* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06.Heart murmur syndrome congenital and acquired heart disease
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Infective endocarditis wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
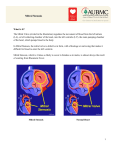
TASHKENT MEDICAL ACADEMY Chair the doctor of the general practice on pediatrics LECTURE 6 courses for students Heart murmur syndrome: congenital and acquired heart disease Compiled by: MD Associate Professor Khanbabayeva D.U. Tashkent 2012 Name of the lecture: heart murmur syndrome: congenital and acquired heart disease For the 6th year students of medical faculty On the lesson - 2 hours PLAN 1. Syndrome is a heart murmur. 2. Functional heart murmur 3. Organic heart murmur 4. Differential diagnosis of functional and organic noise 5. Congenital heart disease 6. Defect - ventricular septal defect of the heart 7. Defect - an atrial septal defect of the heart 8. Tetralogy of Fallot 9. Acquired heart valvular disease 10. Mitral heart disease 11. Aortic heart defect 12. Diagnosis of acquired heart 13. Treatment 14. Prophylaxis REFERENCES 1. N.P.Shabalov. Children's diseases, 3rd edition, Moscow, -2005,-S.360-442. 2. AA Baranov, to Moscow, -2004,-S.360-392. 3. MJ Studenikin. Actual problems of pediatrics. -Moscow, -1988,-p.64-126. 4. R.A.Abdullaev. Clinical lectures on current issues in cardiology. , Tashkent, 1985,-p.161-199. 5. A.F.Tur. Childhood illnesses. , Moscow, 1985, p.354-367,. Diseases of the cardiovascular system occupy a leading position in the structure of human diseases by determining the level of disability and mortality in the population. The origins of many diseases of the circulatory system, usually slow-growing, lie in childhood, especially in the past decade the incidence of cardiovascular disease in children has increased by 3 times. Apparently, before the children of this pathology was more than expected, as in the same period have improved diagnostic capabilities. Noteworthy also increase the number of children with chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, including the disabled. Changed the structure of the cardiovascular morbidity of childhood decreased the frequency of rheumatic heart disease and infectious endocarditis, but increased the proportion of arrhythmia, hypertension, cardiomyopathy and functional disorders. Each year, an increasing number of children with birth defects and cardiometabolic disorders. The development of these diseases are often caused by dysplasia of the connective tissue of the heart, family history and genetic defects. In children, the subjective symptoms of circulatory disease are often absent or minimally expressed. Later, as the child grows, and exposure to a variety of different factors, this pathology is manifested, in some cases leading to death. From the above it follows that not only pediatrician and general practitioner should have an idea about the full spectrum of circulatory disease in children. Should pay attention to the weakness, shortness of breath, complaining, not peculiar to children (heart pain, palpitations) coloration of the skin, chest wall deformity, and fingers, retarded physical development, the presence of a heart murmur on auscultation and timely conduct the necessary examination of the child. Prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system and adverse outcomes associated with heart disease and blood vessels in adults should begin in childhood. Clinical examination of the state of the cardiovascular system should be carried out at any and all children from the newborn period with a measurement of blood pressure in the arms and legs, ECG, echocardiography. In the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of cardiovascular disease plays a major role definition (auscultation) a heart murmur. Auscultation distinguished: 1) functional noise 2) organic noises The function is called noise, non-violation of the anatomical structure of the endocardium. Functional noise in children at any age, most often (30-50%) - in adolescents. In their origin can be set a number of reasons. Functional noise can occur under the influence of noncardiac causes - anemia, compression of large vessels large bronchopulmonary lymph nodes or thymus gland, etc. The study of the sounds of the heart - one of the most integral and valuable techniques in cardiac diagnosis. In the study of heart sounds in children, using auscultation and phonocardiography, pediatrician often finds besides the basic sounds - tones of different nature and origin of the noise. In clinical practice to share noises are heard in the heart in children in both organic and inorganic, or functionality. The former include noise due to congenital anomalies of the heart and great vessels, and the noise created by endocardial disease and related valvular. Functional noise usually means all systolic noise, non-valvular lesions with acquired or congenital heart disease. The detection rate of heart murmurs in children of different age groups varies and increases with age. The physical nature of both organic and functional heart murmur has long attracted the attention of researchers. In the last century it has been suggested that the cause of heart murmurs are oscillations of the particles of blood, resulting in its turbulent flow in the cavities of the heart. Studies in recent years have confirmed the accuracy of these assumptions. Fluctuations in blood particles arising from its turbulent flow in the cavities of the heart or in the initial parts of the large vessels leaving the heart cavities, are transmitted cardiac tissue and their environment. On the way from the heart to the outer surface of the body of the noise fades, being absorbed by the surrounding tissues. A variety of reasons (fever, autonomic-endocrine disorders, exercise, etc.), causing increased heart activity and acceleration of blood flow can improve the turbulence of blood, increase the intensity of such noise. At heart defects mechanism of noise can be easily understood by analyzing the motion of the fluid in the