* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Unit
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
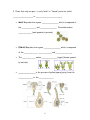
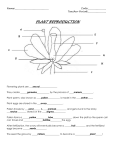
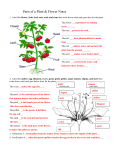
Name: ________________________________ Plant Unit SHS R.Bio Autotrophs- Heterotrophs- There are two (2) types of autotrophs, those that use ______________, and those that use __________________. _______________- turns carbon dioxide and inorganic substances like nitrogen and sulfur into the food they need. __________________- turns light, carbon dioxide and water (ingredients/raw materials) into glucose (food), oxygen and water (products). What is photosynthesis? Word Equation: _________ + ______ ------------- _________ +________+ __________ Chemical Formula: _________+_______------------ _________ + ________+ __________ 1 Chloroplasts in plant cells Chloroplast Three (3) major factors, which affect the rate of photosynthesis: 1. 2. Stop and Jot! 3. 2 Leaves Photosynthesis occurs mostly in the _________________ of the plant. The leaves provide a large _____________________________ for the absorption of ____________. Leaf Structure (Cross Section) • ________________________ - Outer layer of the leaf which has a waxy covering called a ______________________. Main functions of the outer layer is: a). b). c). 3 • __________________________ - Openings in the cuticle and epidermis. • The size of the opening is regulated by _______________ _____________. • Stomates allow the exchange of _______________, ______________________, and __________ between the external environment and internal air spaces. • __________________ are tiny openings in the stem that also allow gas exchange. • Most photosynthesis occurring in the leaves takes place in the _____________________ layer. 4 • ____________________ layer contains ________ ____________ which are surrounded by moist surfaces for the exchange of gases ( ______________________ in and _______________ out). Some photosynthesis takes place here as well. Do you see the chloroplasts in the spongy cells? • ________________ ____________ located in the __________ of the leaves. • The _____________carries water and minerals (up) and ______________ carries food throughout (down and up). The vascular tissue begins in the ___________ and continues through the stem to the leaves. Stop and Jot! 5 Roots The ___________ have three (3) main jobs: A). Anchor- B). Food storage- C). Absorption- Coming off the roots are tiny hairs called ___________ __________. They _______________ surface area so that more ________________ and _________________ can be absorbed by ___________(osmosis) and ______________ _______________. How is water transported once it is inside the roots? _______________ is the evaporation of water vapor through the stomates. There is a pulling force on the column of water in the ______________. It’s called _____________________ __________. 6 Stop and Jot! Use the textbook page 612 to label the flower Flowering Plants Reproduction in flowering plants 1. The flower is a structure specialized for ______________ reproduction. Flowers which have both male and female parts on the same flower are called _________________ or ______________. 7 2. Those that only one part, i.e. only “male” or “female” parts are called __________________ or ________________________ • MALE Reproductive organs: _______________ which is composed of the _____________ and _______________. The anther makes ____________ (male gamete by meiosis). • FEMALE Reproductive organs: _______________ which is composed of the ____________, ____________ and _______________. • The ____________ makes ______________ (eggs) (female gamete by meiosis). • _______________ is the process of pollen (sperm) going from the _____________ to the _____________. 8 1. ________-_______________ is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of the SAME flower or plant. 2. ________ - ______________ is the transfer of pollen from the anther on one flower to the ____________ of a DIFFERENT plant. Cross-pollination is an adaptation which increases variety. • Cross-pollination is accomplished by: 1.____________ 2._____________ 3.__________. Name three (3) traits (characteristics) about the flower that helps cross-pollination: 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _______________ What happens after the pollen (sperm) lands on the stigma? 1. The pollen grain _________________( forms a ___________ _________ which extends into the ______________. 9 ) and 2. Sperm nuclei are formed and _______________ ( ) the ovules. 3. The union of the sperm and ovule results in a ____________. 4. The zygote develops into an ______________ which develops into a _______________. 5. The ovary becomes the ____________. 6. The plant embryo consists of three (3) parts: epicotyl hypocotyl • ________________ - develops into the root • ________________ - develops into the leaves • ________________ - contains stored food (nutrients) for the germinating plant 10 Check here to make sure you labeled the flower correctly. In flowering plants, seeds develop inside a fruit. This is a special adaptation that helps in seed dispersal. There three (3) conditions needed for the seed to grow: 1.______________________ 2. _____________________ 3. _______________________ • Development of a seed into a mature plant requires: 1. cell division (mitosis) 2. differentiation (cells become specialized) 11 3. _______________ • The plants grow in the tips of the ____________ and ___________. • The special tissue found in these regions are called _________________________. Plant Regulation Plants have hormones just like you do. Hormones effect the plant’s _______________ and _______________________ just like your hormones. ______________ are plant hormones that influence division, elongation and differentiation of plant cells. Unequal distribution of ______________ causes unequal growth called _________________, which enhances plant survival. Unequal distribution of auxin can be caused by ___________, _______________ or ______________. 12 Tropisms • ______________________ - • ______________________ - • ______________________ - 13