* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology EOCT Review Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
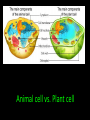
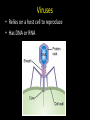
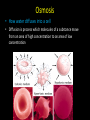
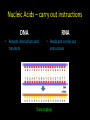
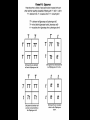
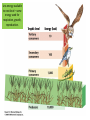
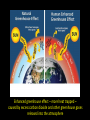
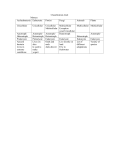
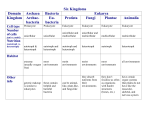
Biology EOCT Review Milton High School Cell Organelles • • • • • • • • Nucleus – holds DNA Cell membrane – what comes in and goes out Mitochondria – powerhouse of the cell Ribosomes – protein synthesis Lysosomes – digestion Cell wall – structural support (ex. plants) Vacuoles – storage Chloroplasts – in plants for photosynthesis Animal cell vs. Plant cell Differences in Cells • • • • • Prokaryote Lacks nucleus No membrane-bound organelles Has a cell wall Has a cell membrane Bacteria Eukaryote • Has a nucleus • Has membrane-bound organelles • Found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists Viruses • Relies on a host cell to reproduce • Has DNA or RNA Osmosis • How water diffuses into a cell • Diffusion is process which molecules of a substance move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Macromolecules • Carbohydrates – glucose and sucrose – Provide quick energy – Polysaccharides are largest • Lipids – fats, oils, waxes – Insoluble in water – Storage of energy • Proteins – basic building materials – Also contain nitrogen – Made of amino acids (there are 20) Nucleic Acids – carry out instructions DNA RNA • Records instructions and transmits • Reads and carries out instructions Transcription Photosynthesis Mitosis vs. Meiosis Mitosis • Generates TWO identical cells • Maintains chromosome number (Diploid number) • Occurs in body cells (somatic cells) Meiosis • FOUR cells are formed • Each with half of the number of chromosomes (Haploid number) • Forms sex cells (gametes) • Requires two cell divisions Genetics • • • • • • • Genes are located on chromosomes Homozygous – both alleles are the same (TT) Heterozygous – alleles are different (Tt) Dominant alleles express themselves Recessive alleles are hidden Phenotype – physical appearance Genotype – set of alleles individual receives Key characteristics of the Kingdoms Characteristics Eubacteria Archaebacteria Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Structure Cell wall Cell wall Body Type Unicellular Nutrition Autotroph and heterotroph Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Mixed Cell wall Cell wall No cell wall Unicellular Unicellular, Multicellular Unicellular, Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Autotroph and heterotroph Autotroph and heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph Some important ecology terms • Community – multiple populations • Abiotic – non-living items in environment • Trophic levels – different levels in food chain – Each level gets energy from level below it – Less energy available as move up to next level • Habitat – where an organism lives • Niche – what an organism does in habitat Less energy available to next level – some energy used for respiration, growth, reproduction. About 10% of available energy is passed to next trophic level Energy is lost as heat through respiration Parasitism – one species benefits and the other species can be harmed (need a host) Tick is an example Commensalism – one species benefits and the other species is neither harmed nor helped The remora and the shark is an example – the remora is a fish which has “suction” disks which allow it to attach to shark without hurting the shark Mutualism – both species benefit A lichen is formed by a relationship between a fungus and a green algae. The fungus anchors the lichen and protects the algae from direct sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations. The green algae performs photosynthesis, providing food for itself and the fungus. Natural selection - results in the evolution of organisms best adapted to the environment Seed-eating Nectar feeding Cause and Effects of Pollution • Excess carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, coal) leads to global climate change • Sulfur dioxide from burning coal causes acid rain – destroys vegetation Acid rain – produced when nitrogen oxide (from car exhaust) or sulfur dioxide (from burning fossil fuels) mixes with rain Enhanced greenhouse effect – more heat trapped – caused by excess carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere