* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals wikipedia , lookup
Emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Sexual stimulation wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Social sharing of emotions wikipedia , lookup
Self-discrepancy theory wikipedia , lookup
Appraisal theory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Expressive suppression wikipedia , lookup
Emotionally focused therapy wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Emotional labor wikipedia , lookup
Emotion in animals wikipedia , lookup
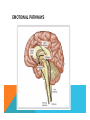
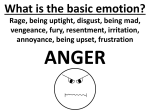
EMOTION - A set of complex reactions to stimuli involving subjective feelings, physiological arousal and observational behaviour - All emotions have three parts: physical, behavioural and cognitive - Emotional Intelligence THE BASIC EMOTIONS -According to research from Paul Ekman, there are 6 basic emotions: Fear, Happiness, Disgust, Surprise, Sadness and Anger. - 4? - Evolutionary & Cross-cultural - Social learning SECONDARY EMOTIONS EMOTIONAL PATHWAYS THEORIES OF EMOTION What physical signs accompanies an intense emotion? THE JAMES –LANGE THEORY Our experience of an emotion is the result of the arousal that we experience. This approach proposes that the arousal and the emotion are not independent, but rather that the emotion depends on the arousal. “We feel sorry because we cry, angry because we strike, afraid because we tremble” ( William James, 1884, p. 190). -fast pathway THE CANNON-BARD THEORY The experience of an emotion is accompanied by physiological arousal. According to this theory “emotion” refers to the simultaneous burst of activity in your brain and the gut reactions. THE SCHACHTER-SINGER THEORY the experience of emotion is determined by the intensity of the arousal we are experiencing, but that the cognitive appraisal of the situation determines what the emotion will be - Misattribution of arousal (love/hate, Capilano suspension bridge experiment). - Epinephrine informed/uninformed study - Slow pathway THE OPPONENT – PROCESS THEORY - emotions unbalance homeostasis. The body’s sympathetic (energizes) system and the parasympathetic (calms) system act to regulate and manipulate our emotions. -the removal of a stimulus that excites one emotion causes a swing to an opposite emotion. Can be classically trained -ex. parachuting COMMUNICATING EMOTION – NON-VERBAL CUES Ø Proxemics Ø Body appearance Ø Body positioning and movement Ø Gestures Ø Facial expressions Ø Paralanguage