* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
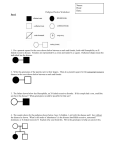
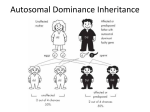
Patterns of Inheritance Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics Chapter 4 OMIM ! Patterns in the pedigree are used to determine how a trait is inherited • • • • • • Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X-linked dominant X-linked recessive Y-linked Mitochondrial inheritance Pedigrees I 1 2 II 2 1 P 3 Pedigrees, cont. Pedigrees, cont. Male or or Affected individual or Proband; first case in family that was identified Mating I II 1 2 3 Parents and children. Roman numerals symbolize generations. Arabic numbers symbolize birth order within generation (boy, girl, boy) ? Dizygotic twins Female Mating between relatives (consanguineous) ? Unaffected individual P P or Offspring of unknown sex or Questionable whether individual has trait Asymptomatic/ presymptomatic Aborted or stillborn offspring Known heterozygotes Carrier of X-linked recessive trait Deceased offspring Infertility Indicates date of death Monozygotic twins d. 1910 d. 1932 Autosomal Recessive Traits ! Characteristics of autosomal recessive traits • For rare traits, most affected individuals have unaffected parents • All children of affected parents are affected • The risk of an affected child with heterozygous parents is 25% Some Autosomal Recessive Traits Pedigree: An Autosomal Recessive Trait Example: Cystic Fibrosis ! Cystic fibrosis • A fatal recessive genetic disorder associated with abnormal secretions of the exocrine glands The CF Gene and Organ Systems Affected by Cystic Fibrosis Cystic Fibrosis Gene Product ! CFTR protein controls the movement of chloride ions across the plasma membrane Example: Sickle Cell Anemia Autosomal Dominant Traits ! Sickle cell anemia • An autosomal recessive disorder • Produces abnormal hemoglobin (blood transport protein) Some Autosomal Dominant Traits ! Characteristics of autosomal dominant traits • Every affected individual has at least one affected parent (except in traits with high mutation rates) • If an affected individual is heterozygous and has an unaffected mate, each child has a 50% chance of being affected • Two affected individuals can have an unaffected child Pedigree: An Autosomal Dominant Trait Example: Marfan Syndrome Aorta ! Marfan syndrome • An autosomal dominant genetic disorder that affects the skeletal system, cardiovascular system, and eyes Vena cava Pulmonary artery Right auricle Area of aorta effected in Marfan syndrome Right auricle Left ventricle Right ventricle Left ventricle Right ventricle Normal Heart Marfan Syndrome Flo Hyman Sex Linked Traits ! X-linked • Pattern of inheritance that results from genes located on the X chromosome ! Y-linked • Pattern of inheritance that results from genes located only on the Y chromosome Distribution of Sex Chromosomes X and Y: Human Sex Chromosomes Males Have Hemizygous Genes ! Hemizygous • A gene present on the X chromosome that is expressed in males in both the recessive and dominant condition X-Linked Dominant Traits ! Affected males produce all affected daughters and no affected sons ! A heterozygous affected female will transmit the trait to half of her children • Sons and daughters are equally affected ! On average, twice as many daughters as sons are affected Pedigree: Hypophosphatemia X-Linked Recessive Traits ! X-linked recessive traits affect males more than females because males are hemizygous for genes on the X chromosome Pedigree: X-Linked Recessive Inheritance X-Linked Recessive Inheritance ! Affected males receive the mutant allele from their mother and transmit it to all of their daughters, but not to their sons • Daughters of affected males are usually heterozygous • Sons of heterozygous females have a 50% chance of being affected Example: Color Blindness ! Color blindness • Defective color vision caused by reduction or absence of visual pigments • Three forms: red, green, and blue blindness Testing For Color Blindness Color Blindness: The Eye ! Defects in cone proteins cause color blindness Genetics in Society: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy ! Dystrophin proteins that normally stabilize the muscle cells during contraction are defective • Plasma membranes are torn apart by muscle contraction, causing death of muscle tissue Hemophilia and History Paternal Inheritance: Y Chromosome Some Genes on the Y Chromosome ! Only males have Y chromosomes • Genes on the Y chromosome are passed directly from father to son ! All Y-linked genes are expressed • Males are hemizygous for genes on the Y chromosome Pedigree: Y-Linked Traits Some Mitochondrial Disorders Mitochondrial Inheritance Pedigree: Mitochondrial Inheritance ! Mitochondria (and genetic disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial genes) are maternally inherited ! Mitochondria are transmitted from mothers to all their offspring through the cytoplasm of the egg Age-Related Phenotypic Expression ! Huntington disease • An autosomal dominant disorder associated with progressive neural degeneration and dementia • Adult onset is followed by death in 10 to 15 years ! Porphyria • An autosomal dominant disorder that leads to intermittent attacks of pain and dementia • Symptoms first appear in adulthood Porphyria variegata -Pleiotropy King George III Symptoms: Red urine, Abdominal pain, Constipation, Rapid pulse, Stupor, Delirium, Convulsions, Madness Two Aspects of Phenotypic Variation ! Penetrance • The probability that a disease phenotype will appear when a disease-related genotype is present (e.g. Polydactyly or Camptodactyly). • 25% penetrance means that only 1/4 of the population with the disease-related genotype show the phenotype. ! Expressivity Incomplete Penetrance ! Camptodactyly • A dominant trait (immobile, bent little fingers) with variable expression one hand affected no penetrance • The range of phenotypic variation associated with a given phenotype (e.g. Camptodactyly: one hand or both hands affected) both hands affected