* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart valve disorder
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
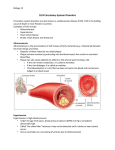
Diseases of the Cardiovascular System Atherosclerosis / Arteriosclerosis Pathological thickening and loss of elasticity of arterial walls “hardening of arteries” due to deposits of atherosclerotic plaques that narrow the arterial lumen. Hypercholesterolemia causes atherosclerosis. This condition places the individual at high risk of stroke, coronary heart disease and heart attack. Circulating blood clot and/or an arterial spasm may block the vessel completely. When atherosclerosis affects the coronary arteries of the heart, it leads to: a. Silent ischemia: blood flow to the heart muscle is interrupted without any pain to provide warning! b. Angina pectoris: chest pain caused by inadequate O2 to the heart muscle cells. This condition may also result from stress-induced spasm of the atherosclerotic coronary arteries. c. Myocardial infarction: when the blockage of a coronary artery is more complete or prolonged. This leads to death of the cardiac muscle cells, or severe heart attack. Heart valve disorder Defects of the heart valves are due to: a. b. c. d. Congenital and genetic abnormalities. Inadequate blood supply to the valve as a result of a heart attack. Bacterial infection of the endocardium; such as subacute bacterial endocarditis. Rheumatic heart disease; such as rheumatic fever during childhood. Heart valve defects are classified into 2 types: incompetent or stenotic. Heart failure Heart failure is a progressive weakening of the heart as it fails to keep pace with the demands of pumping blood thus cannot meet the body demands for oxygenated blood. Mitral valve stenosis, aortic valve stenosis or insufficiency, or weakened ventricles as a result of heart attack may be a cause of the heart failure. Aneurysm Is a sac-like widening or outpocketing of an Artery or a vein that places the vessel at risk of rupturing. The aneurysm may result from: a. Congenital weakness. b. Hypertension or arteriosclerosis may cause gradual weakening of the arterial wall. Deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb Is the formation of clots in the veins of lower extremity. The clot may detach and travel to the heart and pulmonary trunk, then blocks a branch of the pulmonary artery causing Pulmonary Embolism. Congenital heart defects The most common is Ventricular Septal Defect, in which the superior region of the interventricular septum fails to form, leaving a hole between the two ventricles. Hypertension Blood Disorders