* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Osteoporosis wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
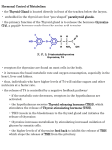
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Thyroid Gland • This gland is located at the front of the neck, below the larynx. • Follicular cells secrete thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), collectively termed “thyroid hormone” (TH) • Other Thyroid cells produce a second hormone “calcitonin” Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone • Produced by the anterior pituitary • Stimulates the normal development and secretory activity of the thyroid • Regulation of TSH release ⟶ Stimulated by thyrotropinreleasing hormone (TRH) ⟶ Inhibited by rising blood levels of thyroid hormones that act on the pituitary and hypothalamus Direct Links to Other Endocrine Axes TRH also help control PRL & GH Indirect Links to Other Systems Glucocorticoid Excess ↓ TSH, TBG, TTR, T3, T4, ↑rT3 Deficiency ↑ TSH Estrogens T4 requirement in hypothyroidism ↑ TSH in postmenopausal women Androgens TBG ↓ T4 turnover in women T4 requirement in hypothyroidism Functions of the Thyroid • Metabolic rate • Regulate protein, carbs and fat metabolism • Increase RBC production • Increase bone formation, decrease bone resorption of Ca+ Regulation of Metabolism • Hormones T3 & T4 increase BMR • Secretion controlled by hypothalamic-pituitarythyroid gland axis • TRH » TSH » T3 & T4 (neg feedback) • Protein and Iodine very important for T3 & T4 production Calcium and Phosphorus Balance • • • • Calcitonin (thyrocalcitonin, or TCT) Reduces bone resorption, lowers serum Ca+ Low serum Ca+ suppress TCT: Elevated serum Ca+ trigger TCT Thyroid Hormone • Major metabolic hormone • The effects of TH are: ⟶ stimulation of growth (in conjunction with growth hormone) ⟶ development of the nervous system in the foetus and infant ⟶ increased basal metabolic rate and increased heat production ⟶ increased alertness, reflexes Thyroid Hormone Hypothalamus TRH Anterior pituitary TSH Thyroid gland Thyroid hormones Target cells Negative feedback regulation of TH release Rising TH levels provide negative feedback inhibition on release of TSH Stimulates Inhibits Pregnancy & the Thyroid Axis Pregnancy Causes: TBG Maternal Thyroid Axis Impacts: Plasma volume T4 production hCG Total [ T4 ] & [ T3 ] fetal T4 synthesis in 2nd & 3rd trimester O2 consumption by fetus, placenta, uterus & mother T4 & T3 pool cardiac output Free T4 Basal TSH I2 requirements BMR Calcitonin • Produced by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland • Antagonist to parathyroid hormone (PTH) • Inhibits osteoclast activity and release of Ca2+ from bone matrix • Stimulates Ca2+ uptake and incorporation into bone matrix Remember:Thyroid also secretes Calcitonin • Calcitonin helps--> • keep Calcium in bones • maintain balance of Calcium and Phosphorus Calcium -- 8.8 - 10.5 Phosphorus - 3 - 4.5 Parathyroid Glands • Four to eight tiny glands embedded in the posterior aspect of the thyroid gland • secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH), a peptide hormone • PTH—most important hormone in Ca2+ homeostasis • Functions ⟶ Stimulates osteoclasts to digest bone matrix ⟶ Enhances reabsorption of Ca2+ and secretion of phosphate by the kidneys ⟶ Promotes activation of vitamin D (by the kidneys); increases absorption of Ca2+ by intestinal mucosa Causes of Hyperthyroidism • • • • • Graves’ disease (Autoimmune) Toxic multinodular goiter Thyroid adenoma (benign tumor) Pituitary hyperthyroidism Excessive use of thyroid hormone Goiter and Exophthalmos in Graves' Disease Hyperthyroidism • • • • More common in women Lab assessment p.1485: T3, T4 TSH (Graves’) Thyroid Scan (RAIU) = increased Interventions • Nonsurgical: monitor V/S, rest, cool environment • Medications: PTU (propylthiouracil), SSKI, beta blockers • Radioactive Iodine Therapy • Remember eye care Interventions • Surgical: total or subtotal thyroidectomy • Preop = antithyroid meds, SSKI • Postop = very important – Monitor for Bleeding, respiratory distress, tetany, weak voice, thyroid storm Causes of Hypothyroidism • • • • Removal or destruction of thyroid Autoimmune (Hashimoto’s Disease) Iodine deficiency Medications (ex.Lithium) Hypothyroidism • • • • More common in women Lab assessment: T3, T4 TSH Monitor for depression Interventions • • • • • Levothyroxine sodium (Synthroid) Avoid sedatives & narcotics Monitor vital signs Monitor for S&S of hyperthyroidism Family teaching re: mental status Myxedema Coma • Hypothyroid Crisis --> rare but serious • Etiology: – acute illness/ trauma – * rapid withdrawal of thyroid meds. – use of sedatives / narcotics – surgery – exposure to cold Myxedema Coma • • • • • temp / BP Na+ blood glucose Lactic acidosis Coma Thyroiditis Acute – Bacterial Pain Temp. Malaise Dysphagia – TX Antibiotics Subacute – Viral Temp. Chills Pain in jaw and/or ear – TX ASA and steroids Thyroid Cancer • Painless nodule in thyroid • Treatment : –RAI –Surgery Hyperparathyroidism Pathophysiology • PTH secretion = Ca+ Phos – increased reabsorption of calcium by kidneys = • increased excretion of Phosphate • Causes –tumors –hyperplasia of parathyroid gland Data Collection : • PTH – renal calculi – nephrocalcinosis – bone decalcification • serum Ca – GI: anorexia, N&V, epigastric pain, constipation, – M/S: fatigue & lethargy – [serum Ca] > 12 mg/dl = mental status Complications: • Renal Failure • Fractures • Collapse of vertebra Collaborative Management : focuses to decrease serum calcium • Diuretic & Fluid Therapy – Lasix /0.9% Na Cl • Drug therapy – Phosphates – Calcitonin -miacalin spray Skel. Release Renal clearance – Calcium Chelators - binds with Ca. -< dec. Levels of free calcium • Parathyroidectomy Hypoparathyroidism • PTH • Etiology (rare) – thyroid / parathyroid surgery – Hypomagnesemia – Idiopathic