* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the PERIODIC TABLE?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
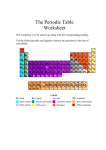
Introduction to the Periodic Table I am Dmitri Mendeleev! I made the PERIODIC TABLE ! The Father of the Periodic Table— Dimitri Mendeleev Mendeleev was the first scientist to notice the relationship between the elements – Arranged his periodic table by atomic mass – Said properties of unknown elements could be predicted by the properties of elements around the missing element Moseley later discovered that the periodic nature of the elements was associated with atomic number, not atomic mass What is the PERIODIC TABLE? o Shows all known elements in the universe. o Organizes the elements by chemical properties. How do you read the PERIODIC TABLE? What is the ATOMIC NUMBER? o o The number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom Or The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom. What is the SYMBOL? o An abbreviation of the element name. What is the ATOMIC WEIGHT? o The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. How do I find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an element using the periodic table? o # of PROTONS = ATOMIC NUMBER o # of ELECTRONS = ATOMIC NUMBER o # of NEUTRONS = ATOMIC _ ATOMIC WEIGHT NUMBER The Periodic Table Column = Group or Family 18 columns on the Periodic Table Row = Period 7 rows on the Periodic Table Metals, Nonmetals, and Only Semi-metals Nonmetals are on the nonmetal on the metal side Metals are to the left of the stair- step Semi-metals, “metalloids,” touch the stair-step right of the stair-step Special Rows on the PT Lanthanides Actinides The Groups of the Periodic Table Group 1: The Alkali Metals – Most reactive metals on the PT – Rarely found free in nature – Color these blue Group 2: The Alkaline Earth Metals – Color these yellow T he Groups of the Periodic Table Groups 3-12: Transition Metals – Found freely and in compounds in nature – Color these green Group 13: Boron Family – Color these red The Groups of the Periodic Table Group 14: The Carbon Family – Color these orange Group 15: The Nitrogen Family – Color these purple The Groups of the Periodic Table Group 16: The Oxygen Family Group 17: The Halogens Group 18: The Noble Gases – Color these brown – Most reactive nonmetals – Color these black – Nonreactive – Color these white Special Groups Lanthanide – Top row of 15 elements at the bottom of the periodic table – Called the rare Earth elements Actinide – Bottom row of 15 elements at the bottom of the table – All are radioactive Metalloids – Stair step group of elements that have properties that act as metals or nonmetals Click here to watch periodic table video Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures What is an ELEMENT? o A substance composed of a single kind of atom. o Cannot be broken down into another substance by chemical or physical means. What is a COMPOUND? o o A substance in which two or more different elements are CHEMICALLY bonded together. A new substance is formed. What is a MIXTURE? o Two or more substances that are mixed together but are NOT chemically bonded. The parts keep their identity. Element, Compound or Mixture? Element, Compound or Mixture? Element, Compound or Mixture? Element, Compound or Mixture? Element, Compound or Mixture? Element, Compound or Mixture? Mixtures Mixtures are classified by how their parts are distributed. – Homogeneous mixtures have parts that are evenly distributed. – Heterogeneous mixtures have parts that are not evenly distributed. Solutions Solutions are a special type of homogeneous mixtures. They have two parts: – Solute – the substance that is being dissolved – Solvent – the substance that is doing the dissolving