* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How are we affecting the environment?
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Wildlife corridor wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
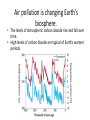
Human Impact on the Environment Earth’s human population continues to grow. • Earth’s human carrying capacity is unknown. • Why is population increasing? – Technology has helped to increase Earth’s population. – – – – – – gas-powered farm equipment medical advancements Plumbing Transportation Electricity Construction machinery How are we affecting the environment? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Pressure on Resources Air pollution Water Pollution Habitat Loss Invasive Species As the human population grows, the demand for Earth’s resources increases. The growing human population exerts pressure on Earth’s natural resources. • Nonrenewable resources are used faster than they form. – coal – Oil • Renewable resources cannot be used up or can replenish themselves over time. – wind – water – sunlight • • Growing use of nonrenewable resources may lead to a crisis. Resources must be properly managed. KEY CONCEPT Fossil fuel emissions affect the biosphere. Pollutants accumulate in the air. • Pollution is any undesirable factor added to the air, water, or soil. • Smog is one type of air pollution. – sunlight interacts with pollutants in the air – pollutants produced by fossil fuel emissions – made of particulates and ground-level ozone • Smog can be harmful to human health. • Acid rain is caused by fossil fuel emissions. – produced when pollutants in the water cycle cause rain pH to drop – can lower the pH of a lake or stream – can harm trees Air pollution is changing Earth’s biosphere. • The levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide rise and fall over time. • High levels of carbon dioxide are typical of Earth’s warmer periods. • The greenhouse effect slows the release of energy from Earth’s atmosphere. – – – – sunlight penetrates Earth’s atmosphere energy is absorbed and reradiated as heat greenhouse gases absorb longer wavelengths Greenhouse gas molecules carbon dioxide rerelease (CO ) infrared radiation methane (CH ) water (H O) 2 4 2 • Global warming refers to the trend of increasing global temperatures. North Pole Water pollution affects ecosystems. • Pollution can put entire freshwater ecosystems at risk. • Indicator species provide a sign of an ecosystem’s health. – amphibians – top predators Frog skin is water-permeable so when they come into direct contact with pollutants, it can cause deformities. Due to biomagnification, pollutants accumulate in higher concentrations as they move up the food chain. Biomagnification causes accumulation of toxins in the food chain. • Pollutants can move up the food chain. – predators eat contaminated prey – pollution accumulates at each stage of the food chain • Top consumers, including humans, are most affected. • Mining and Agricultural Runoff also add to flow of phosphorus • Excessive flow of phosphorus within an aquatic environment can lead to algae blooms • Blooms crowd out other plant species and negatively impact wildlife populations • Nitrogen-rich fertilizers can add too much nitrogen in nearby water • Livestock waste adds large amounts of nitrogen into soil and water • Increased nitrate levels cause plants to grow too rapidly until they use up the supply and die KEY CONCEPT Habitat Loss threatens biodiversity. Preserving biodiversity is important to the future of the biosphere. • The loss of biodiversity has long-term effects. – loss of medical and technological advances – extinction of species – loss of ecosystem stability Loss of habitat eliminates species. • Habitat fragmentation prevents an organism from accessing its entire home range. – occurs when a barrier forms within the habitat – often caused by human development • Habitat corridors are a solution to the problem. – corridors can be road overpasses or underpasses – allow species to move between different areas of habitat Introduced species can disrupt stable relationships in an ecosystem. • An introduced species is one that is brought to an ecosystem by humans. – accidental – purposeful • Invasive species can have an environmental and economic impact. • What can we do? • There are several ways that people can help protect the environment. – control population growth – develop sustainable technology and practices – protect and maintain ecosystems Sustainable development manages resources for present and future generations. • Sustainable development meets needs without hurting future generations. – resources meet current needs – resources will still be available for future use • The timber industry has started to adopt sustainable practices. – Instead of clear-cutting, only selected trees are cut down • Global fisheries have adopted several sustainable practices. – rotation of catches – fishing gear review – harvest reduction – fishing bans