* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OUTLINE FOR ALTERATIONS IN CARDIAC FUNCTION
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
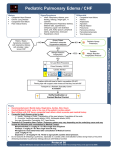
OUTLINE FOR ALTERATIONS IN CARDIAC FUNCTION OBJECTIVES: A. Name the three fetal structures that close to facilitate neonatal circulation. B. Describe the presentation, and management of hypoxemia in an infant. C. Describe the dynamics of congestive heart failure in an infant and a child. D. Complete the study questions for the case study of a 3 mo old child with Down Syndrome with congestive heart failure (CHF). E. Describe the dynamics of pulmonary hypertension and the implications in the child with obstructive heart disease. F. Name one med from each of the four categories of meds used to treat CHF: Digitalis, ACE inhibitors, Beta Blockers, Diuretics. G. Articulate the modalities of supportive care as well as cardiac catheterization and surgical treatments for children with conditions causing CHF. H. State at least three factors that increase the risk of a child having congenital heart disease (CHD). I. Describe the hemodynamics of each of the following CHD: Pulmonary Stenosis, Aortic Stenosis, Coarctation of the Aorta, Patent Ductus Arteriosus, Atrial Septal Defect, Atrio-ventricular canal, Ventricular Septal Defect, Transposition of the Great Arteries, Tetralogy of Fallot J. List the above mentioned congenital heart defects according to two categories: cyanotic/acyanotic ; obstructive/ non-obstructive. K. List the major complications and nursing interventions associated with the child undergoing a cardiac catheterization. L. Describe the pathophysiology, implications for the child and nursing interventions for the six acquired heart diseases presented in this chapter: Rheumatic Fever, Infective Endocarditis, Cardiac Arrhythmias (tachy/brady), Kawasaki Syndrome, Hyperlipidemia, Hypertension. M. READINGS: Ball, J. W. & Bindler, R. C. (2006). Child health nursing: Partnering with children & families. New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 26 p. 889-936, 938(skip medications used with arrhythmias)-953. OUTLINE: I. Transition from fetal to pulmonary circulation. II. Hypoxemia in the infant and child. III. Congestive Heart Failure A. Case Study: 3 mo old with CHF and Down Syndrome B. CHF in Obstructive Defects 1. Pulmonary Hypertension 2. Cardiomegaly C. Medications D. Supportive treatment E. Surgical treatment IV. Congenital Heart Disease A. Developmental implications and assessment B. Factors that increase the risk for CHD C. Acyanotic Heart Defects: pathophysiology, assessment, nursing interventions and implications for the child and family. 1. Obstructive/Acyanotic Heart Defects a. PS b. AoS c. Coarc 2. Non-obstructive/Acyanotic Heart Defects a. PDA b. ASD c. AV canal d. VSD D. Cyanotic Heart Defect: pathophysiology, assessment, nursing interventions and implications for the child and family. 1. Tetrology 2. Transposition 3. Others a. Hypoplastic LV b. Tricuspid Atresia c. Pulmonary Atresia d. Truncus Arteriosus e. Total Anomalous Venous Return V. Acquired Heart Diseases A. Rheumatic fever B. Infective Endocarditis C. Cardiac Arrhythmias 1. Tachy arrhythmias a. sinus tachycardia b. supraventricular tachycardia 2. Bradycardia a. sinus bradycardia b. long Q-T syndrome c. bradycardia based upon age and baseline D. Kawasaki Syndrome E. Dyslipidemia F. Hypertension