* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Print › 8th Grade STAAR Plate Tectonics and Topo Maps
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
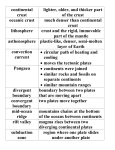
8th Grade STAAR Plate Tectonics and Topo Maps Study online at quizlet.com/_nd0eq Alfred Wegener A German scientist who proposed the theroy of continental drift Ancient Climate Evidence Preserved remains of tropical reefs were found on the Arctic island of Spitsbergen supports the Theory of Continental Drift. Continental Drift The hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations Contour Interval On a topographic map, tells the distance in elevation between adjacent contour lines. Contour Lines Line on a topographic map that indicates an elevation; every point along a contour line has the same elevation. Convection Currents Circular currents in the mantle caused by the magma being heated by the core off the Earth. 27. Convergent Boundary A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other. 28. Crust Earth's outermost layer. Divergent Boundary A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other. Elevation Height above sea level Erosional Features Earth's surface that shows evidence of the natural processes of weathering and the removal and relocation of weathered materials. Fault A break in Earth's crust where continental plates slip past each other. Fossil Evidence Traces of the same prehistoric organisms are found on different continents separated by oceans 14. Harry Hess Proposed the theory of sea-floor spreading where new crust material is created and is destroyed at ocean trenches, which lead to the theory of Plate Tectonics. 15. Inner Core A dense sphere of solid iron and nickel at the center of Earth. 16. Lithosphere Earth's crust and solid upper mantle, broken into tectonic plates 17. Mantle Earth's thickest layer made of hot rock and is less dense than the core, less hot, and has less pressure on it. Mid Ocean Ridge An underwater mountain chain where new ocean floor is formed. 19. Outer Core A layer of molten iron and nickel that surrounds the inner core of Earth. 20. Pangea A supercontinent containing all of Earth's land that existed about 225 million years ago. 21. Plasticity Condition of being able to be shaped or formed. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 18. Puzzle Piece Evidence Supports the Theory of Continental Drift by matching up coast lines from different continents. Rift Valley A deep valley that forms where two plates move apart. Satellite Views Images taken over time that can be used for comparison and interpretation of erosional features. Seafloor Spreading The process that creates new sea floor as plates move away from each other at the midocean ridges. Subduction Process in which one plate moves under another plate, and into the mantle. Takes place at a convergent boundary. Tectonic Plates Sections of the Earth's crust that move due to convection currents. Topographic Map A map that shows the shape of the ground as well as location and elevation of surface features using contour lines. Transform Boundary A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions. 30. Trench Found at convergent boundaries where subduction is occurring. 31. Volcano A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface and is usually found at convergent boundaries. 32. Weathering The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 29.