* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exercises unit 2. Digestive system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Exercises unit 2. Digestive system
1.a. Digestion is the processes which break down food into simple substances
Notice that food is not the same as nutrients.
Food: material, usually of plant or animal origin, that contains substances to mantain life
Nutrient: any substance that nourishes an organism, any substance that is in food
Milk, meat, fish, fruits are food.
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, mineral salts and water are nutrients
1.b. To break down
2.a. Stages (etapas) in the digestive process: ingestion, digestion, absorption, egestion.
Definitions in the book
3a. Ingestion the intake (toma) of food into the body through (a través de) the mouth
3.b.
SELECCION OF WORDS:
filtering machine /
the colored dye coming out in less than two
sucking in water /
seconds /
pump over a Ton of water to get 25grams of food /
millions of nanocanals
1º The body sponge is pierced by milions of nanocanals
2º Lining the inner body wall there are cells with flagella. The movement of flagella moves
the water through the sponge body wall.
3º.The water comes in through the nanocanals and goes out through the osculum
4º. Sponges get their food by sucking in and filtering a big amount of water
5º.The water flow is quite quick
3.c.
SELECCION OF WORDS:
active predators
awaits its prey
weapons
microscopic stinging cells called nematocysts
special capsules
threadlike projectiles loaded with deadly poisons pressure inside builds up until the cover of the
plantlike appearance
capsule blows off
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Polyps and jellyfish are predators although they have a plantlike appearance
Lining the their tentacles there are cells called nematocystes
Nematocustes are capsules full of poison
When the prey touches the tentacles the pressure inside builds up
The cover of the capsules blow off and threadlike projectils pierce the skin of the prey
The prey is dragged to the gastric cavity.
4.- a) and b) Food contains complex substances that can not be absorbed. Digestive juices break
them down
polysaccharides
monosacharides
disaccharides
monosaccharides
fats
fatty acids
proteins
amino acids
vitamins, water and mineral salts don't need digestion (they are fery little)
4.d. Internal digestion: digestion takes place inside of the body, either in the digestive tube or in
a gastric cavity (en un tubo digestivo o en una cavidad digestiva)
Some animals have gastric cavity -with only one opening working as a mouth and as anus- such
as polyps and jellyfish. Be careful: sponges don't have gastric cavity because in reallity digestion
happens inside cells.
Most animals have a digstive tube, with two openings: mouth and anus. Accesory glands
secrete digestive juices into the digestive tube. Digestion takes place in the digestive tube.
External digestion takes place outside the body, such as in spiders: spiders have a pair of
pointed appendages which are used to inject venom into the prey; after that, the spider pumps
digestive enzymes into the prey and then sucks the liquified tissues of the prey, leaving the
empty husk.
4c.- External digestion is not the same as extracellular digestion.
External digestion takes place outside the body (remember spiders)
Extracellular digestion takes place inside the body but before nutrients enter the cells.
Extracellular digestion takes places either in a digestive tube or in a gastric cavity.
Unicellular organisms have intracellular digestion: they haven't got digestive tube or cavity
because they are unicellular. One process by which unicellular organisms (which organisms?
ingest their food is called phagocytosis. In phagocytosis:
1. The cell stretches itself around a food particle
2. After the engulfment the particle will be inside a vesicle
3. A cell lysosome joins the vesicle containing the food particle
4. The digestive enzymes in the lysosome digest the food particle
5. After digestion, nutrients go out of the digestive vesicle into the cell cytoplasm
6. Indigested parts can be expelled out of the cell
)
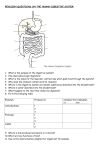
4.e. Digestive system:
– digestive tube includes:
– Mouth where the food is chewed (to chew= masticar)
– Pharynx: the area at the top of the throat where the passages to the nose and
mouth connect.
– Oesophagus: the tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach
– Stomach: where food goes when you swallow it and where gastric digestion takes
place. Only proteins are digested in stomach and just partially digested.
– Small intestine: digestion finishes here and then absorption takes places.
– Large intestine: it finishes the absorption of water, some vitamins and mineral
salts. Undigested food is trasformed into faeces.
– Accessory glands secrete their juices containing digestive enzymes into the digestive
tube:
– Salivary glands
– Pancreas
– Liver, which produces bile
4.e. Let`s clarify some details about the video showing “the digestion in rumiants”
Like other vertebrates, ruminant (including deer, cows...) cannot digest cellulose/fiber.
Digestion in ruminants occurs in a four-chambered stomach. Plant material is initially taken into
the Rumen, where it is exposed to bacteria than can break down cellulose. The Reticulum allows
the animal to regurgitate ("RUMINATION, chew its cud"). Food is then passed to the Omasum,
for further mechanical processing. The mass finally goes to the true stomach, the Abomassum,
where the digestive enzyme lysozyme breaks down the bacteria so as to release nutrients.
•
•
•
•
•
Where is cellulose digested?
The relationship between the cow and bacteria living in its rumen is called mutualism. What
does it mean?
From the rumen , food passes to...
and the to...
where it is re(at this point cell walls are already partially
digested.
Our stomach is similar to …
in cows.
Why does the video say “ the elegant
mechanism of rumination”?
5.a. From the definition in your book I point out “passage of nutrients...”; blood carries … to...”
5.b. Already done
6.a.From the definition I point out “elimination of indigested...”, “...transform into feaces”
6.b. Excretion is the process of collecting and expelling outside waste substances produced by
cellular metabolism, such as CO2 and urea. These waste substances come from the interior of
cells. Kidneys and other similar structures and respiratory systems play a role in excretion. Urine
is produced by kidneys after filtering blood – o hemolymph in insectsEgestion is the elimination of undigested food. These waste substances don't come from
the interior of cells because they never went out of the digestive tube. The waste product
expelled by egestion is faeces.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
1. Breathing is about inhaling and exhaling. Respiration is about interchanging gases with blood.
2. To carry out efficently gas exchange between the environment and the body, the surface for
gas exchange have to be thin, moist=damp and covered IN vessels
3.- Cutaneous respiration is efficient in earthworms because:
– earthworms live inside soils, so their skin is always damp
–
–
because of the humidity in soil, the skin can be thin without risk of dehydration
cutaneous respiration is not efficient in round animals; it's more efficient in long,
cilindrical or flat animal where the surface is porportionally bigger