* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
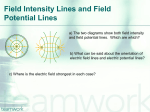
17.1 Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference 17.2 Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field 17.3 Equipotential Lines 17.4 The Electron Volt, a Unit of Energy 17.5 Electric Potential Due to Point Charges Objectives: 1. Students will explain the principles of electric potential energy. 2. Students will relate electric potential to potential difference. 3. Students will connect electric potential to potential energy. 4. Students will explain the relationship between electric potential and electric field. 5. Students will demonstrate the use of equipotential lines. 6. Students will explain the relationship of electric potential to point charges. Homework: 1-19 odd p. 489 Formula Search –Find all formulas state the units and purpose for making calculations. Vocabulary to Know: Electric potential Gravitational potential Potential energy Equipotential lines Conservative force Equipotential surfaces Electrostatic force Electric dipole Electric field Electron volt Kinetic energy Joules Test charge Absolute potential Work Volt Voltage 17.1 Electric Potentail Energy and Potential Difference: 1. Why is potential energy a conservative force? 2. Why is an electrostatic force conservative? 3. Describe the change in electric potential energy. 4. How is work significant to the change in electric potential energy? 5. Explain how the conservation of energy is conserved in situations that involve electric potential energy. 6. How is electric potential related to potential difference? 7. How is electric potential related to work? 8. What is the unit of potential difference? 9. How can gravitational potential energy be used as an example of electric potential energy? 10. Create a list of examples that show potential differences. 11. What relationship does mass have with potential energy and speed? 17.2 Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field: 1. Why is electric potential easier to use than electric field to describe charge? 2. How can the units of electric field be written as volts? 3. What is the general relation between electric field and volts? 17.3 Equipotential Lines: 1. What is an equipotential surface? 2. What is the relationship of electric field to an equipotential surface? 3. Draw two examples of equipotential lines. 4. What is an electric dipole? 5. State the principles that govern the drawing of equipotential lines. 17.4 The Electron Volt, a Unit of Energy: 1. Compare and contrast the electron volt with a joule. 17.5 Electric Potential Due to Point Charges: 1. Define the relationship of variable in equation 17.5. 2. Draw and explain figure 17-9. 3. How can electric potential be an advantage in solving problems?