* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding Electromagnetic Induction and Electromagnetism
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
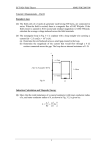
Understanding Electromagnetic Induction and Electromagnetism Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Electromagnetism Relates to the magnetic field generated around a conductor when current is passing through it. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Coil Coil – A number of turns of wire wound around a core to produce magnetic flux (an electromagnet) or to react to a changing magnetic flux (an inductor). Electromagnet – A magnet consisting of a coil wound on a soft iron or steel core. When current is passed through the coil, a magnetic field is generated and the core is strongly magnetized to concentrate the magnet field. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Left-hand rule If the fingers of the left hand are placed around the wire so that the thumb points in the direction of the electronic current flow, the fingers will be pointing in the direction of the magnetic field being produced by the conductor. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Magnet Terms Maxwell – One magnetic line of force or flux is called a Maxwell. Magnet Flux (φ) – The magnetic lines of force produced by a magnet. Weber – 108 Maxwells. Flux Density (β) – A measure of the strength of a wave. Flux Density (β) = Magnet Flux(φ)/Area (A) Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Magnet terms (continued) Magnetomotive Force (mmf) – A force that produces a magnetic field. mmf = I(current) × N(turns) = I × N (ampere-turns) Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Magnetizing force (H) Magnetizing Force – Also called magnetic field strength, it is the magnetomotive force per unit length at any given point in a magnetic circuit. I × N mmf H= = l l Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Reluctance (R) Reluctance – Resistance to the flow of magnetic lines of force. Magnetic Reluctance (R) = mmf/φ Measured in Ampere-Turns/Weber Electric Resistance (R) =V/I Measured in Ohms Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Permeability (µ) The measure of how much better a material is as a path for magnetic lines of force with respect to air, which has a permeability of 1. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Magnetic Permeability (µ) = 1/(R) reluctance Electric Conductance (G) = 1/ (R) resistance Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Permeabilities of various materials Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Flux density (Β) vs. magnetizing force (H) Β-Η curve – A curve plotted on a graph to show successive states during magnetization of a ferromagnetic material. Saturation Point – The point beyond which an increase in one of the quantities produces no increase in the other. Hysteresis – A lag between cause and effect. With magnetism, it is the amount that the magnetization of a material lags the magnetization force due to molecular friction. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Remanence or Retentivity – The amount of a material that remains magnetized after the magnetizing force has been removed. Coercive Force – Magnetizing force needed to reduce the residual magnetism within a material to zero. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Applications of electromagnetism Magnetic type circuit breaker Electric bell Relay Solenoid-type electromagnet Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Relay Relay – An electromechanical device that opens or closes contacts when a current is passed through a coil. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Solenoid Solenoid – A coil and movable iron core that, when energized by an alternating or direct current, will pull the core into a central position. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Electromagnetic induction Electromagnetic Induction – The voltage produced in a coil due to relative motion between the coil and magnetic lines of force. Faraday’s Law – When a magnetic field cuts a conductor, or when a conductor cuts a magnetic field, an electric current will flow in the conductor if a closed path is provided over which the current can circulate. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Electromagnetic induction (continued) Lenz’s Law – The current induced in a circuit due to a change in the magnetic field is so directed as to oppose the change in flux, or to exert a mechanical force opposing the motion. Weber – A unit of magnetic flux. One weber (108 maxwells) is the amount of flux that, when linked with a single turn of wire for an interval of one second, will induce an electromotive force of one volt. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Generator Generator – A device used to convert a mechanical energy input into an electrical energy output. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Parts of a generator Armature – The rotating or moving components of a magnetic circuit Stator – The stationary components of a magnetic circuit Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Generator operation Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Moving coil microphone Microphone – Electroacoustic transducer that responds and converts a sound wave input into an equivalent electrical wave output. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen End of Electromagnetic Induction and Electromagnetism Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen