norther and southern hemispheres. (P.18) a. Equator b. Relief Map 3. The difference between an area's highest and lowest points is the area's (P.25) a. Relief b. Slope 4. The contour interval on a particular map (P.26) a. Is always the same b. Varies with steepness 5. The shape of the land is called (P.24) a. Slope b. Topography 6. Is the physical or chemical breakdown of rocks (P.115) a. Abrasion b. Weathering 7. Ice, plant roots, and moving water can all cause weathering (P.116) a. Exfoliation b. Mechanical 8. Explains the meaning of each symbol on a map (P.17) a. Map Legend b. Map Scale 9. What are the location points for POINT A on the map below? a. 30 N, 60 W b. 30 S, 60 W 10. What are the location points for POINT b on the map below? a. 20 S, 20 E b. 20 N, 20 W March 11, 2009 8th grade Science: Mrs. Bryant Chapter 3 Quiz Modified Name: ___________________________ Date:____________________ Period____ I. Mitosis A. B. C. D. E. Identify the Stages: 1. Telophase_______ 2. Anaphase_______ 3. Metaphase______ 4. Prophase_______ 5. Interphase______ II. Meiosis A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Identify the Stages: 1. Prophase I ______ 2. Telophase II and Cytokinesis ______ 3. Metaphase I ______ 4. Anaphase II ______ 5. Telophase and Cytokinesis _______ 6. Metaphase II _______ 7. Anaphase I _______ 8. Prophase II _______ Vocabulary a. _____a chemical that contains information for an organisms growth and functions b. _____DNA wrapped around proteins in like thread around a spool and compacted into structures c. _____ normal sequence of development and division of a cell d. _____ process of new tissue growth e. _____ one organism produces one or more new organisms that are identical toitself and that live independently of it Word Bank 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. DNA Chromosomes Cell cycle Regeneration Asexual reproduction Axis of Rotation Definition: an imaginary line about which a turning body, such as Earth rotates Revolution Definition: The motion of body around another, such as Earth in its orbit around the sun. Season Definition: One part of a pattern of temperature changes and other weather trends over the course of a year Equinox Definition: A time of year when daylight and darkness are nearly equal for most of Earth Solstice Definition: A position and time during which which one hemisphere gets the maximum area of sunlight, such as the summer solstice Mare Definition: Dark plain of solidified lava that look like “seas” on the moon Eclipse Definition: An event in which one object in space casts a shadow onto another Tides Definition: This occurs because the Moon's gravity changes the Earth's shape Impact Crater Definition: A round pit left behind on the surface of a planet or other body in space after a smaller object strikes the surface. How the moon was formed Definition: At the time Earth formed 4.5 billion years ago, other smaller planetary bodies were also growing. One of these hit earth late in Earth's growth process, blowing out rocky debris. A fraction of that debris went into orbit around the Earth and formed into the moon. Chapter 1 Test Science: Mrs. Bryant “History of Life on Earth” MODIFIED Name________________________________ Date_______________________ Period______ 1. Scientists use 2 approaches to dating fossils. (Fill in the blank) a.______________________________________________________________ b.______________________________________________________________ 2. True or False: Unicellular organisms are made of a single cell. Fossil record show this beginning about 3.8 billion years ago. 3. True or False: Protozoa were the first animal species. 4. The Permian extinction occurred: (Choose the correct answer) A. About 250 million years ago in which 90 percent of the species living in the ocean became extinct. B. 65 million years ago the fossil record ends for dinosaurs; caused by an asteroid that hit Earth. 5. The Cretaceous extinction occurred: (Choose the correct answer) A. About 250 million years ago in which 90 percent of the species living in the ocean became extinct. B. 65 million years ago the fossil record ends for dinosaurs. 6. True or False: Charles Darwin studied fossils and animals while aboard the Beagle. 7. Charles Darwin noticed many differences in _________ _and _____________ on the ___________________________ islands. Some _____________________ had short necks and some had________________________________. (Fill in the blank) 8. True or False: Darwin discovered that bluebirds had different shaped beaks and were different sizes. 9. True or False: Darwin knew from personal experience that breeders can produce new varieties of an animal over time. This was called natural selection. 10. Natural selection is: A. when members of a species best suited to their environment die out at a higher rate. B. when members of a species best suited to their environment survive and reproduce at a higher rate. (Choose the correct answer) Match the following from the Word Bank: A. ______ When an organism reproduces, it usually produces more offspring than the environment can support. B._______ Within a species, there are natural differences in traits. C._______ When a mutation occurs that makes an individual better able to survive than other members of the group. D._______This becomes more apparent over several generation. The ones that survive longer are more likely to reproduce more offspring. E._______ The evolution of a new species from an existing species. F._______ Similarities in structure;these were once fully functional in an ancestral group but are now reduced and unused. Word Bank 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Adaptation Speciation Overproduction Selection Vestigial organs Variation Axis of Rotation: J Revolution: I Season: G Equinox: H Match the picture and the word(s) with the word bank below. Solstice: F Mare:D Eclipse: E Tides: B Impact Crater: C How the moon was formed: A Word Bank (1) ______Definition: an imaginary line about which a turning body, such as Earth rotates (2)______Definition: The motion of body around another, such as Earth in its orbit around the sun. (3)______Definition: One part of a pattern of temperature changes and other weather trends over the course of a year. (4)______Definition: A time of year when daylight and darkness are nearly equal for most of Earth (5)______Definition: A position and time during which which one hemisphere gets the maximum area of sunlight. (6)______Definition: Dark plain of solidified lava that look like “seas” on the moon (7)______Definition: An event in which one object in space casts a shadow onto another (8)______Definition: This occurs because the Moon's gravity (9)______Definition: A round pit left behind on the surface of a planet or other body in space after a smaller object strikes the surface. (10)______Definition:At the time Earth formed 4.5 billion years ago, other smaller planetary bodies were also growing. One of these hit earth late in Earth's growth process, blowing out rocky debris. A fraction of that debris went into orbit around the Earth and formed into the moon. 4. The vibrations caused by an earthquake is called: a. epicenter b. seismic wave 5. In an earthquake, the point underground where the rocks first begin to move is called: a. focus b. epicenter 6. The point on Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake is called the: a. epicenter b. fault spot 7. An instrument that constantly records ground movements is called: a. barometer b. seismograph Inner Core Definition: I am a ball of hot, solid metals at Earth's center (P.10). Subduction Definition: I am one plate sinking beneath another (P.30). Pangea Definition: I'm the name that Alfred Wegener gave to the huge supercontinent that he proposed had once existed (P.16). Continental Drift Definition: I'm the hypothesis that proposed that Earth's continents were once joined in a single landmass and then gradually moved apart (P.14). Outer Core Definition: I'm the layer of liquid metals that surrounds the inner core. (P.10). Crust Definition: I'm the thin layer of rock that surround Earth (P.11) Convection Definition: I'm the transfer of heat within a material. (P.17). Lithosphere Definition: I'm Earth's crust and the very top of the mantle combined. (P.11). Mantle Definition: I'm Earth's thickest layer, measuring nearly 2900 kilometers. (P.11) Rift Valley Definition: I occur where tectonic plates move apart. (P.23).