* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Froehlich`s Physics
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
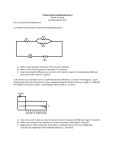
Physics Whiteboards – Electrical Potential and Electrical Potential Energy 1. An electron is in a constant electric field of 3.5 x 103 N/C directed along the negative y-axis. a. What is the force on the electron? b. If the electron is released, how much kinetic energy does it have after it has moved 10 cm? 2. Two fixed charges, –3.0 µC and –5.0 µC are 0.40 m apart. a. Where should a third charge of –1.0 µC be placed so that the third charge is in electrostatic equilibrium? (That is, from the point of view of the third charge, it experiences zero net force.) b. Consider the same question as above with a +7.0 µC charge. 3. What is the electrical potential at the center of an equilateral triangle with 20 cm sides, with charges at the vertices of +4.0 µC, +4.0 µC, –4.0 µC? 4. In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the electrons can exist only in circular orbits of certain radii. a. Will larger orbits have higher, lower, or equal potential than a smaller orbit? Why? b. Determine the potential difference between two orbits of radii 0.21 nm and 0.48 nm. 5. It takes +5.5 J of work to move two charges from a large distance apart to 1.0 cm from one another. If the charges have the same magnitude, a. how large is each charge, and b. what can you tell about their signs? 6. Calculate the voltage necessary to accelerate a beam of protons initially at rest, and calculate their speed if they have a kinetic energy of a. 3.5 eV b. 4.1 MeV c. 8.0 x 10–16 J 7. Two large parallel plates are separated by 3.0 cm and connected to a 12 V battery. Starting at the negative plate and moving toward the positive plate on a 45° diagonal for a distance of 1.0 cm, what value of potential would be reached, assuming the negative plate were defined as zero potential? 8. In a Van de Graaff linear accelerator, protons can be accelerated through a potential difference of 20 MV. a. What is their kinetic energy if they started from rest? Give your answer in eV and joules. b. How would your answer change if you were accelerating alpha particles (2 protons and 2 neutrons) instead? wb_10.doc – froehlich Physics Whiteboard Extras – Potential, Potential Energy, and Work Some constants: Charge of a proton (+) or electron (-) Mass of an electron Mass of a proton ±1.6 x 10–19 C 9.11 x 10–31 kg 1.67 x 10–27 kg 1. Two protons are held at rest, 5.0 x 10–12 m apart. When released, they fly off in opposite directions. How fast will they be moving when they are far from each other? 2. An electron gun shoots electrons (seriously!) at a metal plate 4.0 mm away in a vacuum. The gun is at a potential of 100 V; the target is at 95 V. How fast must the electrons be moving as they leave the gun if they are to reach the plate? 3. An electron has a speed of 6.0 x 105 m/s as it passes point A on its way to point B. Its speed at B is 1.2 x 106 m/s. What is the potential difference between A and B, and which has the higher potential? 4. Two metal plates are attached to the two terminals of a 1.50 V battery. How much work is required to carry a +5.0 µC charge across the gap from the negative plate to the positive plate? How much work would be requried if you now move it back? wb_10a.doc – froehlich