* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tectonic Control of CO2
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
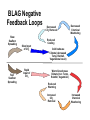
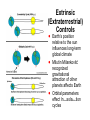
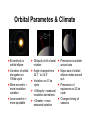
Intrinsic (Earth Bound) Mechanisms ! Earth’s crust is a thin veneer atop molten rock (mantle) ! Continental crust (2.7 gm/cm2) is less dense ! Ocean crust (3.2 gm/cm 2) is more dense ! Lithosphere (crust and upper mantle) rides over semimolten, higher density (>3.6 gm/cm 2) lower mantle (asthenosphere 100-350 km) ! Earth’s center comprised of molten magma rich in Fe +2 Tectonic Plates ! Lithosphere of 15 major plates w/rates from <1 to 10 cm/yr ! Plates consist of both continental and oceanic areas; move as a rigid unit ! Interactions along plate margins control crustal features ! Divergent boundaries where plates move apart ! Convergent boundaries where plates collide ! Transform boundaries where plates slide past one another Tectonic Plate Movement Video Tectonic Control of CO2 – BLAG ! B L A G Hypothesis ! Seafloor spreading & subduction rates control CO2 input to atmosphere ! C comes from reservoir in rock record ! Changes in atmospheric CO2 impacts climate ERNER AGASA ND ARRELS FAST SPREADING arbon SLOW SPREADING BLAG Negative Feedback Loops Slow Seafloor Spreading Fast Seafloor Spreading Slow Input of CO2 Rapid Input of CO2 Decreased CO2 Removal Decreased Chemical Weathering Reduced Cooling Cold Icehouse Climate (decreased Temp, Rainfall, Vegetational cover) Warm Greenhouse Climate (incr. Temp, Rainfall, Vegetation) Reduced Warming Increased CO2 Removal Increased Chemical Weathering Closed Loop Carbon Cycling HCO3- ions ! Atmospheric CO2 stored in dissolved HCO3- ions carried to oceans via rivers ! Marine plankton use HCO3- to build skeletons ! Skeletons deposited as oozes ! Carbonate sediments subducted, melted, incorporated ! CO2 released to oceans/atmosphere via volcanism CO2 Removal The Uplift/ Weathering Hypothesis Arethusa & Storm Mts. – Alberta, Canada ! Climate is driven by Chemical Weathering; not a negative feedback ! Average weathering rate controlled by available fresh rock & mineral surfaces ! Smaller the weathered particle, greater surface area for chemical reaction ! Areas of tectonic uplift enhance exposed surfaces Crowfoot Mountain, Alaska Mineral Creek, Alaska Uplift ! Mass wasting removes overlying debris, exposing fresh bedrock ! Earthquakes dislodge rock debris ! Steep slopes foci of rainfall ! High mountains create own wet circulation patterns (monsoons) ! Glacial ice enhances weathering ! Subduction rates steady over time; total amount of high Steep Slope mountain terrane likely Mass Mt. Slopes Wasting Glaciers Precipitation constant over time ! Continent-continent collision result in high Increased Rock mountain terrane Fragmentation ! Natural extent of exposed rock may set natural limit on cooling Increased intensity due to uplift Weathering and CO2 Removal ! Chemical weathering thermostat controlled by other 99% of Global Cooling continental area UPLIFT Extrinsic (Extraterrestrial) Controls Aphelion Perihelion ! Earth’s position relative to the sun influences long-term global climate ! Milutin Milankovitæ recognized gravitational attraction of other planets affects Earth ! Orbital parameters effect In sola tion cycles cicent rRadia Orbital Parametes & Climate ! Eccentricity is orbital ellipse ! Variation of orbital elongation on 100ka cycle ! More eccentric = more insolation variation ! Less eccentric = more equitable ! Obliquity is tilt of axial rotation ! Angle changes from 22.1E to 24.5E ! Variation on 41 ka cycle ! <Obliquity = seasonal insolation varies less ! >Greater = more seasonal variation ! Precession is wobble around axis ! Major axis of orbital ellipse rotates around sun ! Precession of equinoxes on 22 ka cycle ! Changes timing of seasons Sycophant or Cycle Phase? Milankoviæ & Ice Sheets ! Summer insolation is weak ! Summer insolation is strong ! Less radiation in high latitudes (>65E) ! More radiation in high latitudes (>65E) ! Less radiation cools regional climate ! More radiation heats regional climate ! Reduction in summer ablation ! Increased summer ablation ! Snow accumulation & ice ! Snow pack melts; ice sheet sheet growth shrinks