* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Orbit and the Seasons
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Antikythera mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Lunar effect wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
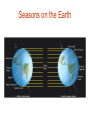
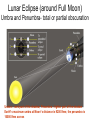
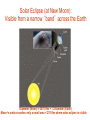
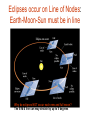
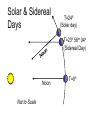
Earth’s Orbit and the Seasons Seasons on the Earth Receives only half the heat and light 1 KW/m2 1 KW/m2 1 m2 2 m2 In winter a bundle of light is spread over a bigger area than in summer owing to the inclination away from the Sun Phases of Moon: Earth-Sun Positions What time of day does the new moon rise and set ? What time of day does the full moon rise and set ? ‘Horns’ of a crescent moon always point away from the Sun Phases of Moon and Time Full Moon rises at dusk and sets at dawn The New Moon rises and sets with the Sun (lies in the same direction as the Sun) Lunar Eclipse (around Full Moon) Umbra and Penumbra- total or partial obscuration Umbra – dark part of the shadow; Penumbra – lighter part of the shadow Earth’s maximum umbra at Moon’s distance is 9200 Kms; the penumbra is 16000 Kms across Total Solar Eclipse: Total obscuration of the Sun by the Moon, possible because the angular size of Moon equals Sun’s Solar Eclipse (at New Moon): Visible from a narrow ‘band’ across the Earth Diameter (Moon) = 3476 Km = ¼ Diameter (Earth) Moon’s umbra reaches only a small area < 270 Km where solar eclipse is visible Annular Solar Eclipse: (when the tip of moon’s umbra doesn’t quite reach the earth) Eclipses occur on Line of Nodes: Earth-Moon-Sun must be in line Why do eclipses NOT occur each new and full moon? The E-M-S line can may deviate by up to 5 degrees Solar and Sidereal Day • How long is one day ? • From noon (Sun directly overhead) to noon ? • How long does it take for the Earth to complete one rotation on its axis ? Orbital and angular motion of the Earth Rotation period of Earth must be less than one solar day Solar & Sidereal Days T=24h (Solar day) T=23h 56m 04s (Sidereal Day) Noon Not to Scale T=0h • The earth moves each day by 1 degree in its orbit around the Sun. So each day the earth has to rotate a bit more to reach the noon position • To rotate one extra degree requires 24 x 60 ---------- = 4 minutes 360 • Solar day (noon-to-noon = 24 hours) is rotation period with respect to the Sun 4 minutes longer than the true rotation period of the Earth with respect to the stars called the Sidereal day = 23h 56 m • 366 sidereal days per year Solar and Lunar Calendar • • • • Rotation of the earth = 1 solar day Revolution around the sun = 365.2422 d Orbital period of moon = 1 month = 29.5306 d Lunar OR solar calendars are possible, but not both since a month is not (i) exact no. of days, and (ii) year is not exact no. of lunar months 12 x 29.5306 = 354.3672 days, not one year • Solar calendar is the one most widely used • Roman Julian Calendar year = 365 d + leap yr Gregorian-Julian Calendar • Problem with Julian Calendar average yr is 365.25 d, 11 minutes too long ! • By the 1500’s, the time of Pope Gregory, the calendar was ahead of astronomical time keeping by more than two weeks • Gregorian reform: Century years not divisible by 400 are ordinary years, not leap years (Example: 1700 AD was not a leap year, but 2000 AD was) Motions of the Earth: Rotation on its axis (day), Revolution or orbit around the Sun (year), and Precession of the Polar N-S axis Position of the north star changes due to the slow precession of the Earth’s axis due to the gravity of the Sun – just like the wobbling axis of a spinning top Precession and the location of Polaris: Period 26,000 Yrs