* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Sheet Answers Word Doc
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
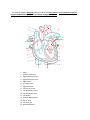
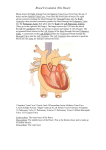
Cardiovascular System Test Review Name: _____________________ 1. The covering of the heart Pericardium 2. What is the function of arteries in the circulatory system? Carry blood away from the heart 3. Blood enters the right hand side of the heart through the….. Superior and Inferior Vena Cava 4. When does a fetus’ heart begin beating? 4th week 5. Arteries and veins are attached by …..? Capillaries 6. What is a sphygmomanometer used for? To measure blood pressure 7. What separates the right and left ventricles from each other? Septum 8. What does this image represent? Label each wave and indicate what happens in the heart during each wave. Graphic record of the heart’s action currents P-wave – contraction of atria R T P QRS-wave – contraction of ventricles T-wave – relaxation of ventricles Q S 9. Explain what pericarditis is. Inflammation of the pericardium due to infection – linings stick together 10. The AV bundle is also known as….. Bundle of His 11. What is a heart murmur? Abnormal heart sound that identifies the leakage of blood through the valves in the wrong direction 12. The most important risk factor for congestive heart failure is: A. Diabetes B. High blood pressure C. High cholesterol D. A heart attack 13. This is also known as the pacemaker of the heart. Sinoatrial node (SA node) 14. Explain what the foramen ovale is. Opening between the right and left atria, which bypasses the lungs, and closes with the first breath 15. A heart valve with 3 flaps. Tricuspid valve 16. Where on the heart is the stethoscope placed during an examination? Apex 17. Explain the path a red blood cell takes from the superior vena cava to the aorta. Vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary valve, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral (bicuspid) valve, left ventricle, aortic valve, and aorta 18. What is a normal blood pressure reading? 120 80 19. What is myocardial infarction? Heart attack 20. The branching of main arteries is called…. A. Myocardial infarction B. Aortic arch C. Anastomosis D. Common ileac 21. The artery that supplies blood to the heart is the ….. Coronary artery 22. When the blood pushes against the artery walls when the ventricles contract, it is called the ……………. pressure. Systolic 23. Where in the body does the heart lie? Lies within the mediastinum, behind the sternum, and rest on the diaphragm 2/3 of the heart is on the left side of the body 24. Where will you find the mitral valve? Between the left atrium and left ventricle 25. Which part of the heart wall is responsible for reducing friction? Epicardium 26. Why are the aortic and pulmonary valves referred to as being ‘semi-lunar’? They have leaflets shaped like half-moons 27. What are the top and bottom chambers of the heart called? The top chambers are atria and the bottom chambers are ventricles 28. What are the differences between an artery and a vein – Name 2! An artery moves oxygenated blood away from the heart and a vein moves deoxygenated blood toward the heart 29. What happens to your target heart rate as you age? It decreases 30. Label the diagram AND then indicate the blood flow with arrows. Use a red pencil to indicate oxygenated blood and a blue pencil to indicate deoxygenated blood. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Aorta Superior Vena Cava Right Pulmonary Artery Right Pulmonary Veins Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right Ventricle Inferior Vena Cava Left Pulmonary Artery Left Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve Aortic Valve Left Ventricle Descending Aorta