* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Air Pressure, Forces, and Motion
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
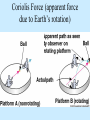
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
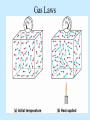
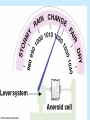
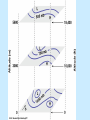
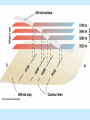
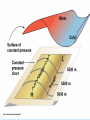
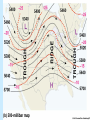
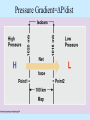
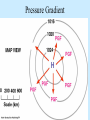
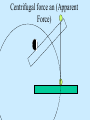
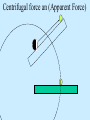
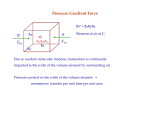
Air Pressure, Forces, and Motion Meteorology 101 Dr. Robert M MacKay Pressure density Mass Volume M r V Temperature Volume The Gas Law P=C*density*Temp P=2.87 r T Gas Laws Gas Laws Constant P as T increases V Increases/decreases Constant V as T increases P Increases/decreases Constant T as V increases P Increases/decreases Constant V,T as M increases P Increases/decreases Gas Laws Constant P as T increases V Increases/decreases Constant V as T increases P Increases/decreases Constant T as V increases P Increases/decreases Constant V,T as M increases P Increases/decreases Mercury Barometer Pressure Measurement 1013 mb = 1013 hPa Millibar hectoPascal 1013 mb 29.92 in Hg 76 cm Hg 760 mm Hg 760 Torr 14.7 psi Station Pressure + Elevation(meter)/10 = Sea Level Pressure Newton’s Laws of Motion Newtons 3 laws of motion 1. Law of inertia 2. Net Force = mass x acceleration (F=MA) 3. Action Reaction 1st Law (Law of Inertia) Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. acceleration = 0.0 unless the objected is acted on by an unbalanced force 1st Law Inertia (The intrinsic tendency of an object to rest changes in motion) Mass is a measure of an object’s inertia Mass is also a measure of the amount of an object’s matter content. (i.e. protons, neutrons, and electrons) Newton’s 2nd Law • Net Force = Mass x Acceleration • F = MA Newton’s Law of Action Reaction (3rd Law) • You can not touch without being touched For every action force there is and equal and oppositely directed reaction force Forces that influence the wind 1. Pressure Gradient Force 2. Coriolis Force 4. Friction On average gravity nearly balances the vertical Pressure gradient (hydrostatic balance) Pressure Gradient=∆P/dist Pressure Gradient Centrifugal force an (Apparent Force) Centrifugal force an (Apparent Force) Coriolis Force (apparent force due to Earth’s rotation) Coriolis Force Coriolis Force Coriolis Force Coriolis Force