* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar and Punctuation Glossary
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
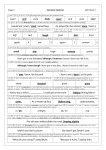
Term Grammar and Punctuation Glossary Definition Examples Adjective An adjective gives more information about The little, green bird pecked the juicy a noun. apple. The apple was delicious. Adverb An adverb gives more information about a verb, an adjective, another adverb or a clause. An adverb tells you how, when, where or how often something happens. Joe quickly ate three apples. Joe ran fast. Joe ran faster than Jim. Joe ran the fastest. He is very shy. A clause is: either a complete sentence or part of a sentence which contains a subject and a verb He was running along the beach. Running along the beach Adverbial phrase Clause A word or phrase that gives more information about a verb or clause. An adverbial can be an adverb, a phrase or a subordinate clause. Cohesion/Golden Cohesion refers to the ways in which the writer makes the different parts of a text Thread link together, for example by: grouping sentences together in paragraphs using particular words and phrases to link ideas linking different paragraphs together Complex sentence An main clause joined to one or more subordinate clauses. Compound sentence Contains 2 main clauses joined by a conjunction. Suddenly, thunder struck. As fast as lightning, he sped down the road. Being careful not to spill anything, pour the mixture into the bowl. The man walked at a slow steady pace towards the door. He was happy. Because he won the race A visit has been arranged for the Year 6 class, to Mountain Peaks Field Study Centre, on July 18th, leaving school at 9.30am. This is an overnight visit. The centre has extensive grounds in which a nature trail has been designed. During the afternoon, the children will follow the nature trail… As mentioned earlier… Because he had won the race, the boy was very happy. The boy was very happy because he had won the race. At cat crept up the tree as the bird pecked an apple. Conjunction Grammar and Punctuation Glossary A conjunction links words or groups of words within a sentence. Co-ordinating conjunctions join words which are of the same importance within the sentence Dash Determiner Hyphen Modal verb Parenthesis A subordinating conjunction joins a subordinate clause that is dependent on the main clause and can’t stand alone. A dash introduces further information and can be used instead of a colon, comma or occasionally brackets. After a dash there may be a list or subordinate clause. A determiner goes in front of a noun and its adjectives to help to tell you which person or thing the sentence is about, or how much or how many of them there are. A hyphen is used to join two or more words that should be read as a single unit. A hyphen is shorter than a dash. Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb. Modal verbs are used for expressing: possibility, ability or likelihood – can, could, may, might, should necessity – must, ought to, should the future – shall, will, would Brackets ( ) commas , and dashes – can all be used to separate a word or phrase that has been added to a sentence as an explanation or afterthought. The word or phrase inside the brackets, commas or dashes is called a parenthesis. Co-ordinating conjunctions: and, but, so, yet. Subordinating conjunctions: although, because, if, since, while. (Often used in informal writing) The fire spread quickly – I was scared. We catch the bus-the blue one-at 3:15pm. He is reading a book. He is reading the book. This book is better than that book. Tongue-tied Football-mad Monster-like Man-eating shark Can, could, will, would, may, might, shall, should, must and ought to. You should do your home learning. You must do your home learning. I looked up, squinting because of the sun, and saw the birds flying across the sky. Grammar and Punctuation Glossary Prefix A prefix is a group of letters added before a word or base to change its meaning and form a new word dis + appear = disappear im + possible = impossible un + well = unwell sub + marine = submarine Phrase A phrase is a collection of words working together but with no verb. Smashing into a fence Preposition A preposition usually comes before a noun She waved to her mother and watched her or pronoun. It often shows place or as she disappeared in the fog at the direction. bottom of the street. The cat stayed under the table until the dog left the room. Relative clause A relative clause is a subordinate clause that changes a noun. Before the first test After the devastation The person who phoned me last night is my best friend. The car, which was bright red, sped down the street. Relative pronoun A relative pronoun is a pronoun that (Who, whom, whose, which, that) The person who phoned me last night is my best friend. The car, which was bright red, sped down the street. Semi-colon A semi-colon is used to join two complete sentences into a single written sentence. The two sentences are felt too closely related to be separated by a full stop. There is no connecting word. The film was brilliant; I had a great time. Simple sentence An independent clause that contains a subject and a verb. It is a complete thought. The boy was very happy. introduces a relative clause. Grammar and Punctuation Glossary Subordinate clause A clause containing a subject and a verb and which cannot stand alone. It adds information to the main clause. Because it was raining, playtime was indoors. He ran to the bus stop because it was pouring with rain. Synonym Synonyms are different words with the same or similar meanings Crazy, mad Immense, titanic Suffix A suffix is a group of letters added after a word or base to form a new word. Verb A verb often names an action but it can also describe feelings or states. Word family Words related to each other by a combination of form, grammar and meaning. They share a common base, to which different prefixes and suffixes are added. fast + er = faster sad + ness = sadness joy + ful = joyful hope + less = hopeless apple + s = apples advert + ise = advertise I play football. They skip quickly. We eat spaghetti. Bob is seven today. Teach, teacher Big, little (size) Noise, noisy, noiseless