* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Biology IV:
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
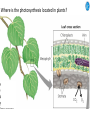
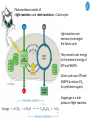
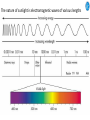
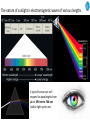
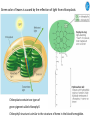
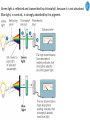
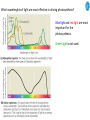
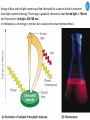
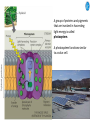
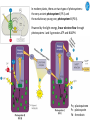
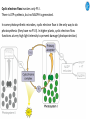
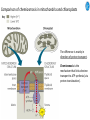
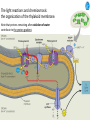
Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Why is it important to study photosynthesis? Because increasing photosynthesis efficiency by just 1% would solve food supply problems forever! Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is kind of like cellular respiration but backwards Spongebob Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Organisms that can perform photosynthesis are called photoautotrophs. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Where is the photosynthesis located in plants? Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Where is the photosynthesis located in plants? Photosynthesis takes place on inner membranes and spaces of chloroplasts located in mesophyll cells (green tissues). Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Using «heavy» oxygen isotope 18O, it has been found that oxygen released during photosynthesis comes only from water. 16 18 O O O O O Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Photosynthesis consists of «light reactions» and «dark reactions» = Calvin cycle. Light reactions are necessary to energize the Calvin cycle. They convert solar energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH. Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH to reduce CO2 (to synthesize sugars). Oxygen gas is a side product of light reactions. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis The nature of sunlight is electromagnetic waves of various lengths Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis The nature of sunlight is electromagnetic waves of various lengths A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 nm to 700 nm (visible light spectrum). Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Green color of leaves is caused by the reflection of light from chloroplasts Chloroplasts contain two types of green pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll structure is similar to the structure of heme in the blood hemoglobin. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Green light is reflected and transmitted by chlorophyll, because it is not absorbed. Blue light, in contrast, is strongly absorbed by this pigment. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Which wavelenghts of light are most effective in driving photosynthesis? Blue light and red light are most important for the photosynthesis. Green light is not used. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Information about the action spectrum of photosynthesis was first obtained long time ago due to an elegant experiment performed with filamentous alga called Spirogyra. In that experiment, aerobic bacteria were attracted to alga portions illuminated with blue and red light, becuase only those parts were producing oxygen (photosynthesis). Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Information about the action spectrum of photosynthesis was first obtained long time ago due to an elegant experiment performed with filamentous alga called Spirogyra. In that experiment, aerobic bacteria were attracted to alga portions illuminated with blue and red light, becuase only those parts were producing oxygen (photosynthesis). Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Energy of blue and red light converts purified chlorophyll to a state in which its electrons have higher potential energy. This energy is gradually released as heat (far red light, > 700 nm) and fluorescence (red light, 650-700 nm ). In chloroplasts, such energy is not lost, but is captured to power photosynthesis. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis A group of proteins and pigments that are involved in harvesting light energy is called photosystem. A photosystem functions similar to a solar cell. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis In modern plants, there are two types of photosystems: the very ancient photosystem I (PS I) and the evolutionary young one, photosystem II (PS II). Powered by the light energy, linear electron flow through photosystems I and II generates ATP and NADPH. Pq - plastoquinone Pc - plastocyanin Fd - ferredoxin Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis A mechanical analogy for linear electron flow during the light reactions. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Cyclic electron flow involves only PS I. There is ATP synthesis, but no NADPH is generated. In some photosynthetic microbes, cyclic electron flow is the only way to do photosynthesis (they have no PS II). In higher plants, cyclic electron flow functions at very high light intensity to prevent damage (photoprotection). Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Comparison of chemiosmosis in mitochondria and chloroplasts The difference is mainly in direction of proton transport. Chemiosmosis is the mechanism that links electron transport to ATP synthesis (via proton translocation). Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis The light reactions and chemiosmosis: the organization of the thylakoid membrane. Note that protons remaining after oxidation of water contribute to the proton gradient. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis The Calvin cycle is responsible for fixation and reduction of atmospheric CO2 using energy from the light reactions. Rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase) is the key enzyme for the life on our planet. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis Photorespiration The full name of RubisCO is ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxidase, because at low CO2 concentartions it can bind oxygen instead of CO2. Photorespiration occurs in hot and dry weather when stomata are closed and CO2 cannot enter the leaf. Photorespiration leads to the loss of the fixed CO2, thus strongly decreasing the efficiency of photosynthesis. Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis C4 photosynthesis Plants in dry and hot climates developed a modification of CO2 fixation which results in very low level of photorespiration (very high photosynthesis effciency) even when stomata are closed. Because the first product of CO2 fixation in such plants is a compound with four carbon atoms, this type of photosynthesis is called C4 photosynthesis, while plants with normal photosynthesis are called C3 plants (phosphoglycerate = 3 carbon atoms). C4 plant examples • maize (Zea mays), • sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) • sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) • millet (Panicum miliaceum) • switchgrass (Panicum virganum) and many strong weeds No light reactions → no O2 release Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis The principle difference between C3 and C4 plants is that, in C4 plants, mesophyll cells function as a pump to increase CO2 concentration near RubisCO Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis CAM photosynthesis (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) In CAM plants, CO2 fixation and Calvin cycle are separated in time (day/night) Cell Biology IV: Photosynthesis PHOTOSYNTHETIC HUMANS By year 3015??? Thank you for your attention! Some of the modern animals receive part of their energy from the sunlight because of the symbiosis with algae. According to the Japanese computer-based scientific forecast, in about 1000 years from now humans will also perform photosynthesis, due to the progress in biotechnology.