* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Left Ventricular Function - St. Luke`s Roosevelt Ultrasound Division
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
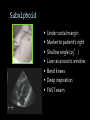
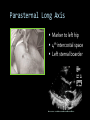
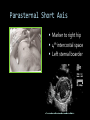
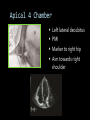
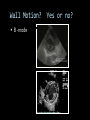
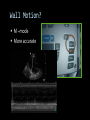
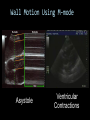
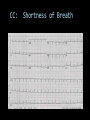
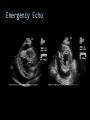
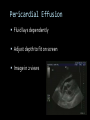
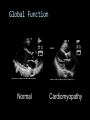
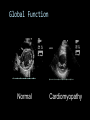
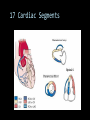
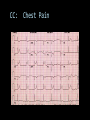
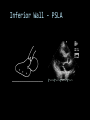
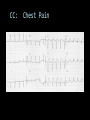
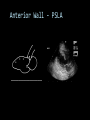
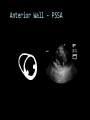
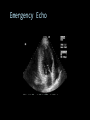
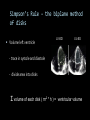
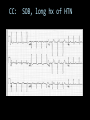
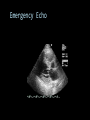
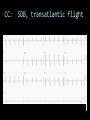
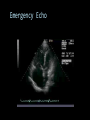
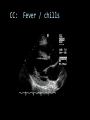
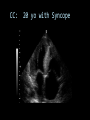
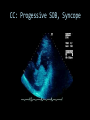
CARDIAC ULTRASOUND Turandot Saul, M.D., RDMS St. Luke’s Roosevelt Hospital New York, NY Cardiac Windows Cardiac Windows Subxiphoid Parasternal long axis Parasternal short axis Apical 4 chamber Ultrasound probe Low Frequency Curved Array Subxiphoid Under costal margin Marker to patient’s right Shallow angle (15°) Liver as acoustic window Bend knees Deep inspiration FAST exam Parasternal Long Axis Marker to left hip 4th intercostal space Left sternal boarder Parasternal Short Axis Marker to right hip 4th intercostal space Left sternal boarder Apical 4 Chamber Left lateral decubitus PMI Marker to right hip Aim towards right shoulder Yes / No Questions Wall Motion? B -mode Yes or no? Wall Motion? M –mode More accurate Wall Motion Using M-mode Asystole Ventricular Contractions Yes / No Question CC: Shortness of Breath Emergency Echo Pericardial Effusion Fluid lays dependently Adjust depth to fit on screen Image in 2 views Cardiac Function Systole Left Ventricular Function Fills at low enough pressures to not cause pulmonary congestion Deliver enough blood to periphery at high enough pressure to perfuse tissues No one quantity measures these assessments of performance Ejection fraction Ultrasound for LV Function Strengths Can assess morphology Cheap No radiation Portable Readily available Ultrasound for LV Function Limitations Finding an acoustic window - narrow inter-costal spaces - all regions of LV not visualized in all patients - obesity - intervening lung tissue in pt with COPD - musculoskeletal deformities Ejection Fraction • Qualitative - visual inspection - severity: mild, moderate, severe - focality - global: reported in intervals of 510% - regional: 17 segments Global Function Normal Cardiomyopathy Global Function Normal Cardiomyopathy 17 Cardiac Segments CC: Chest Pain Inferior Wall - PSLA Inferior Wall - PSSA CC: Chest Pain Anterior Wall - PSLA Anterior Wall - PSSA CC: SOB 3 weeks later Emergency Echo Ejection Fraction • Quantitative - accuracy, reproducibility limited - assumes symmetric shape of LV cavity Simpson’s Rule – the biplane method of disks Volume left ventricle LV-ED LV-ES - trace in systole and diastole - divide area into disks Σ volume of each disk ( πr2 * h ) = ventricular volume Simpson’s Rule – the biplane method of disks EF is calculated : LV diastolic volume - LV systolic volume LV diastolic volume Normal > 50% 35 - 50% moderately depressed <35% severely depressed Edge detection software x 100% Superiority of Visual Versus Computerized Echo Estimation of Radionuclide LVEF - Amico, A. American Heart Journal, 1989 Blinded study, 44 patients Gold Standard - equilibrium radionuclide angiography (ERNA) 7 different echocardiographic methods Best correlation - subjective estimation by experienced cardiologist Accuracy of Emergency Physician Assessment of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction – Randazzo, M. Academic Emergency Medicine, 2003 Cross-sectional observational study, convenience sample 115 patients Three-hour training session LVEF poor, moderate, or normal Formal echo within four hours interpreted by cardiologist LVEF correlation 86.1% overall agreement Highest (91%) in normal LVEF category, 70.4% poor LVEF, 47.8% moderate LVEF Clinical utility Patients with active chest pain - regional wall motion abnormality - high sensitivity for ischemia or infarction - moderately specific Prognostic information short and long term Limitations Operator dependence - inter/intra observer variability is 10-30% Limited utility - MR high EF but little forward flow - AS low EF but possibly reversible Diastole CC: SOB, long hx of HTN Emergency Echo Diastolic Dysfunction Impaired diastolic relaxation LV wall thickness usually increased Increase LA size Other Pathology CC: SOB, transatlantic flight Emergency Echo Right Ventricle Increased pulmonary vascular resistance - right ventricular dilation Limited accuracy in the diagnosis of PE Trans-esophageal echocardiography: sensitivity for central PE 82% CC: Fever / chills CC: 20 yo with Syncope CC: Progessive SOB, Syncope Reources UptoDate: Noninvasive methods for measurement of left ventricular systolic function Zipes: Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Diseases. Elsevier Inc, 2007. Directed bedside transthoracic echocardiography: preferred cardiac window for left ventricular ejection fraction estimation in critically ill patients. American Journal of Emergency Medicine Volume 25, Issue 8 (October 2007) - Copyright © 2007 W. B. Saunders Company Accuracy of emergency physician assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction and central venous pressure using echocardiography. Randazzo MR - Acad Emerg Med - 01-SEP-2003; 10(9): 973-7 Determination of left ventricular function by emergency physician echocardiography of hypotensive patients. Moore CL - Acad Emerg Med - 01-MAR-2002; 9(3): 186-93 Subjective visual echocardiographic estimate of left ventricular ejection fraction as an alternative to conventional echocardiographic methods: comparison with contrast angiography. Mueller X - Clin Cardiol - 01-NOV-1991; 14(11): 898-902 Superiority of visual versus computerized echocardiographic estimation of radionuclide left ventricular ejection fraction. Amico AF - Am Heart J - 01-DEC-1989; 118(6): 1259-65 The Yale Atlas of Echocardiography http://www.med.yale.edu/intmed/cardio/echo_atlas/contents/index.html