* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
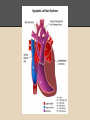
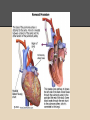
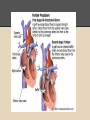
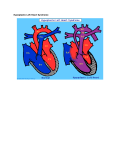
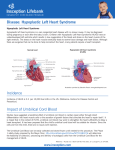
Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome By: Tyler Nickels, Amanda McKellar, Kassie Herp, Zachary Zwiernikowski, & Amanda Mathy Background ● Congenital defect that occurs when parts of the left side of the heart do not develop completely. - Examples: mitral valve, aorta, aortic valve, left ventricle ● Right side must compensate by providing body & lung circulation; eventually right side fails. ● Foramen ovale must be kept open to maintain adequate circulation Background ● Symptoms are similar to anyone with oxygen depletion cyanosis o tachycardia o pounding heart o cold extremities o rapid breathing o lethargy o Background ● Frequency: o 2-3% of all congenital heart defects o 2-3 cases per 10,000 live births o most common form of functional single ventricle heart disease Background ● Significance o about 10% of infants born with this condition also have other birth defects o if left untreated, HLHS is responsible for 25-40% of all neonatal cardiac death Background ● Risk factors: o More common in males than females o Environmental teratogens o Etiology: no known cause Interventions: Non-surgical ● Medications are used to strengthen the heart and lower the heart’s physical workload o Prostaglandin E1 (Misoprostol) Vasodilation ● Nutrition is regulated with high-calorie formulas Interventions: Surgical ● Surgeries do not cure HLHS, but can help to restore heart function. ● Multiple surgeries are needed before blood flow can be properly bypassed past the poorly functioning parts of the heart. Interventions: Norwood Procedure Occurs within first 2 weeks of baby’s life ● Creation of new aorta and connection to right ventricle ● Reroute blood flow from right side of heart to pulmonary arteries ● Baby may look blueish after procedure due to the mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygenpoor blood Interventions: Bi-direction Glenn Shunt Occurs at 4-6 months of age ● Creates direct connection between pulmonary artery and superior vena cava to return oxygen-poor blood from upper part of body to the heart Interventions: Fontan Procedure Occurs between 18 months and 3 years of age ● Connect pulmonary artery and inferior vena cava ● Allows rest of blood coming from lower part of body to go to the lungs ● Oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood no longer mixes in heart Interventions: Post-surgical ● Infants may still have lifelong complications, even after successful surgeries ● Regular follow-up visits with a cardiologist are required to monitor progress ● Heart transplants may be needed if heart becomes weak after surgery Diagnostic Procedures ● Physical exams o ● ● ● ● Elevated HR & breathing, weak pulses, abnormal heart sounds Cardiac Catheterization EKG Echocardiogram X-ray of chest Treatment ● NICU at birth o Ventilator may needed ● Medication: Prostaglandin E1 (Misoprostol) o Vasodilator of the ductus arteriosus ● Surgery o o As infant and toddler Possible surgeries in 20’s & 30’s ● Transplant o alternative (?) to 3-step surgery Nursing Role: Care of patient ● ● ● ● ● Consistency Nurse to Nurse Report Assessment Monitor response Intracardiac catheters Nursing Role: Care of parents ● ● ● ● Educate Informed decision Relate Support Nursing Role: Nursing Diagnosis ● Delayed Growth and Development r/t inadequate oxygen and nutrients to tissues ● Decreased Cardiac Output r/t structural alterations Nursing Role: Interventions r/t diagnosis ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Oxygen Therapy Family coping Monitor lung sounds for pulmonary edema Semi-fowlers position Closely monitor fluid intake Sodium restricted diet Provide normal sleep and wake times to promote growth and development Expected Outcomes: Mother -Medication Administration -Doctors Appointments -Coping with stress Expected Outcomes: Baby -75% -Heart transplant -Surgery in 20s-30s References CDC. (2014). Facts about hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/hlhs.html MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. (2008). Hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Retrieved from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001106.htm Ladwig, G. B., & Ackley, B. J. (2014). Guide to Nursing Diagnosis (4th ed.). Maryland Heights, MO: Elsevier. Marshall, A. (2015, January 22). Hypoplastic left heart syndrome. In Wolters Kluwer Health. NCBI. (2013, November 5). Hypoplastic left heart syndrome. In PubMed Health. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002096/#adam_001106.disease.causes Soetenga, D., & Mussatto, K. A. (2004, December). Management of infants with hypoplastic left heart syndrome integrating research into nursing practice. Critical Care Nurse, 24(6), 46-66. Retrieved from http://ccn.aacnjournals.org/content/24/6/46.