* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is active transport? Moves materials against a conc. gradient
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Exercise physiology wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
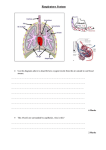
What is active transport? What are features of cells that carry out lots of active transport? What are examples of situations where active transport is used? What is the function of the alveoli? What are the adaptations? What products are absorbed in the small intestine? How is the gut adapted for effective absorption? Moves materials against a conc. gradient; requires energy; carried out by proteins in the cell membrane Many mitochondria Marine birds & mammals have salt glands to pump out salt into the sea; uptake of mineral ions in the roots; transport of glucose out of the gut & kidney tubules into the blood. Point of gas exchange in the lungs; increase surface area in lungs; good blood supply maintains conc. gradient; thin walls for easy diffusion; moist surface for easy diffusion Glucose (from carbohydrates); amino acids (from proteins); fatty acids & glycerol (from lipids) Large surface area (villi, microvilli); rich blood supply (maintains conc. gradient); moist surfaces for substances to dissolve; short diffusion pathway Guard cells open & close the stomata to control carbon dioxide going into & out of the leaf; water evaporates through stomata (again controlled by guard cells); guard cells are controlled by water moving in & out of them by osmosis How do gases move into & out of a leaf? What factors affect the rate of transpiration? Temperature (particles have more energy: more diffusion); wind (maintains a conc. gradient); humidity (lowers the conc. gradient) Use a potometer; as water evaporates from the leaves, it is pulled along tubes; a measurement of water can be made using the scale; this shows the volume of water lost. How can we transpiration? measure the rate of What are the features of an artery? What are the features of a vein? What are the features of a capillary? What is in the blood? Why does your heart rate increase when you exercise? What other changes take place when you Carries blood away from the heart; thick walls; small lumen; thick layer of muscle + elastic fibre Carries blood back to the heart; thin walls; small lumen; valves Carries blood to the respiring cells; walls a single cell thick; tiny vessel; narrow lumen Plasma (carries urea, glucose, amino acids, ions & CO2); red cells (carry O2); white cells; platelets; large proteins. Muscles contract more; need more energy; from respiration; heart pumps more blood, carrying more O2; taking away more CO2 & lactate. Breathe more deeply & more quickly; exercise? What is anaerobic respiration? What is oxygen debt? What is the role of the kidney? What is dialysis? Advantages & disadvantages of a kidney transplant How could we grow microbes safely in the lab? How do yeast help make bread? How do yeast help make alcohol? How do we use bacteria to make yoghurt? muscles use up stores of glycogen; vasodilation allows blood to flow to skin surface (cools) Glucose lactic acid (+ energy); less energy than aerobic respiration; can’t do this for more than a few se Anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid; this needs to be broken down using oxygen; O2 debt = amount of O2 needed to break down lactic acid Filter waste from the blood; reabsorbs all of the sugar (active transport); reabsorbs as much water as the body needs; reabsorbs some ions Used by people with kidney failure; blood leaves body & flows between partially permeable membranes; on the other side of the membranes is dialysis fluid; the conc. gradient makes unwanted substances diffuse out of the blood; these include urea & excess mineral ions. Advantages: eat what you want; do not need time consuming dialysis; live a normal life. Disadvantages: Need a donor (rare); rejection risk; needs to take drugs every day All equipment is sterile to prevent contamination; agar plates are carefully inoculated with microbes; plates are incubated at room temperature (low) to reduce growth of pathogens; after use, all equipment is heated to kill microbes & thrown away. Yeast mixed with sugar to give it an energy source for respiration; yeast + sugar mixed with water + flour & left somewhere warm; as yeast cells respire aerobically they produce CO2 making the bread rise; yeast cells are killed during the cooking process Large no. of yeast in the absence of oxygen; yeast respire anaerobically (fermentation); they break down sugar to produce ethanol + bacteria to warm milk; keep mixture warm so bacteria grow; bacteria break down lactose (sugar) in milk for respiration; producing lactic acid; this makes milk solidify into yoghurt Good O2 supply for respiration; stirrer (keeps microbes in suspension – less crowding); water cooled jacket (removes excess heat from respiration; pH probe & temperature probe How do we get the maximum yield from a fermenter? Lag: growth is slow initially as there a few microbes to ÷. Log: growth is exponential (fastest growth rate). Stationary: growth slows as factors become limiting. Death: microbes die as conditions become unfavourable What is happeneing in the growth curve? How can yeast produce fuel for your car? Advantages & disadvantages of ethanol as fuel? What is a biogas generator? Advantages of burying a biogas generator underground? Ethanol based fuels can be produced from: anaerobic fermentation of cane sugar; glucose derived from maize starch using carbohydrase Advantages: carbon neutral; fewer emissions. Disadvantages: lots of plant material required initially; should we grow food crops instead? Faeces & urine from agriculture; anaerobically fermented; produces methane Less temperature fluctuation; less visual impact; withstand pressure build up; ease of adding slurry