* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Locating the Epicenter of an Earthquake WS
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
1908 Messina earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Casualties of the 2010 Haiti earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant wikipedia , lookup
2011 Christchurch earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2010 Canterbury earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
1570 Ferrara earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1992 Cape Mendocino earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
2008 Sichuan earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2010 Pichilemu earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake (1974 film) wikipedia , lookup
1960 Valdivia earthquake wikipedia , lookup
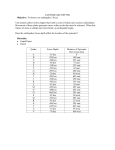
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 10 WORKSHEET LOCATING THE EPICENTER OF AN EARTHQUAKE Name __________________ To figure out where an earthquake happened, you need to use the data recorded for the same earthquake from at least three seismograph stations. This data is recorded as a seismogram. You will also need a map, a ruler, a pencil, and a compass for drawing circles on the map. Sample Seismograms: Intervals are marked by the small lines printed just below the squiggles made by the seismic waves (the time may be marked differently by other seismographs). The distance between the beginning of the first P wave and the first S wave tells you how many seconds the waves are apart. This number will be used to tell you how far your seismograph is from the epicenter of the earthquake. 2 Procedure: 1. 2. 3. 4. For each of the three seismograms, measure the distance between the first P wave and the first S wave. Then record the S-P lag times or differences in the data table. Use a ruler or a piece of paper and the Time-Travel Graph to find the distance of each station from the epicenter of the earthquake. These are the radii of your circles. Use a compass, ruler and the given map scale to construct a circle around each of the three cities. Locate and label the epicenter of the earthquake. (All of the circles should overlap. This point is the approximate epicenter of the earthquake.) EXAMPLE: THE POINT WHERE THE THREE CIRCLES INTERSECT IS THE EPICENTER OF THE EARTHQUAKE. THIS TECHNIQUE IS CALLED 'TRIANGULATION Questions: 1. What is meant by amplitude? ___________________________________________________________________ 2. What happens to the amplitude as you get farther away from the epicenter? ___________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the minimum number of seismograms needed to locate an earthquake using this technique? Why? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 3 Seismic Station Data: Balboa Heights (BH) Boulder Colorado (BC) Mexico City (MC) Data Table: Use the seismograms on the next page to determine the S-P time difference or lag times. Record these in the table below. Seismograph Location 1. Balboa Heights 2. Boulder Colorado 3. Mexico City S-P Time Difference (min) Distance to Epicenter (km) 4 Time-Travel Graph: Use a ruler or a piece of paper and the Time-Travel Graph below to find the distance of each station from the epicenter of the earthquake. These will be the radii of your circles. Refer to the map on the following page. Use a compass, ruler and the given map scale to construct a circle around each of the three cities. Locate and label the epicenter of the earthquake. 5 Location 1. Balboa Heights 2. Boulder Colorado 3. Mexico City Distance (km)