* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 5 Unit Picturing Polygons
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Curvilinear coordinates wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
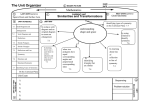
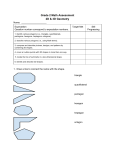
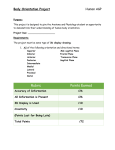
LISBON SCHOOL DEPARTMENT UNIT DESIGN OUTLINE Unit Title: Picturing Polygons Unit Designers: DJ Thorne, Jamey Martin, Marcia Jolicoeur, Candace Barrett Level(s): 5th grade Content Area: Career Prep English Language Arts Time Span: Health/PE Mathematics 8 weeks M&C Languages Science & Tech Social Studies Visual & Perf. Arts Summary of Unit: Students will work with solid figures, learning their features such as edges, vertices, and faces. Classifying the objects support students’ understanding of how the shapes are similar and different. An understanding of how to describe position and direction in two dimensions is completed in two ways. First, working on a Cartesian plane by locating points to determine distance both horizontally and vertically and secondly by measuring angles in degrees. Students continue to work with two dimensional objects by identifying and creating figures with rotational or line symmetry. Additionally, they show symmetry and create patterns by sliding, rotating, or reflecting the figures. Content Standards/Performance Indicators: MATHEMATICS Geometry C.1. Students identify, describe, and classify solid figures. a. Identify edges, vertices, and faces in three-dimensional figures. b. Describe and classify solid figures according to the number of edges, faces, and vertices as well as the shapes of faces. C.4. Students understand how to describe position and direction in two dimensions. a. Locate points on the Cartesian plane. b. Determine horizontal and vertical distance on the coordinate plane. c. Measure angles in degrees. C.5. Students reflect, slide, and rotate plane figures. a. Identify figures with rotational or line symmetry. b. Create figures with rotational or line symmetry. c. Slide, rotate, or reflect figures to create patterns or demonstrate congruence. ELA Reading A.1. Students read and draw conclusions from texts, within a grade appropriate span of text complexity, by applying their knowledge and strategies of comprehension, vocabulary, alphabetics, and fluency. b. Demonstrate ownership of appropriate vocabulary by effectively using a word in different contexts and for different purposes. Approved for posting by CART 5.4.2011 1/4 COMMON CORE: Geometry - 5.G Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems. 1. Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. Understand that the first number indicates how far to travel from the origin in the direction of one axis, and the second number indicates how far to travel in the direction of the second axis, with the convention that the names of the two axes and the coordinates correspond (e.g., x-axis and x-coordinate, y-axis and y-coordinate). 2. Represent real world and mathematical problems by graphing points in the first quadrant of the coordinate plane, and interpret coordinate values of points in the context of the situation. Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties. 3. Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that category. For example, all rectangles have four right angles and squares are rectangles, so all squares have four right angles. 4. Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties. Key Pre-Requisites: Knowledge: Shapes can have lines of symmetry. If shapes are congruent they are the same. Shapes have attributes. Some shapes can be classified as quadrilaterals and triangles. Skills: Identify the line of symmetry. Recognize congruent figures. Identify parallel lines, perpendicular lines, and sides. Identify and sketch quadrilaterals and triangles. Enduring Understandings: Ordered pairs can be used to find location on a Cartesian plane. Classifying aids in understanding of similarities and differences. Knowing degrees of angles gives you the ability to describe location and position. Essential Questions: How can the representation of points on a Cartesian plane be applied in the real world? Key Knowledge and Skills students will acquire as a result of this unit: Knowledge: Vocabulary: vertices, solid figures, 3-D, base, Cartesian plane, coordinates Solid shapes are three dimensional, with edges, vertices and faces. 3-D shapes have names such as: prism, pyramid, cylinder, and sphere. Patterns can be created by sliding, rotating and reflecting figures with lines of symmetry. Skills: Identify edges, vertices and faces of three dimensional objects. Classify 3-D shapes into prism, pyramid, cylinder, and sphere. Create patterns and show congruency by sliding, rotating, and reflecting figures. Use a protractor to measure and draw angles. Locate, plot, and label coordinates on a Cartesian plane. Approved for posting by CART 5.4.2011 2/4 How will students provide evidence of their understandings? Determine an understanding of pre-requisites through a pre-assessment. Through assessment and feedback from the activities listed below. Summative End-of-unit assessment. Teaching and Learning experiences used to help students understand: Differentiated instruction will be provided based on formative assessments. Hook: Play Battleship. Introduce essential questions and key vocabulary. Introduce enduring understandings. Review attributes of quadrilaterals and triangles: lines of symmetry, congruent shapes, parallel and perpendicular lines, number of sides. Introduce quadrants of a Cartesian plane. Introduce the X and Y axes of a Cartesian plane. Introduce and practice locating, plotting, and labeling coordinates on a Cartesian plane. Assess and give feedback and provide opportunity for additional learning. Create polygons with lines of symmetry on a Cartesian plane. Introduce and practice sliding, reflecting, and rotating polygons over the X or Y axis on a Cartesian plane. Assess and give feedback and provide opportunity for additional learning. Introduce the classification of solid figures. Use protractors to measure and draw angles. Assess and give feedback and provide opportunity for additional learning. Introduce and practice rotational symmetry. Assess and give feedback and provide opportunity for additional learning. Provisions for Extending Learning: Classify other 3D solid figures; tetrahedron Draw polygons with multiple lines of symmetry on a Cartesian plane. Create a design with a variety of polygons that include slides, reflections, and rotations. How will technology be used to increase student achievement? Use computer to slide, reflect, and rotate basic shapes. Instructional Resources: Picturing Polygons, Investigation Unit Math-drills.com 3D shapes Geoboards Approved for posting by CART 5.4.2011 3/4 VOCABULARY FOR THIS UNIT: Polygon: triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, septagon/heptagon, octagon, nonagon, decagon, hendecagon, dodecagon, vertex/vertices angle: acute, obtuse, right degrees edges faces rotational symmetry line symmetry Cartesian Plane (coordinate grid) x-axis y-axis quadrants horizontal vertical slide reflect (flip) rotate two-dimensional three-dimensional congruent attributes/characteristics parallel perpendicular regular/non-regular polygon triangles: equilateral, isosceles, scalene, right triangle, acute triangle, obtuse triangle quadrilaterals: rectangle, square, parallelograms, trapezoid, rhombus ordered pairs/coordinates solid figure prism cylinder sphere pyramid protractor Attach a copy of the unit assessment tool, including criteria for evaluation of student performance/product. Prisms, Pyramids, and Polygons Approved for posting by CART 5.4.2011 4/4