* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download circular powerpoint
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
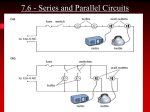
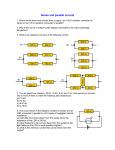
Electric Circuits Explaining Electric circuits P5.5 Measuring resistance P5.4 Resistors in parallel P5.1 Static electricity P5.2 Current and voltage P5.4 Resistors in Series Introduction Electric Circuits 21st Century P5.1 – 5.5 Electric Circuits • • • • • P5.1 Static Electricity P5.2 Current and Voltage P5.4 Resistors in series P5.4 Resistors in Parallel P5.5 Measuring resistance We will be examining the above sections and any formulas relating to them. Task Use the presentation and your own knowledge to complete the electric circuits work sheet. You will then use this sheet to complete some past paper questions. Electric Circuits Explaining Electric circuits P5.5 Measuring resistance P5.4 Resistors in parallel P5.1 Static electricity P5.2 Current and voltage P5.4 Resistors in Series Static Electricity Some staff felt that shock therapy was going too far to What is it? Static charge is literally charge that cannot move. It is static. The charge in this case is an electric charge. The particles that move are electrons. They have a negative charge. How to create it Demonstration of static electricity Experimenting with static charge Uses of static electricity photocopiers and laser printers spray painting cars filtering factory smoke heart defibrillators Electric Circuits Explaining Electric circuits P5.5 Measuring resistance P5.4 Resistors in parallel P5.1 Static electricity P5.2 Current and voltage P5.4 Resistors in Series Current and Voltage Definition - Current • A flow of electric charge – Usually electrons Definition - Voltage The amount of energy transferred to or from charges when they pass between two points Conductors and insulators • Conductors have large numbers of free electrons. This makes it easy for current to flow through them. • Insulators have very few free electrons. This makes it hard for current to flow through them. Measuring current • We use a ammeter to measure current. The unit of current is the amp. An ammeter is wired in series. Measuring voltage • Voltage is measured using a voltmeter. It is measured in volts (V) a voltmeter is connected in parallel Electric Circuits Explaining Electric circuits P5.5 Measuring resistance P5.4 Resistors in parallel P5.1 Static electricity P5.2 Current and voltage P5.4 Resistors in Series Resistors in series Resistance • All electrical components have resistance. They convert the energy from the electrons into other forms of energy, often heat. • If there are multiple components we need to be able to add them together. Components can be connected in series or parallel Formula • Components in series follow one after the other whereas components in parallel run along side by side. • We can add resistors in series together with the following formula :- RT R1 R 2 R3 ....... Units • The unit for resistance is the ohm. Additional Notes • If an component has a high resistance it converts a large amount of electrical energy as the current flows through it. • i.e A lamp with a high resistance will change more electrical energy into light Electric Circuits Explaining Electric circuits P5.5 Measuring resistance P5.4 Resistors in parallel P5.1 Static electricity P5.2 Current and voltage P5.4 Resistors in Series Resistors in parallel Resistors in parallel • We also need to be able to add resistors in parallel. • Parallel resistors run side by side • This gives an extra route for the current to flow through • Because of this the overall resistance is less than the resistance of any individual resistor Formula This is the formula for calculating the total resistance of resistors in parallel 1 1 1 1 ...... RT R1 R2 R3 Additional notes • The gradient of the line in a current voltage graph represents the value of the resistance. The steeper the line the higher the resistance. Electric Circuits Explaining Electric circuits P5.5 Measuring resistance P5.4 Resistors in parallel P5.1 Static electricity P5.2 Current and voltage P5.4 Resistors in Series Measuring resistance Measuring resistance • The size of the current flowing in a circuit depends on the voltage of the cell and the resistance of the circuit. • This means that the size of the resistance can be found if we know the current and voltage in a circuit Formula • Voltage = Current X Resistance • V=IR V = Voltage I = Current R = Resistance Units • Voltage is measured in volts (v) • Current is measured in amps (A) • Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω) Current voltage graph • The graph opposite shows current passing through a resistor plotted against the voltage across a resistor. As it is a straight line it shows if we double the voltage we will double the current Electric Circuits Explaining Electric circuits P5.5 Measuring resistance P5.4 Resistors in parallel P5.1 Static electricity P5.2 Current and voltage P5.4 Resistors in Series