tube. Noises occur in tubes of variable section when driving in these fluids. They owe their origin to a turbulent motion of fluid particles and the vibration of the tube walls. If you increase the rate at which fluid under pressure and squeeze tube, it creates the conditions for a maximum of amplified noise. Functional mechanisms of noise are very diverse. Noise can be caused by turbulence in the blood vessels. Acceleration of blood flow may occur with anemia (due to the decrease in blood viscosity), fevers, adrenergic influences. In these cases, there are conditions for a more pronounced turbulent blood flow, systolic noise "exile" in the main blood vessels of the heart are usually short - takes 1/3 - 1/2 systole. The correct assessment of the noise helps monitor the dynamics, since the age of functional noise or weaken or disappear altogether. Organic noises are heard in the defeat endocardium - heart valves. Differential diagnostic features of functional and organic noise FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES OF NOISE NOISE NOISE ORGANIC 1 tone soft, undefined, music hard, tough, blowing 2 Duration Short takes less ¬ largest part of systole long, occupies a large part of the system ¬ toly 3 Irradiation Distribution little, does not extend beyond the limits of the heart is well propagates to the heart area and beyond 4 Changing the load varies greatly, often weakens changes little, often amplified 5 Relationship with tones not usually associated connected 6 Registration for Low or srednechastot PCG-tion, is a smaller part of systole, with tones of high frequency is not related, occupies most of systole, usually associated with tones Diastolic murmur of childhood in most cases have an organic genesis. Atelocardia UPU - morphological abnormalities of the heart and great vessels. CHD usually formed by 2-8-week fetal development as a result of breakdown of the processes of embryogenesis. CHD observed with an average of 8.5 per 1,000 live births. Etiology. Specific causes of CHD are unknown. They are often associated with chromosomal abnormalities. Most often detected trisomy of chromosomes 21, 18 and 13. defects in the genetic code and violations of embryogenesis may be acquired under the influence of the fetus and the mother of some adverse factors (radiation, diabetes, alcoholism, drug abuse, maternal endocrine disease, viral infections, transferred a woman in one trimester, pregnant reception of certain drugs). Importance in causing diseases of the heart and blood vessels are of mixed viral-virus and enterovirus infection, transferred fetus in utero. Pathogenesis. These factors, affecting the fetus during critical moments in the development, violate the structure formation of the heart, cause dysplastic changes of the entire skeleton. Is incomplete, incorrect or untimely closing walls between the atria and ventricles, valves defective education, lack of rotation of the primary heart tube to form aplazirovannyh ventricles and wrong location of major vessels are stored holes inherent in the fetal circulation. Fetal hemodynamics usually without suffering, and the child is born well developed. In this case, the UPU appear only in a few months or weeks, and sometimes for the second or third year. Depending on the characteristics of blood flow in the large and the small circle of the UPU is divided into 3 groups: Classification of congenital heart disease Hemodynamic without cyanosis (WAN) with cyanosis (blue) Overflow of the pulmonary circulation ASD VSD Open arterial (Batalov) duct transposition of great vessels With the depletion of the pulmonary circulation Isolated pulmonary stenosis Tetralogy of Fallot With the depletion of the systemic circulation aortic stenosis Aortarctia Vices Overflow pulmonary circulation up to 80% of all CHD. They are united by the presence of abnormal communication between the large and small circulation and discharge of blood from the venous to the arterial system. Overflow of the right heart leading to their gradual hypertrophy, resulting in discharge direction can be reversed, resulting in growing and total defeat of the heart and circulatory failure. Overflow of a small circle contributes to acute and later chronic diseases of the respiratory system. At the core of depleted defects of the pulmonary circulation is often narrowing of the pulmonary artery. Inadequate venous oxygen saturation leads to constant hypoxia and cyanosis, underdevelopment, the formation of fingers in the form of "clubbing". When vice depleted systemic circulation vessels of the lower half of the body get a little blood. With chronic left ventricular failure, often with ischemic or with coronary artery disease. The clinical picture. It depends on the size and location of the defect barriers, degree of narrowing of the vessel, the direction of discharge of blood and changes in this direction, etc. For small defects, the clinical manifestations may be absent. AMS should be suspected in identifying gaps in the physical development of the child, the appearance of dyspnea when moving, pale or cyanotic color of the skin. On examination of the chest may reveal a "heart hump" on palpation of areas of the heart - systolic or systolic and diastolic tremor. Auscultation, pay attention to the split tone, accent II tone of the aorta or pulmonary artery. For the majority of defects can listen systolic rough, sometimes scraping noise. He often carried on his back, and usually does not change with a change in body position and load. The special features of the "blue" vices, combined with the narrowing of the pulmonary artery (tetralogy of Fallot), except for total cyanosis include favorite position rest on his haunches and odyshechno-cyanotic attacks associated with spastic narrowing of the outflow tract of the right ventricle, and acute hypoxia of the brain. During the UPU has a frequency: 1. Initial phase of adaptation. After birth, the child adapts to hemodynamic instability caused by CHD. 2. Relative phase compensation occurs for 2-3 year life and can last for years. The child's condition and its development is enhanced by myocardial hypertrophy and hyperfunction of different parts of the heart. 