* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US Climate Science and Cyberinfrastructure
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
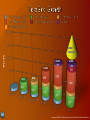
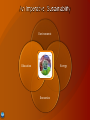
Timothy L. Killeen Assistant Director for the Geosciences Directorate National Science Foundation Clifford A. Jacobs Division of Atmospheric Sciences National Science Foundation GEO NCSA 2015 Strategic Planning Process April 21, 2010 New Outlook • Administration • Key players • Climate Research Program NSF’s Climate Research •Special emphasis within NSF •Description of program SEES – Science, Engineering, and Education for Sustainability GEO Support for Cyberinfrastructure • Infrastructure • Planned National investment in R&D to ≥ 3% of GDP S&T in the stimulus/recovery package FY2009 / FY2010/2011 budgets • NSF, NIH, DOE-science, NIST, NOAA, NASA, DoD basic research Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Education • science labs, teacher training, clean energy ($1.5B over 5 yr) Clean energy / climate • $150B over 10 yr for clean energy & efficiency; ARPA-E; energy centers of excellence; climate science Courtesy of Paul Filmer, National Science Foundation John Holdren, White House Science Advisor Carol Browner, White House Climate and Energy Czar Steven Chu Jane Lubchenco, NOAA Administrator Secretary of Energy Nancy Sutley, Council on Environmental Quality Lisa Jackson, EPA Administrator Courtesy of April Burke, Lewis-Burke Associates DOE OS +3.9% DOE EERE +6.4% (ARRA $1.6 Billion) EPA +38% (ARRA $16.8 Billion) (ARRA $7.2 Billion) NOAA +2.5% NASA +5% (ARRA 830 Million) NSF +8.5% (ARRA $1 Billion) (ARRA $3 Billion) FY 2010 President’s Request compared to FY 2009 enacted ARRA = American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 Courtesy of April Burke, Lewis-Burke Associates Source: NSF FY2010 Budget Request to Congress Presidential Priorities • Protecting our nation from the serious economic and strategic risks associated with our reliance on foreign oil and the destabilizing effects of a changing climate • Advancing energy and climate security via promoting economic recovery efforts, accelerating job creation, and driving clean energy manufacturing Expanded Commitment Global Change Research FY 2011 Budget • Improve understanding of climate change and its impacts • Mitigate US greenhouse gas emissions and move toward clean energy economy • Adapt to climate change impacts Climate Change Adaptation (assessment & response) Climate Change Science (understanding & forecasting) From presented by Shere Abbott, Associate Director for Environment, 1 February 2010 Climate Change Mitigation (mitigation & response) Expect that CCSP scope, composition and responsibilities will be revisited and reauthorized by Congress All 21 of Synthesis and Assessment publications completed Unified Synthesis Product: Global Climate Change Impacts in the United States • Summarizes climate change science, current and future impacts, integrates those results from those around the world. Courtesy of Paul Filmer, National Science Foundation Integrated scientific-societal issues Interactions among the climate, human, and environmental systems U.S. climate observing system including physical, biological, and social observations Coupled Earth system models Adaptation Courtesy of Paul Filmer, National Science Foundation NSF's FY 2010 Budget Request is $7.045 billion, an increase of $555 million (8.5 percent). Focus on Climate Change: • New Climate Change Education Program ($10.0 million in FY 2009 and FY 2010); • Increase for NSF contribution to the Climate Change Science Program (36.6 percent increase to $299.91 million); and • New NSF-wide focus on Climate Research. $197M in funding in FY10 across NSF 8 NSF Directorates involved in Climate Research $10M for New Climate Change Education in FY09/FY10 (BIO, GEO, OPP and E&HR partnership) Increase NSF contribution to USGCRP (to $299.91M) Environmental Observation including changes from human activities, adaptation, and mitigation Modeling of Basic Natural and Human Processes & their interactions Fundamental Research, Including Experiments Must be interdisciplinary Approaches are creative and high risk Research involves problems that cannot be undertaken in the core programs Research support is shared across multiple directorates Water: Sustainability and Climate (WSC) • LOI received: 311; Full proposal deadline: 4/15 Ocean Acidification (OA) • LOI received: 127; Full proposal deadline: 4/26 Climate Change Education Partnership, Phase 1 (CCEP-1) • LOI deadline: 4/23; Full proposal deadline: 5/24 Dimensions of Biodiversity (DB) • LOI deadline: 5/7; Full proposal deadline: 6/8 Decadal and Regional Climate Prediction Using Earth System Models (EaSM) • LOI deadline: 5/24; Full proposal deadline: 6/25 • American Recovery Act GEO investments: $601M • FY2010: 10.2% increase over FY2009 • Includes Agency-wide climate initiative • FY2011: President’s budget request includes a 7.4% increase for GEO Priority Guidance: NSF should continue to increase emphasis on innovation in sustainable