* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12PClec5Tec
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
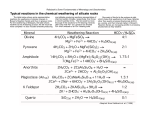
1/30/12 Why is Earth Habitable? Sun has increased in strength by 25% to 30% since the earth was formed. If true, why has Earth’s climate been relatively stable? Tectonic Control of Climate Tues – Graduates: Research questions due Thurs – Outline and references due Natural thermostat that allows its climate to warm up during greenhouse eras Without boiling oceans and to cool off during icehouse eras without freezing solid. What controls atmospheric CO2? 1 – Volcanoes release carbon from Rocks into the Atmosphere. 2 – Weathering of silicate minerals Removes CO2 from the atmosphere and sequesters it in the shells of Carbonaceous marine organisms. The process of chemical erosion that consumes atmospheric CO2 is known as hydrolysis. 1 1/30/12 CO2 Balance The slow weathering of granite and other silicate rocks, and the associated consumption of atmospheric CO2, must be balanced by the rate of CO2 input by volcanoes. This does not imply that both have been constant throughout time. In fact, these two rates most certainly have varied in response to Earth’s tectonic processes. Given that the release of CO2 by volcanoes is controlled entirely by tectonic processes that are not affected by changes in climate, we must conclude that the rate of chemical weathering is the climatic thermostat that regulates climate. aka Spreading rate hypothesis after Berner, Lasaga, and Garrels CO2 is expelled into the atmosphere from two sources 1 – The margins of divergent plates where magma carrying CO2 erupts into ocean water. 2 – The margins of convergent plates where portions of subducting plates melt and rise to the surface where CO2 and other gases are released. The BLAG spreading rate hypothesis Proposes that increased spreading rates lead to increased release of CO2 by magma into the atmosphere. BLAG Spreading Hypothesis 2 1/30/12 The BLAG hypothesis • Globally averaged spreading rates • Faster spreading = more CO2 and vice versa • Also factors in silicate weathering as a negative feedback • Timescale of 10s of Ma • Only reliable for last <170 Ma because older ocean crust has been destroyed • Sea level records (high when spreading is fast) can also be used to estimate spreading Negative Feedback in BLAG Upli7 Weathering Hypothesis: Scenario 1 Upli7 Weathering Hypothesis: Scenario 1 3 1/30/12 Upli7 Weathering Hypothesis: Scenario 1 Upli7 Weathering Hypothesis: Scenario 2 Upli7 Weathering Hypothesis Nega>ve Feedback or… 4 1/30/12 Posi>ve Feedback? Uplift Weathering Hypothesis: CO2 Removal The Uplift Weathering Hypothesis looks at chemical weathering as the active driver of climate change, rather than as a negative feedback that moderates climate change. As the rate of mountain building increases over Earth’s surface, the abundance of freshly exposed, unweathered rock increases, which in turn increases the total amount of chemical erosion and CO2 withdrawal taking place. 5