* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Taxonomy (Classification) and Phylogeny (Cladistics)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
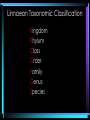
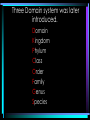
Taxonomy (Classification) and Phylogeny (Cladistics) • Classification is the grouping of objects based on physical similarities. In biology when doing this with organisms, it is called taxonomy. • It is predominately based on morphology. • Linnaeus and Whittaker gave us this system • Classifies diverse organisms into “like groups” based on traits. As the traits become more specific, fewer and fewer organisms are together. Linnaean Taxonomic Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Three Domain system was later introduced. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species • Domain Archaea The Three Domains – Ancient prokaryotes • Domain Bacteria – Modern prokaryotes • Domain Eukarya- all eukaryotic cells – plantae, animalia, fungi, protista • Taxonomists give a unique scientific name to each species they know about whether it’s alive today or extinct. (not to be confused with taxidermist) • The scientific name comes from one of two “dead” languages – Latin or ancient Greek. Binomial Nomenclature • a two part naming system for writing scientific names. • The genus name is written first (always Capitalized) • The species name is written second (never capitalized). • Both words are – italicized if typed or underlined if hand written. FELIS CONCOLOR – Felis concolor or F. concolor • Cladistics /Phylogeny- is a relatively new system of classification that uses shared derived traits to establish evolutionary relationships. • A derived trait is a feature that evolved only within the group under consideration. • A phylogenetic tree based on a cladistic analysis is called a cladogram. • Out-group is the least related group, will be found on the far left of our diagrams! • Synapomorphies = derived characteristics • Clade = A group of organisms and their common ancestor.