energy technologies and education as a top priority. NSB offers the following specific guidance to NSF: • “Strengthen systems approaches in research programs.” • “Develop and strengthen interdisciplinary systems approaches for research programs in the natural and social sciences that focus on environmental, social, and economic issues fundamental to the future energy economy.” SEES will generate the discoveries in climate and energy science needed to inform societal actions for environmental and economic sustainability. • Emergence of new areas of research that help close key gaps in the knowledge base. • Development of new models for research, specifically employing integrative, systemic approaches. • Generation of new integrated understanding of the interplay of environment, energy, and the economy. SEES portfolio totals $765.5 million in 2011. Dear Colleague Letter signed by all NSF Assistant Directors and Office Heads issued in March 2010 SEES Web Site: www.nsf.gov/sees $28M over two years for new research program emphasizing change and complexity in earth system processes Goals: • foster an inter-disciplinary and multi-scale understanding of Earth’s dynamic systems • catalyze research in areas poised for a major advance in understanding • improve observing networks and modeling capabilities to more realistically simulate complex earth systems and forecast disruptive events • improve understanding of the resilience and sustainability of earth systems following disruptive events. OOI Operations and Management – 2011 brings a ramp-up in O&M support for the OOI Regional Class Research Vessels – 2011 will see continued planning for the construction of up to three Regional Class Research Vessels starting in 2012. NCAR-Wyoming Supercomputer Center – 2011 sees the continuation of support for the construction of a new community supercomputer center. NCAR-Wyoming Supercomputing Center Project (NWSC) This project encompasses the design and construction of a world class center for high performance scientific computing in the atmospheric and related geosciences. NSF FY 2011 request includes an $11m augmentation for NCAR to cover increased support for climate change activities as well as preparation for the transition of computing operations to NWSC. [email protected] [email protected] Total NSF Funding (dollars in billions) 10 8 6 9.5 3.0 ARRA 6.5 6.9 2009 2010 8.3 7.4 7.8 2011 2012 8.9 9.5 10.2 10.9 4 2 0 2013 2014 Fiscal Year (FY) FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2015 2016 2017 Science, Engineering, and Education for Sustainability (SEES +$35M to $230M) Follow-on to 2010 Climate Research activity Improve American Competitiveness through investments in science and technology to foster economic growth; improve the quality of life; and strengthen our national security. Support researchers at the beginning of their careers through NSF's Graduate Research Fellowship and Faculty Early Career Development programs. Educate science and engineering technicians through the Advanced Technological Education program, which focuses on two-year colleges Encourage promising high-risk research that could fundamentally alter our understanding of nature, revolutionize fields of science, and lead to radically new technologies. Make climate change research and education a priority. To predict future environmental conditions and to develop strategies for responding to global environmental change. Establish a climate change education program to help develop the next generation of environmentally engaged scientists and engineers. Modeling , scaling, complexity Geosciences Fundamental research Biological Sciences Environmental observation Office of Polar Programs Adaptation Education and human Research MISSION BUDGET Development of collaborative computational science CI Annual Expenditures within all of NSF: $865M • Research and development of comprehensive CI • Application of CI to solve complex problems in science and engineering • CI Expenditures in Other Parts of NSF: $680M • OCI FY09 Budget: $199M+80M (ARRA) NSF CYBERINFRASTRUCTURE EXPENDITURES Provide stewardship for computational science at NSF, in strong collaborations with other offices, directorates, and agencies Supports the preparation and training of current and future generations of researchers and educators to use Cyberinfrastructure to further research and education goals OCI OTHER NSF Virtual Organizations for Distributed Communities High Performance Computing Data & Visualization/ Interaction Learning & Work Force Needs & Opportunities http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2007/nsf0728/index.jsp Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Modeling and simulation Computers Data analysis & visualization Data services User support Text Training Visualization services People Courtesy of University of Indiana Common user environments 2007-8 Track 2 – TACC 2008-9 Track 2 – UTK 2009-10 Track 2 – PSC 2010-11 Track 2 – TBD 2011 Track 1 – NCSA Tools for educators Science Gateways Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation NSF seeks to deploy/support