* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
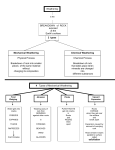
Benchmark 3 Science Study Guide S6E5 A-Crust, Mantle, Core 1. What happens to the temperature as you travel to the center of the Earth? IT GETS HOTTER. --------------------------------------------------------------2. What happens to the density as you travel to the center of the Earth? IT GETS DENSER. --------------------------------------------------------------3. Put the layers of Earth’s interior in order from highest to lowest temperature. INNER CORE, OUTER CORE, MANTLE, CRUST --------------------------------------------------------------4. The thickest layer of Earth’s interior is the MANTLE; the thinnest layer is the CRUST. --------------------------------------------------------------5. What is the composition of each layer? Continental Crust: GRANITE Outer Core: LIQUID IRON & NICKEL Oceanic Crust: BASALT Inner Core: SOLID IRON & NICKEL Mantle: IRON & MAGNESIUM --------------------------------------------------------------- 6. What mechanical layer is composed of the crust and upper mantle? LITHOSPHERE --------------------------------------------------------------7. What mechanical layer does the lithosphere ride/move on top of? ASTHENOSPHERE -------------------------------------------------------------8. Why do lithospheric plates constantly move? CONVECTION CURRENTS IN THE MANTLE -------------------------------------------------------------9. Why is the inner core solid? BECAUSE OF THE PRESSURE OF EARTH’S LAYERS --------------------------------------------------------------10. Label the layers of Earth’s Interior. (1) CRUST (2) INNER CORE (3) MANTLE S6E5 A 2 1 4 3 (4) OUTER CORE ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 11. Identify the bar for each layer of Earth’s interior. A= crust B= mantle C= inner core D= outer core S6E5B: Minerals 1.Identify the criteria that define a mineral. Are minerals organic or inorganic? INORGANIC Are they solid, liquid, or gas? SOLID Are they man made, or do they occur in nature? OCCUR IN NATURE Does each mineral have a unique crystal structure? YES 2. What are rocks composed of? MINERALS 3. Luster, or the way LIGHT is reflected, is a property of minerals. 4. Abbey and Catherine found several rocks on their trip to South America. After they returned home, they took their hand lens and began observing the different types of rocks unearthed. One rock was limestone, another was pumice, and lastly was marble. Catherine and Abbey noticed that all the rocks they found had tiny bits of shiny mica in them. Based on this observation, what can we conclude about mica? ALL THREE ROCKS ARE COMPOSED OF MINERALS THAT INCLUDE MICA________________________ S6E5 C & D: Rocks & Rock Cycle 1.How are rocks classified? By their process of FORMATION 2.How are igneous rocks formed? MAGMA OR LAVA __________ that cools and hardens. 3.How are sedimentary rocks formed? Sediment that is COMPACTED & CEMENTED TOGETHER. 4.How are metamorphic rocks formed? They are CHANGED by HEAT & PRESSURE. 5.What type of rock is being described? IGNEOUS_ A.This rock is formed by cooling magma. SEDIMENTARY B.This is formed underwater. It is made up of bits of shells and skeletons of sea animals cemented together. METAMORPHIC C. This rock is formed by Limestone that has been exposed to lots of heat and pressure becomes this type of rock. SEDIMENTARY D. This rock is formed when tiny grains of sand become cemented together. IGNEOUS E. This rock is formed by quickly cooled lava. 6. Rocks exposed to water break down, or WEATHER. 7. Rocks change from one type of rock to another because of the ROCK CYCLE 8. According to the rock cycle, what processes are missing? A. B. F. C G E. D. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. COOLS & HARDENS WEATHERING & EROSION WEATHERING & EROSION COMPACTING AND CEMENTI HEAT & PRESSURE HEAT & PRESSURE MELTING S6E5 E & F: Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift 1.Describe how lithospheric plates move at a transform boundary. The lithospheric plates slide past one another and create severe earthquakes. -----------------------------------------------------------------2. What geologic event occurs at a transform boundary? SEVERE EARTHQUAKES --------------------------------------------------------------------3. Sea-floor spreading is an example of a DIVERGENT boundary. Plates pull apart and MAGMA moves to the surface forming a chain of underwater mountain range called MID-OCEAN RIDGE. -----------------------------------------------------------------4.The place where two tectonic plates collide and one slides underneath the other is called a SUBDUCTION zone. This happens at a CONVERGENT boundary. An oceanic TRENCH, or deep narrow cut in the ocean floor is created. ----------------------------------------------------------------5. Alfred Wegener developed a hypothesis that stated THAT ALL THE CONTINENTS WERE ONCE CONNECTED & BROKE APART. 6. Where do most volcanoes and earthquakes occur? Near PLATE BOUNDARIES ---------------------------------------------------------------S6E5 G: Fossils 1.What do fossils reveal about Earth’s past?(2) SURFACE AND CLIMATE CHANGES -----------------------------------------------------------------2.What does the law of superposition state? thE TOP LAYER IS THE YOUNGEST WHERE THE YOUNGEST FOSSILS ARE FOUND. THE BOTTOM LAYER IS THE OLDEST WHERE THE OLDEST FOSSILS ARE FOUND. --------------------------------------------------------------------__________________________________________ _______________________________________. C, BECAUSE IT’S ON THE BOTTOM 3. A, BECAUSE IT’S ON THE TOP 4. S6E5 H I J Soil and Soil Conservation 1. SOIL composed or made up of weathered rock and decaying organic material. --------------------------------------------------------------2. The organic (living) material that decomposes and mixes with soil is called HUMUS. ---------------------------------------------------------------3. Identify the layers of soil. ON TOP (A): TOPSOIL; NEXT LAYER (B) IS SUBSOIL; NEXT IS PARTIALLY WEATHERED BEDROCK (C) ; BOTTOM LAYER IS BEDROCK (D) ------------------------------------------------4. What horizon of soil would you find… B Subsoil? D Bedrock? A Topsoil C Partially Weathered Bedrock D Parent Rock A Most Humus 5. What method of soil conservation is being described? CONTOUR PLOWING (A)Plowing in curves rather than straight lines WIND BREAKS (B) trees planted around fields to reduce erosion TERRACING (C) carving flat steps into cliffs and hills to reduce erosion CROP ROTATION (D) planting more than one crop in a field within a year ---------------------------------------------------------------6. How did humans cause the Great Dust Bowl? LIVE STOCK OVERGRAZING, OVERPLOWING, NO CROP ROTATION ------------------------------------------------------------ S6E5 D: Weathering and Erosion Types of Mechanical Weathering 1. Water seeps into cracks of rocks and freezes and expands, causing the rock to break into pieces. This is known as ______________________________. 2. Roots of plants grow into cracks ,getting larger, breaking the rock into smaller pieces. This is known as ________________________. Types of Chemical Weathering 3. Iron comes in contact with oxygen, causing rust to form. This process is called ______________________. Chemical or Mechanical Weathering: Place a “C” for Chemical weathering, or a “M” for Mechanical weathering by each statement. 4. _________Wind 5. _________Oxidation (Rust) 6. _________Acid Precipitation 7. _________Ice Wedging 8. _________Hydrolysis (Water Reaction) 9. _________Temperature Change 10._________Root Action 11. What are the five agents of erosion. ____________________ ______________________ ____________________ _________________ ________________ 12. What agent of erosion is being described? _____________ created the Great Lakes _____________ causes avalanches and rock slides _____________ created the Grand Canyon _____________ Creates sand dunes 13. Explain creep. 14. The steeper the slope, the faster the ________________ moves down it, and the more ________________ occurs.