* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The measure of Cosmological distances
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
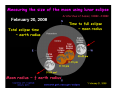
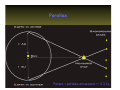
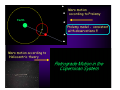
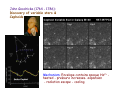
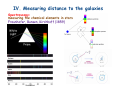
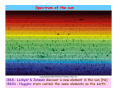
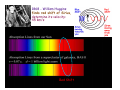
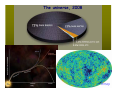
The measure of Cosmological distances Asaf Pe’er Space Telescope Science Institute How far is Jupiter ?? I. Science at ancient times Greece, c. 300BC What is the size of earth ? First measurement of earth’s radius: Eratosthenes of Cyrene (276BC- 196 BC) Syene, Egipt Eratosthenes: Earth circumference =40000 km → Earth radius = 6000 km Measuring the size of the moon using lunar eclipse Aristarchus of Samos, 310BC- 230BC Total eclipse time ~ earth radius Moon radius ~ ¼ earth radius Time to full eclipse ~ moon radius Given moon radius, distance is simple geometry Distance to the moon ~380.000 km (240.000 mi) Geocentric (=earth at the center) vs. Heliocentric (=sun at the center) universe Aristotle (384BC - 322BC) Aristarchus of Samos (310BC - 230BC) Why Geocentric ? 1. "we see" 2. if the earth moves, where is the wind ? 3. Gravity – everything is attracted to the center of the universe 4. Parallax: stars don't move ! Parallax Parsec = paralax-arcsecond =~ 3.3 l.y. But some stars do move.. Retrograde motion of Mars The universe according to Ptolemy Ptolemy: 83-161 AD Circle - “Perfect” shape Mars motion according to Ptolemy Ptolemy model - consistent with observations !!! Mars motion according to Heliocentric theory II. Rise of Heliocentric Cosmology Nicolaus Copernicus (1473 - 1543) Advantages: 1. Correct 2. Simple Disadvantage: 1. Less accurate than geocentric model 2. Copernicus was unknown Tycho Brahe (1546 - 1601): Accurate measurements of planet orbits Johannes Kepler (1571 - 1630): Planets move in ellipses (not circles) around the sun Kepler’s laws of planetary motion helped Newton to develop the theory of Gravity Next breakthrough: the Telescope (1608) Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642): First astronomer to use a telescope Moon has craters ! (= not perfect sphere !) Jupiter has moons ! (= not everything rotates around earth !) Even the sun has spots ! (= sun is not perfect !) “Smoking gun”: Venus phases Cannot be explained by Geocentric model Measuring the distance to the sun Giovanni Cassini (1625 - 1712) 1672- Cassini & Richer measure the distance to Mars Using Kepler’s laws, Cassini deduce the distance to the sun: 150.000.000 km = 1 Astronomical unit (1 A.U.) III. Measuring distance to the stars William Herschel (1738 - 1822) Herschel’s 20 foot reflector Found new planet (Uranus)Discover Infra-Red lightFirst map of the sky: Idea: All the stars are the same. Therefore, bright stars are closer. Herschel’s model of the milky way: Stars are ordered inspace. We are part of the Galaxy. - But he could not scale the size of the galaxy 1838: First measurement of distance to a star Friedrich Bessel (1784 - 1845) 61 Cygni Distance = 100,000,000,000,000 km (= 11 light years) →Scaling the milky way: width = 10.000 l.y., (today: 100.000 l.y.) Thickness = 1.000 l.y. The great debate Charles Messier (1730 - 1817): deep sky catalogue of Nebulae M31 “The great debate”: Are nebulae part of the milky way galaxy - or not ? John Goodricke (1764 - 1786): Discovery of variable stars & Cepheids Mechanism: Envelope contains opaque He2+ heated - pressure increases- expansion - radiation escape - cooling Henrietta Leavitt (1868 - 1921): 1908: Discovery of periodicityLuminosity relation in Cepheids 25 Cepheids at the small Magellanic cloud → All at same distance from us 1917: Shapley & Hertzsprung measured the distance to a Cepheid allow the use of Cepheids as “Standard candles” 1918: Harlow Shapley measures the milky way Cepheids in Globular clusters Size of the milky way: 100.000 l.y. ; Thickness = 1.000 l.y What about the nebulae ? Edwin Hubble (1889 - 1953): I. 1923 - Discovery of Cepheids in Andromeda galaxy Hooker 100-inch telescope Distance to M31: 900.000 light years >> Milky way !! IV. Measuring distance to the galaxies Spectroscopy: measuring the chemical elements in stars Fraunhofer, Bunsen, Kirchhoff (1859) Spectrum of the sun 1868 - Lockyer & Janssen discover a new element in the sun (He) 1860’s - Huggins: stars contain the same elements as the earth. 1868 - William Huggins finds red shift of Sirius, determine its velocity: 45 km/s Red Shift 1912: Vesto Slipher measures red shift of galaxies V ~ 300-1000 km/s Strangely, most of the galaxies are receding from us ! Hubble’s law Velocity = Distance × H0 H0 = Hubble’s constant = 70 (km/s) / Mpc Edwin Hubble (1889 - 1953): II. 1929 - Discovery of distance - velocity relation in galaxies Baade (1952) & Sandage (1954) corrected the value of H0 Mpc = Mega (Million)-parsec; Parsec = parallax-arcsecond =~ 3.3 l.y. V. The big bang theory and beyond Back in time, all the matter was concentrated in a very small region Albert Einstein (1879 - 1955) 1915: General Theory of relativity -- universe collapse (Gravity); Cosmological constant Λ 1922: Alexander Friedman Universe expands ! 1927: Georges Lemaitre Further proofs for universe expansion & “Big bang” Ralph Alpher (1921 - 2007): Universe: 90% H, 9% He 1948: Alpher, Bethe, Gamow H, He production in big bang Alpher, Gamow & Herman cosmic microwave background (CMB) 1964: Penzias & Wilson discover the CMB 1991- Fluctuations in the CMB (COBE satellite): “embryos” of galaxies Mather & Smoot, 2006 Nobel prize The future 1998: A surprising twist Astronomers led by Adam Riess (STScI), Saul Perlmutter (Berkeley) - The universe accelerates !!! The universe, 2008 Wmap