a world-class HPC machine of unprecedented capability to empower the U.S. academic research community Machine is called “Blue Waters” and will be located at the NSCA at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Award of $207M effective October 1, 2007 for 5 years Blue Waters will be completed/operational 2011 Available for use on “Grand Challenge” projects with users selected via a competitive process Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Blue Waters General Characteristics • Based on IBM PERCS • 1 petaflops sustained performance on real applications Blue Waters System Characteristics • > 200,000 cores using multicore POWER7 processors • > 32 gigabytes of main memory per SMP • > 10 petabytes of user disk storage • > 100 Gbps external connectivity (initial) • Fortran, Co-Array Fortran, C/C++, UPC, MPI/MPI2, OpenMP, Cactus, Charm++ Blue Waters Interim Systems at NCSA • POWER 5+ and POWER6 software and application development testbeds Blue Waters System Training and Support Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation NSF Solicitation to deploy/support HPC machines to a wide range of researchers nationwide Two machines completed with two more planned Systems are used in various research simulation & modeling projects Machine operating costs/maintenance/user support $7.5M/yr-$9M/yr Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Fall 2006 $59 million award • $30 million system • 4 years of operating costs Ranger • Peak performance of 579 teraflops • Over 60,000 processing cores • 125 TB memory • 1.7 PB Available since Feb, 2008 Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation 2007 • University of Tennessee at Knoxville $65 million, 5-year project • Partners at ORNL, TACC, NCAR Kraken • • • • • Cray XT5 8256 compute nodes, 66,048 computational cores More than 100 terabytes of memory 2,300 trillion bytes of disk space Peak performance of more than 607 teraflops Full production Feb 2009 Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation TFLOPS Blue Waters >2010 2100 >1500 684 850 Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Image courtesy of g3D, Inc. Courtesy of National Center for Atmospheric Sciences Four primary goals: • Provide reliable digital preservation, access, integration, and analysis capabilities for science/engineering data over decadeslong timeline • Achieve long-term preservation and access capability in an environment of rapid technology advances • Create systems and services that are economically and technologically sustainable • Empower science-driven information integration capability on the foundation of a reliable data preservation network Each project needed to develop a model for shared governance and the standards and protocols to enable interoperability Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Redefine the role of University Libraries to include scientific data as special collections Building on JHU Library success with Sloan Digital Sky Survey and National Virtual Observatory Initial focus on observational data about astronomy, turbulence, biodiversity and environmental science Especially suited to terabyte-scale data sets but with strong focus on “the long tail of small science.” Project led by researchers at Johns Hopkins University Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Designed to enable long-term access to and use of preserved earth observation data • Projects will include: The spread of diseases, the impact of human behavior on the oceans, relationships among human population density and greenhouse gas production Will build using an evolutionary development process Data are diverse and complex – multi-scale, multidiscipline, multi-national Project led by the University of New Mexico Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Develop the future simulation, optimization and analysis tools that use emerging petascale computing Will advance frontiers of research in science and engineering with a high likelihood of enabling transformative research Areas examined include: • -Climate Change • -Earthquake Dynamics • -Storm Surge Models • -Supernovae simulations http://nsf.gov/pubs/2008/nsf08592/nsf08592.pdf Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation Goals: • Provide network connections linking U.S. research with peer networks in other parts of the world • Stimulate the deployment and operational understanding of emerging network technology and standards in an international context • Support science and engineering research and education applications Proposals due Aug. 21, 2009 • ~$40M over 5 years http://www.nsf.gov/funding/pgm_summ.jsp?pims_id=503382 Courtesy of Office of Cyberinfrastructure, National Science Foundation • Networking and Information Technology R&D Program: $1.17 billion • U.S. Global Change Research Program: $370 million • National Nanotechnology Initiative: $401 million ARRA allowed NSF to make 4,599 competitive awards and will support the construction of the Alaska Region Research Vessel (renamed: Sikuliaq “New Ice suitable for walking on”) Environment Education Energy Economics