* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download congenital heart disease - Easymed.club
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Marfan syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
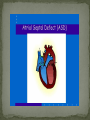
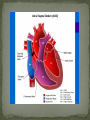
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
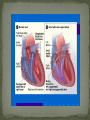
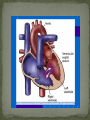
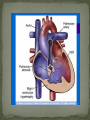
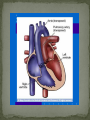
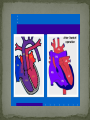
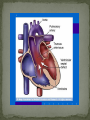
Dnipropetrovsk Medical Institute of Conventional and Alternative Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and pediatric CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE lecture №6 ~1% in the general population (6-8 per 1000 live births) Incidence in stillborns (3-4%), aborted fetus (10-25%), premature infants (2%) Diagnosis made in 40-50% by one week of age, in 50-60% by 1 mo of age Recurrence risk - if h/o one affected sibling – VSD, PDA 3% TOF, ASD2.5% Tricuspid atresia, Ebstein anomaly1% Inheritance- Dominant pattern – ASD, supravalvular aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Aortic regurgitation Marfan Syndrome: Aortic dilatation, aortic & mitral incompetence 5 % associated with Chromosomal anomalies: Trisomy 13, 18 (>90%), 21 (50%) 18 Trisomy - VSD, PDA, DORV 13 Trisomy - Dextocardia,VSD, PDA 21 Trisomy Downs syndrome - A-V canal defect, VSD Turner’s syndrome (40%) - Coarctation of aorta, aortic stenosis Deletion chromosome 22q11: Di George syndrome Familial cardiomyopathies: HCM, DCM Occur equally among males and females, but— More common in males: aortic stenosis, coarctation of the aorta More common in females: PDA, ASD High altitude Maternal Ds a) Diabetes: TGA ,VSD, situs inversus, single ventricle, hypoplastic left ventricle b) SLE: Congenital heart block 3. Maternal Infections: Rubella: PDA, pulmonary stenosis, VSD, ASD Mumps: Endocardial Fibroelastosis 4. Maternal Drugs: Lithium: Tricuspid valve abnormalities, Ebstein’s Anomaly Thalidomide Alcohol abuse: VSD - warfarin, anticonvulsants, antimetabolites , Phenytoin : Variable 1. Acyanotic 2. Cyanotic lesions Acyanotic volume load -L→R shunts pressure load obstr. ventric. outflow -ASD stenosis -VSD -AV canal -Patent ductus arterisus - Pulmonary valve - Aortic valve stenosis - Coarctation of aorta Cyanotic ↑ pulmonary flow ↓ pulmonary flow • TGA • Single ventricle • Truncus arteriosus • TAPVR w/o obstruction • TOF • Pulmonary atresia • Tricuspid atresia • TAPVR with obstruction Absence of cyanosis Frequent chest infections -Due to decreased lung compliance which leads to frequent respiratory tract infections Precordial bulge Excessive sweating - Tendency for CCF Failure to thrive - due to poor oxygen saturation in the growing tissues, persistent heart failure, and frequent respiratory infections with undernutrition Cardiomegaly Shunt & flow murmurs Plethoric lung fields Absence of cyanosis or frequent chest infections Normal precordial shape Forcible/heaving cardiac impulse, without cardiomegaly Delayed S2 Ejection systolic murmur, with thrill Absence of diastolic murmurs Normal sized heart with normal pulmonary vascularity Ventricular hypertrophy on ECG Chest pain- severe aortic stenosis lead to myocardial ischemia Cyanosis- Occurs under following circumstances 1. Reduced pulmonary blood flow in defects with right ventricular outflow tract obstruction 2. R→L as in tetralogy of Fallot 3. Discordant ventriculoarterial connections – TGA 4. Mixing of venous and arterial blood – truncus arteriosus or single ventricle Hypercyanotic Spells Fallot's tetralogy and defects with Fallot's physiology **Due to pulmonary infundibular stenosis Clubbing Polycythemia Murmurs FTT Heart Failure occurs in following situations : Volume overload- all defects with L →R shunt like VSD,ASD,PDA Pressure overload - in pulmonary and aortic valve stenosis Intrinsic myocardial diseases cardiomyopathies, Decreased or increased diastolic fillings tachyarrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. 1. 2. 3. Chest X-ray: shape & size of heart, vascularity, pulmonary edema, lung & thoracic anomalies ECG: Hypertrophy Hematology: anemia (? Physiological, iron deficiency), polycythemia Echocardiography/Doppler Echo: intracardiac anatomy of all structural defects , hemodynamic data regarding pressure gradients across valves, cardiac contractility, flow, vegetations 6.Cardiac catheterisation: calculates 02 saturation, shunt volumes, pressures, etc Indications Preoperative identification of the lesions Preoperative physiological assessment of pulmonary artery pressure and press gradient Therapeutic interventional procedures 1.Baloon dilatation of stenotic valve and coarctation of aorta 2. Blade and baloon atrial septoplasty 3. Non- surgical closure of PDA ,ASD 4.Catheter ablation of arrythmogenic focus by pacemaker implantation 7. Exercise testing 8. MRI 9. Angiocardiography 10.Interventional catheterisation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Early identification of problem Supportive management: Treatment of heart failure Prevent frequent RTIs Maintain required weight , Hb Infective endocarditis prophylaxis Regular follow-ups Surgical management Three major types Ostium secundum most common- 50-70%, In the middle of the septum in the region of the foramen ovale Ostium primum -30% Low position Form of AV septal defect Sinus venosus Least common-10% Site-at entry of superior venacava into right atrium Mitral valve prolapse associated in ~20% with ostium secundum or sinus venosus defect Thank you for attention