* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Packet - Unit 15 Populations and Natural Selection Short
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
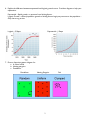
Eastern Regional High School Honors Biology Name:___________________________ Period:______ Date:________________ Unit 15 – Populations and Natural Selection Review Packet 1. Explain how a limiting factor keeps a population near its carry capacity. environmental factors restrict population growth – these can be interspeficif interations or abiotic factors, normally competition for resources – some individuals win the competition, others lose 2. Describe the difference between density dependent and density independent factors in your answer. Dependent – densely populated areas feel these pressures more – occur all the time – “daily pressure” Independent – Doesn’t matter how many individuals there are – rare events that affect all populations equally 3. Explain how evolutionary pressure from natural selection regulates population growth. Only the strong survive when limiting factors begin to put pressure on a population – individuals unfit for survival do not reproduce and pass on genes 4. Explain the process of coevolution and provide at least one example in nature. Coevolution – two organisms are closely connected through an interspecific relationship, such that when one species changes the other will evolve reciprocal adaptations. “Arms Race” 5. Explain the difference between K and r reproductive strategies. K – few offspring, great care for young, keep their population close to its carry capacity (K) r – many offspring, little care for young, populations unstable due to maximize reproductive rate 1 6. Explain the difference between exponential and logistic growth curves. Provide a diagram to help your explanation. Exponential – Rapid growth, no pressure from limiting factors Logistic Growth – slowed population growth as limiting factors begin put pressure on the population – Only the strong survive Logistic – S Shape Exponential – J Shape 7. Draw a dispersion pattern diagram for a. A school of fish b. Nesting penguins c. Dandelions Dandelions Nesting Penguins 2 Fish 8. Explain the difference between convergent and divergent evolution. Divergent evolution- the process of two or more related species becoming more and more dissimilar. Convergent evolution - unrelated species become more and more similar in appearance as they adapt to the same kind of environment. 9. Describe the process of natural selection. Natural selection is the gradual process by which biological traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of the effect of inherited traits on the differential reproductive success of organisms interacting with their environment. It is a key mechanism of evolution. 10. Explain the central dogma of evolution. 3 11. Describe three strategies/adaptions that are a result of co-evolution. Birds beak shapes and flower shapes Thorns on shrubs to prevent herbivory Shark Teeth Cheetah and antelope speed 12. Explain the difference between punctuated equilibrium and gradualism. (5 points) Gradualism - selection and variation that happens more gradually. Over a short period of time it is hard to notice. Small variations that fit an organism slightly better to its environment are selected for Punctuated equilibrium - change comes in spurts. There is a period of very little change, and then one or a few huge changes occur, often through mutations in the genes of a few individuals. 13. Explain the differences between Type 1, II and III organisms on a survivorship curve. (5 points) Type 1 – Die Old – K strategists Type II – Die Whenever Type III – Die Young – r Strategists 4