* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 - Tissues PPT
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
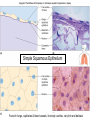
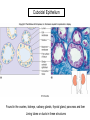
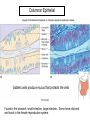
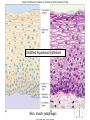
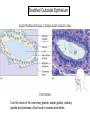
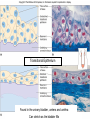
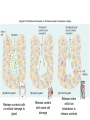
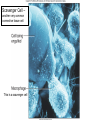
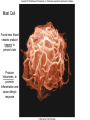
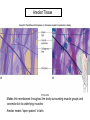
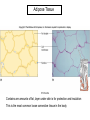
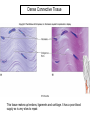
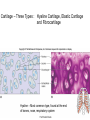
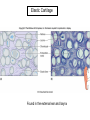
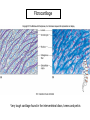
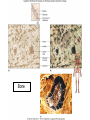
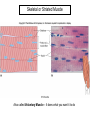
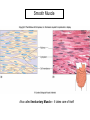
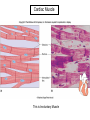
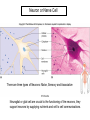
Chapter 5 Tissues The study of tissues is called Histology Atoms Macromolecules Cells Tissues Epithelial Cells Nerve Cells Connective & Muscle Cells There are FOUR major types of tissues in the body. Epithelial Tissue forms a covering A characteristic of epithelial tissues is one side is exposed to the outside of the body or to an internal space. The other side is anchored to connective tissue by a nonliving layer basement membrane Simple Squamous Epithelium Found in lungs, capillaries & blood vessels, line body cavities, very thin and delicate Cuboidal Epithelium Found in the ovaries, kidneys, salivary glands, thyroid gland, pancreas and liver Lining tubes or ducts in these structures Columnar Epithelial Goblets cells produce mucus that protects the cells Found in the stomach, small intestine, large intestine. Some have cilia and are found in the female reproductive system. Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium These line the tubes of the respiratory system to remove dust and micro-organisms Goblet Cells produce mucus to trap the particles Stratified Squamous Epithelium Skin, mouth, esophagus Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Line the ducts of the mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands and pancreas. Also found in ovaries and testes Stratified Columnar Epithelium Found in the pharynx, urethra, ductus deferens Transitional Epithelium Found in the urinary bladder, ureters and urethra Can stretch as the bladder fills Exocrine Glands – Deliver secretions by way of a duct or tube to the inside or outside of the body Release contents with no cellular damage to gland Release content with some cell damage Release entire cells that breakdown to release contents Table 05.04 The common structural protein is Colla Mostmost common structural protein is Collage Called Yellow Connective Tissue Fibroblast – most common connective tissue cells Their fibers strengthen tissues Scavenger Cell – another very common connective tissue cell This is a scavenger cell Mast Cell Found near blood vessels produce heparin to prevent clots Produce histamines to promote inflammation and cause allergic response Areolar Tissue Makes thin membranes throughout the body surrounding muscle groups and connects skin to underlying muscles Areolar means “open spaces” in latin Adipose Tissue Contains are amounts of fat, layer under skin is for protection and insulation This is the most common loose connective tissue in the body Reticular Tissue Thin collagenous fibers provide a framework to internal organs such as the liver and spleen Dense Connective Tissue This tissue makes up tendons, ligaments and cartilage. It has a poor blood supply so is very slow to repair. Cartilage – Three Types : Hyaline Cartilage, Elastic Cartilage and Fibrocartilage Hyaline – Most common type, found at the end of bones, nose, respiratory system Elastic Cartilage Found in the external ear and larynx Fibrocartilage Very tough cartilage found in the intervertebral discs, knees and pelvis Bone Blood – it is a liquid connective tissue The Plasma is what holds the blood together Skeletal or Striated Muscle Also called Voluntary Muscle – It does what you want it to do Smooth Muscle Also called Involuntary Muscle – It takes care of itself Cardiac Muscle This is Involuntary Muscle Neuron or Nerve Cell There are three types of Neurons: Motor, Sensory and Associative Neuroglial or glial cell are crucial to the functioning of the neurons, they support neurons by supplying nutrients and cell to cell communications.