* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 2 Lecture Notes
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
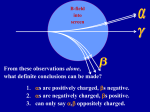
What produces a gravitational field? A gravitational field exerts a force on? Mass Mass What produces an electric field? Electric charge An electric field exerts a force on? Electric charge What produces a magnetic field? Moving electric charge A magnetic field exerts a force on? Moving electric charge? Direction of Magnetic Force tail out of in to page page Drawing vectors in head Direction of magnetic force is “sideways” force is perpendicular to both v and B use “right-hand rule” to find direction F = q v B sinq ConcepTest Magnetic Force A positively charged beam enters into a magnetic field region as shown. What is the direction of B? y 1)+ y (up) 2) – y (down) 3) + x (right) 4) + z (out of page) 5) – z (into page) x Radius of Circular Orbit magnetic force: F qvB centripetal accel: v2 a R x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x v x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x Fx x x x x +q R Newton's 2nd Law: F ma mv R qB 2 v qvB m R This has useful experimental consequences ! B ConcepTest Magnetic Force x x x x x x x x x x x x Two particles of the same charge enter a magnetic field with the same speed. Which one has the bigger mass? x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x A 1) 2) 3) 4) B A B both masses are equal impossible to tell without weighing the particles as are ionized Helium (bare Helium nuclei) 2-protons, 2-neutrons (positively charged) bs are simply electrons(negatively charged) qa = -2qb ma=7296mb R=? v= /2Vm/q /B Velocity Selector Consider a positively charged ion entering a region where the electric and magnetic fields are uniform and perpendicular to each other. If the particle moves in a straight line, what is its velocity in terms of E and B? x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x E For the magnetic force: direction magnitude up F = qvB For the electric force? direction magnitude down F = qE Sum of the forces on the particle? v=E/B Zero (not accelerating) |FE| = |FB| qE = qvB B Ratio of charge to mass for an electron e– “gun” An electron is accelerated from rest across a potential difference and then enters a region of uniform magnetic field, as shown at right. What is the “charge to mass ratio”, q/m, of the electron? What is the speed of the electron? ½ mv2 = qV DV e– B x x x x x x R x x x x x x (Work-Energy Theorem) What is the radius of the electron’s orbit? R = mv / qB Algebra: determine q/m q / m = 2V / R2B2 (Earlier today) (Solve second Eq for v and plug into first) ConcepTest I 1 2 I 3 I I If all wires carry the same current I, for which of the loops above is the magnitude of the net force greatest? A) Loop 1 B) Loop 2 C) Loop 3 D) same for all ConcepTest Magnetic Force A rectangular current loop is in a uniform magnetic field. What direction is the net force on the loop? (a) + x (b) + y (c) zero (d) – x (e) – y z B y x ConcepTest If there is a DC current in the loop in the direction shown, the loop will A) move up B) move down C) rotate clockwise D) rotate counterclockwise E) some combination of moving and rotating N S a b The force on the top segment of the rectangular loop is 1)up. 2)down. 3)into screen. 4)out. 5)left. 6)right 7)zero. a b The force on the bottom segments of the rectangular loop is 1)up. 2)down. 3)into screen. 4)out. 5)left. 6)right 7)zero. a b The force on the left segment of the rectangular loop is 1)up. 2)down. 3)into screen. 4)out. 5)left. 6)right. 7)zero. a b The force on the right segment of the rectangular loop is 1)up. 2)down. 3)into screen. 4)out. 5)left. 6)right. 7)zero.