* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Update in Heart Failure
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
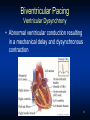
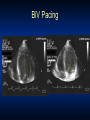
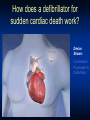
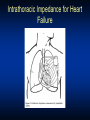
Heart Failure: Living with a Hurting Heart Congestive Heart Failure • Heart (or cardiac) failure is the state in which the heart is unable to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the tissues or can do so only from high pressures Braunwald 8th Edition, 2001 Heart Failure Heart A heart failure heart has a reduced ability to pump blood. Risk Factors for Heart Failure • Coronary artery • Diabetes disease • Congenital heart defects • Hypertension (LVH) • Valvular heart disease • Other: – Obesity • Alcoholism – Age • Infection (viral) – Smoking – High or low hematocrit level – Obstructive Sleep Apnea CAD=coronary artery disease; LVH=left ventricular hypertrophy. Classification of HF: Comparison Between ACC/AHA HF Stage and NYHA Functional Class ACC/AHA HF Stage1 NYHA Functional Class2 None A At high risk for heart failure but without structural heart disease or symptoms of heart failure (eg, patients with hypertension or coronary artery disease) B Structural heart disease but without symptoms of heart failure C Structural heart disease with prior or current symptoms of heart failure D Refractory heart failure requiring specialized interventions I Asymptomatic II Symptomatic with moderate exertion III Symptomatic with minimal exertion IV Symptomatic at rest 1Hunt SA et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;38:2101–2113. 2New York Heart Association/Little Brown and Company, 1964. Adapted from: Farrell MH et al. JAMA. 2002;287:890–897. How Heart Failure Is Diagnosed • Medical history is taken to reveal symptoms • Physical exam is done • Tests – Chest X-ray – Blood tests – Electrical tracing of heart (Electrocardiogram or “ECG”) – Ultrasound of heart (Echocardiogram or “Echo”) – X-ray of the inside of blood vessels (Angiogram) Heart Failure Treatments: Medication Types Type What it does •ACE inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme) •Expands blood vessels which lowers blood pressure, neurohormonal blockade •ARB (angiotensin receptor blockers) •Similar to ACE inhibitor—lowers •Beta-blocker •Reduces the action of stress blood pressure hormones and slows the heart rate •Digoxin •Slows the heart rate and improves the heart’s pumping function (EF) •Diuretic •Filters sodium and excess fluid from the blood to reduce the heart’s workload •Aldosterone blockade •Blocks neurohormal activation and controls volume Device Therapy: Biventricular Pacing Biventricular Pacing Ventricular Dysynchrony • Abnormal ventricular conduction resulting in a mechanical delay and dysynchronous contraction Overview of Device Therapy 9 BiV Pacing Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Key Points • Indications – Moderate to severe CHF who have failed optimal medical therapy – EF<30% – Evidence of electrical conduction delay • Timing of Referral Important – Patients often not on optimal Medical Rx – Patients referred too late- Not a Bail Out Defibrillators (ICD’s) Heart Failure and Sudden Cardiac Death Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) – Your heart suddenly goes into a very fast and chaotic rhythm and stops pumping blood – Caused by an “electrical” problem in your heart – SCD is one of the leading causes of death in the U.S. – approximately 450,000 deaths a year – Patients with heart failure are 6-9 times as likely to develop sudden cardiac death as the general population How does a defibrillator for sudden cardiac death work? Device Shown: Combination Pacemaker & Defibrillator Implantable Cardiac Defribrillators EBM Therapies Relative Risk Reduction Mortality 2 year ACE-I 23% 27% Β-Blockers 35% 12% Aldosterone Antagonists 30% 19% ICD 31% 8.5% Who should Consider an ICD? • Patients with weakend heart, New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class II and III heart failure, and measured left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 35% • Patients who meet all current requirements for a cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device and have NYHA Class IV heart failure; Other Therapies? • Transplant • Artificial hearts • New “gadgets” to help doctors manage heart failure Heart Transplantation • A good solution to the failing heart– get a new heart • Unfortunately we are limited by supply, not demand • Approximately 2200 transplants are performed yearly in the US, and this number has been stable for the past 20 years. Worldwide Heart Transplants Newer Generation Artificial Hearts Future Tech Intrathoracic Impedance for Heart Failure One of the Best Devices for Monitoring Heart Failure What have we learned? In Summary…. • Heart failure is common and has high mortality • Drug therapy improves survival – Betablockers, ACE-I, aldosterone antagonists • Newer device therapies are showing promise for symptom relief and improved survival – Biventricular pacing, ICD’s • Transplants remain rare, but technology for mechanical assist devices continues to improvestay tuned!