* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L A cell is the basic unit of all living things. Life processes are the
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
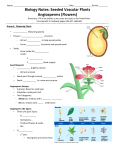
L A cell is the basic unit of all living things. Life processes are the functions a living thing must carry out in order to stay alive and reproduce. Nutrients are substances that are needed for an organism to live and grow. Similar cells working together form a tissue. Different tissues working together form an organ. A plant cell has a cell wall and chloroplasts. An animal cell does not. The cell wall is the tough outer covering of a plant cell that gives the cell its rigid shape. The nucleus is the control center of a cell’s activities. Chloroplast is the structure in which food making occurs. It contains chlorophyll. Cytoplasm is a jellylike substance that fills much of the cell. A vacuole is a large storage area in a cell filled with a liquid that contains various substances. A cell membrane is a thin layer surrounding all cells that allows water and dissolved materials into and out of the cell. Photosynthesis is the food-making process of plants. During photosynthesis plants take in sunlight, CO2, and water to make glucose (sugar) which they use for food. Plants then give off oxygen as a waste gas. Roots absorb water and anchor the plant into the ground. Stems connect the roots to the leaves and keep the plants upright. The leaves are the food-making factory of plants. Leaves take in CO2 and sunlight and release oxygen. Stomata are the holes in leaves that bring in CO2 and release oxygen. Tropism is the plant’s response to its environment. Chlorophyll is the chemical in chloroplasts that makes plants green and helps cause photosynthesis. Germination occurs when a plant first begins to grow out of its seed. An embryo is a plant that is still in the seed. This is the beginning stage for any living thing. A seedling is a plant that has just begun to grow above ground. A cone is the part of a conifer plant that produces pollen or seeds. Producers (plants) are living things that make their own food. Consumers (animals) are living things that get their food from eating other living things. Fertilization occurs when pollen lands on a stigma and fertilizes the ovary, growing a new plant. The seed coat is the part of the seed that protects the embryo. The stamen is the male part of the flower that produces pollen necessary to make seeds. The pistil is the female part of the flower that takes in pollen from the stamen to make seeds. Petals attract animals to plants to help with pollination. The fruit is the part of a flower that forms around a seed. Vegetables are the parts of some plants that form near or on the roots. The life cycle of flowering plants 1. The flowers are ready to be pollinated. 2. Seeds develop and are scattered. 3. Seeds absorb water and begin to swell 4. The seed germinates. 5. The plant grows and flower buds appear.