* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TRIANGLE PROPERTIES • Interior angles of a triangle add up to
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
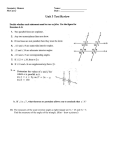
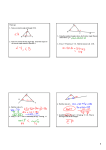
TRIANGLE PROPERTIES • Interior angles of a triangle add up to 180°. This property can be deductively proven, so it is a theorem. PQ AB example: Given: P C Q Prove: ∠CAB + ∠ACB + ∠CBA = 180° A statement reason PQ AB given ∠ACP = ∠CAB alternate interior angles ∠BCQ = ∠CBA alternate interior angles B ∠ACP + ∠ACB + ∠BCQ = 180° angles on a line add up to 180° ∠CAB + ∠ACB + ∠CBA = 180° substituting equal angles Q.E.D. An exterior angle (external angle) of a triangle is the angle between one side of a triangle and the extension of an adjacent side. C exterior angle B A D Use the second triangle (above right) to draw other exterior angles. example: Prove the conjecture, "an exterior angle at a vertex of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two interior angles in the triangle." C Given: ∆ABC with exterior angle ∠CAD Prove: ∠CAD = ∠ABC + ∠ACB B D A Statement Reason ∠CAB + ∠CAD = 180° angles on a line are supplementary ∠CAD = 180° − ∠CAB subtraction property ∠CAB + ∠B + ∠C = 180° sum of angles in a triangle ∠B + ∠C = 180° − ∠CAB subtraction property ∠CAD = ∠B + ∠C transitive property Q.E.D. Theorem: An exterior angle at a vertex of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two interior angles in the triangle. exercise: Find the measure of each unknown angle. 46° 67° 1 2 20° 4 110° 3 ∠1 = ∠3 = ∠2 = ∠4 = ∠5 = 9 38° 8 6 7 130° ∠6 = ∠8 = ∠7 = ∠9 = 5 USING TRIANGLE PROPERTIES • Interior angles of a triangle add up to 180°. • If a triangle is isosceles, then the angles opposite the equal sides are equal. • If a triangle is equilateral, then all the angles are equal to each other and 60°. • An exterior angle at a vertex of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two interior angles in the triangle. exercise: Given: ∆ ABC is equilateral A ∠ADC = 35° Prove: ∠CAD = 25° B statement ∆ ABC is equilateral C D reason given property of equilateral triangles ∠ACD = ° ∠ADC = 35° angles in a triangle add up to 180° ∠CAD + 120° + 35° = 180° substitution ∠CAD = 25° Q.E.D. exercise: Determine the interior angles of the triangle. (x + 5)° x° (6x − 25)° Answer: exercise: Determine the perimeter of the isosceles triangle. (2x + 17) cm (3x − 20) cm (5x − 25) cm Answer: exercise: Determine the interior angles in the triangle. Answer: