* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islamic Empires
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic extremism in the 20th-century Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Romania wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Europe wikipedia , lookup
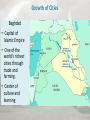
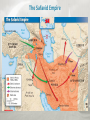
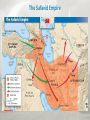
Islamic Empires After the early spread of Islam, three large Islamic empires formed–the Ottoman, Safavid, and Mughal. Main Ideas • Muslim armies conquered many lands into which Islam slowly spread. • Trade helped Islam spread into new areas. • Three Muslim empires controlled much of Europe, Asia, and Africa from the 1400s to the 1800s. Muslim armies conquered many lands into which Islam slowly spread. •After Muhammad’s death, Abu Bakr became the first caliph, the title that Muslims use for the highest leader of Islam. •Caliphs were not religious leaders, but political and military leaders. •Abu Bakr directed a series of battles against Arab tribes who did not follow Muhammad’s teachings. He had united Arabia into a unified Muslim state by his death in AD 634. Muslim armies conquered many lands into which Islam slowly spread. •Muslim armies battled tribes that did not follow Muhammad’s teachings. •The Muslim armies united Arabia, then defeated the Persian and Byzantine empires. •Christians and Jews could continue to practice their own religion. •Muslim forces invaded Spain and conquered it in AD 711. Trade helped Islam spread into new areas. • Along with their trade goods, Arab merchants took Islamic beliefs to new lands. • Islam spread to India, Africa, and Southeast Asia. • Trade brought new products to Muslim lands. • Travelers learned how to make paper from the Chinese. • Merchants brought crops of cotton, rice, and oranges from India, China, and Southeast Asia. • Muslim merchants set up trade businesses in Africa. • Muslims generally practiced tolerance, or acceptance, with regard to the people they came in contact with. Growth of Cities Baghdad • Capital of Islamic Empire • One of the world’s richest cities through trade and farming. • Center of culture and learning Growth of Cities Cordoba • By the AD 900s, was the largest and most advanced city in Europe • Showplace of Muslim civilization Three Muslim empires controlled much of Europe, Asia, and Africa from the 1400s to the 1800s. • The great era of Arab Muslim expansion lasted until the 1100s. • Three non-Arab Muslim groups built large, powerful empires that took control of much of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire • Ottomans were Muslim Turkish warriors who took territory in the mid-1200s. • They had new gunpowder weapons. • Mehmed II and Suleyman I led conquests that turned the Ottomans into a world power. • Ottomans took control of the eastern Mediterranean and pushed farther into Europe from 1520–1566. • They would control these areas until the early 1800s. Ottoman Empire The Safavid Empire The Safavid Empire • Safavids were Persian Muslims. • A conflict arose over who should be caliph among the Safavids, Ottomans, and other Muslims. • Islam split into two groups. 1. The Shia thought that only members of Muhammad’s family could become caliphs. 2. The Sunni thought it did not matter as long as they were good Muslims and strong leaders. • The Safavids blended Persian and Muslim traditions. • The Safavid Empire lasted until the mid-1700s. The Safavid Empire The Mughal Empire The Mughal Empire • The Mughal Empire was located in northern India and was comprised of Turkish Muslims from Central Asia. • Babur established the Mughal Empire, but it grew mostly under an emperor named Akbar. • Akbar’s tolerant policies allowed Muslims and Hindus to live in peace. • The Taj Mahal was built in Agra, India by Shah Jahan as a tomb for his wife. • In the late 1600s, an emperor reversed the tolerant policies, which led to conflicts and the end of the empire. Cultural Achievements Muslim scholars and artists made important contributions to science, art, and literature. Main Ideas • Muslim scholars made lasting contributions to the fields of science and philosophy. • In literature and the arts, Muslim achievements included beautiful poetry, memorable short stories, and splendid architecture.