* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
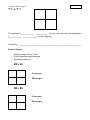
PAGE 7 Genetics Unit Biology II Genetics Notes Day 1 Warm up-What is the definition of genetics? _________________________________________________________________ Gregor Mendel (1860’s) • Father of genetics. • Studied pea plants. • Performed experiments with pea plants. • Used a __________________________ approach. Why do pea plants work well for genetic study? • ___________ __________ - have male and female structures - Can do self-fertilization • • • ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Can cross-pollinate them - Cross Pollinate = Manually take __________ from one pea plant and place it on the ____________ of another pea plant. Mendel’s Experiment • Step 1 - ______________________________________________________ – Let the plants self fertilize repeatedly. • Purple plants self-fertilized to make ONLY __________ offspring • White plants self-fertilized to make ONLY __________ offspring – – Collected seeds from these plants. These were the PARENTAL GENERATION ( __ __________________) Genetics Unit Biology II • Step 2 - ______________________________________________________ – Purple flowers cross pollinated with white flowers. – Collected and grew the seeds from these plants – Called this the First Filial Generation (____) – ___________________________________ • Step 3 - ______________________________________________________ – He collected and grew these seeds – Called this the ____ generation. – Purple flowers grew AND White flowers grew – _______________________________________ Mendel studied many traits of Pea Plants • • • • • ____________________________________________________________. Seed color (yellow or green). ____________________________________________________________. Pod color (green or yellow). He always found that there was a 3:1 ratio! Terms to Know • ________________: the alternative traits that are passed down -Example: mom passed down the allele for blue eyes while dad passed the allele for brown. • ________________: The expressed form of the trait. • ________________: The trait that is not expressed when the dominant allele is present. EXAMPLE: Allele for brown (dom) eyes from dad Allele for blue (rec) eyes from mom Child will have brown eyes. PAGE 8 Genetics Unit Biology II • _________________: The two alleles that are passed down are the same. -Example: Both pea plant parents passed down the allele for purple flowers. • _________________: The two alleles that are passed down are different. -Example: One pea plant parent passed down the allele for white flowers and one passed down the allele for purple flowers • _____________________: The set of alleles that an organism has. -PP (homozygous dominant) -Pp (heterozygous) -pp (homozygous recessive) • _____________________: The physical appearance. -purple (homozygous dominant) -purple (heterozygous) -white (homozygous recessive) List 10 Phenotypes List 10 Genotypes 1._______________ 2._______________ 3._______________ 4._______________ 5._______________ 6._______________ 7._______________ 8._______________ 9._______________ 10.______________ 1._______________ 2._______________ 3._______________ 4._______________ 5._______________ 6._______________ 7._______________ 8._______________ 9._______________ 10.______________ Genetics Unit Biology II Genetics Notes Day 2 Warm Up – What is the difference between a genotype and phenotype? Provide an example of each. Genotype: Phenotype: Punnett Squares Punnett Square = ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ • • __________________________________________________________ __________________ & _______________ alleles are represented by _____________. A _______________ letter is used for dominant alleles. A __________ _____ letter is used for recessive alleles. • EXAMPLE (Tall or short) • • T = dominant allele t = recessive allele Homozygous dominant Genotype = _____ Phenotype = __________ Heterozygous Genotype = _____ Phenotype = __________ Homozygous recessive Genotype = _____ Phenotype = __________ CREATING A PUNNETT SQUARE • The letters representing the alleles from one parent are placed along the top of the square. • The letters representing the two alleles from the second parent are placed along the side of the square. PAGE 9 Genetics Unit Biology II T t x T t The genotype (____________ ____________) can be used to predict the phenotype (___________ _____________) of the offspring. Probability: ________________________________________________________ Punnett Squares: • • • Help you keep track of traits. Predict genotype and phenotype. Calculate probability. BB x bb Genotypes: Phenotypes: BB x Bb Genotypes: Phenotypes: Genetics Unit Biology II ___ Bb A. Mendel ___ bb B. Monohybrid cross ___ BB C. Dihybrid cross ___ father of genetics D. Phenotype ___ Blood type AB E. Genotype ___ letters like (Ff) F. Heterozygous ___ traits like (freckles) G. Dominant ___ 4 square Punnett square H. Recessive ___ 16 square Punnett square I. Cross pollination ___ pollen from one plant transferred to another J. Co-dominant Fun facts: Genetics Unless you are an identical twin, your DNA is unique. Fingerprints are unique to each person, even identical twins. Your gender and physical characteristics are determined by your DNA. Genes exist in pairs; one half comes from a person's mother and the other half from the individual's father. Humans have at least 30,000 genes. Goldfish have more genes than humans do