3. The terminal phase is associated with a gradually developing myocardial dystrophy, kardiospazmom, reduced coronary blood flow. Complications AMS can be complicated by bleeding in the brain, heart attack, and the addition of infective endocarditis. Laboratory tests. In the analysis of blood "blue" defects detected reduced PaO2 and PaCO2 increase, increase in red blood cells, hematocrit and concentration Hb. On ECG detect signs of hypertrophy and overload individual chambers of the heart: right heart - with "blue", left - with the "pale." PCG to record systolic and diastolic sounds. Echocardiography allows visualization of defects partitions. When X-rays reveal cardiomegaly, cardiac shadow defiguratsiyu (mitral, smooth waist, aortic "shoe" with tetralogy of Fallot). When full, the evils of a small circle, increased vascular pattern. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis. The diagnosis of CHD were based on the early appearance of fatigue, dyspnea, cyanosis, "heart hump", jitter over the area of the heart, cardiomegaly, and heavyduty noise carried out on the back. Diagnosis is confirmed by detection of ECG signs of overload hypertrophy and heart chambers, fixing noise PCG, visualization blemish on echocardiography, the detection of violations of arterial blood gas analysis. Identify the configuration change of heart on the chest radiograph. Differential diagnosis in infancy, early childhood spend with birth early and late carditis. After 3 years with non-rheumatic carditis, rheumatic fever, bacterial endocarditis, cardiomyopathies. It is also necessary to differentiate between a CHD. Congenital heart disease with the enrichment of the pulmonary circulation 1. Ductus arteriosus (PDA). This defect connects the initial portion of the aortic arch to the pulmonary artery near its bifurcation. Most newborns CAP ceases to function in the first hours or days after birth. Preservation of function flow after the newborn period should be regarded as congenital. Hemodynamic disturbances - is reset blood from the aorta to the pulmonary artery, resulting in an overflow of the pulmonary circulation and overload left chambers of the heart. With the development of pulmonary hypertension is overloaded and the right ventricle. Clinically at the end of the first year and the second or third year of life. Heart borders extended to the left and up, in the second intercostal space to the left of the sternum auscultated systolic and then sistolodiastolichesky (machine) noise, which takes place at the apex of the heart, neck vessels and the aorta in the interscapular space, II tone on pulmonary strengthened. Further noise may subside or disappear altogether, indicating that pulmonary hypertension, there is shortness of breath and cyanosis. Attenuation is threatening symptoms suggestive of approaching the terminal phase defect. The maximum blood pressure is normal, the minimum - sharply reduced. Pulse pressure is high. X-rays: an increase in the left heart and blood circulation in the lungs. 2. Atrial septal defect (ASD) This is one of the most common defects. Hemodynamic instability - defined discharge of arterial blood to the left to the right, which leads to an increase in minute volume of pulmonary circulation. Malformation detected at birth or within the first year of life, the rest of it is diagnosed later, usually at the age of 2-5 years Have a history of addiction to repeated respiratory infections and pneumonia. Complaints of shortness of breath, fatigue, pain in the heart. Heart borders expanded across and to the right. Auscultated not rough systolic murmur in the second and third intercostal space on the left of the sternum, II tone in the pulmonary artery and enhanced split. X - ray images lung shadows expanded. Transverse shadow hearts enlarged by right heart and pulmonary artery. Prognosis depends on the size of the defect and the severity of hemodynamic disturbances. 3. Ventricular septal defect (VSD) This is one of the most common congenital heart defects. It can be placed in the membranous or muscular part of the septum in the form of an oval, round or coneshaped holes. The hole diameter is from 1 to 30 mm. Hemodynamics - discharge of blood from the left ventricle to the right, the overflow of the pulmonary circulation and an overload of both ventricles. Hemodynamic disturbances occur in children aged 2-4 months, when reduced pulmonary vascular resistance. More favorable clinical course are defects in the muscular part of the septum. Children with high VSD has complaints of shortness of breath, coughing, cyanosis, weakness, fatigue, frequent lung infections. Pale skin, with a load - cyanosis. Auscultation left of the sternum in the third or fourth intercostal space is defined by systolic tremor which has taken place over the entire area of the heart and back. X-rays: increased pulmonary vascular markings. Heart size can be increased to varying degrees with the increasing predominance of the left, both ventricles, or just right. The prognosis of small defects is not accompanied by hemodynamic instability. If severe, with the development of heart failure, surgery is needed. Birth defects from depleted pulmonary circulation The impoverishment of the pulmonary circulation - the result of barriers to the outflow of blood from the right ventricle. 1. Isolated pulmonary stenosis (ISLA). Undivided leaflets lead to a narrowing of the valve opening, reducing blood flow in the pulmonary circulation and right ventricular overload, cough, enlarged the boundaries of the heart in the transverse size. In the second intercostal space to the left of the sternum auscultated rough systolic murmur, II tone on the pulmonary artery is weakened, I reinforced the tone at the top. X - ray of right heart and pulmonary artery usually. 2. Tetralogy of Fallot This is one of the most common defects that occur with cyanosis: A) pulmonary stenosis B) high VSD B) transposition of the aorta D) right ventricular hypertrophy Hemodynamic instability: 1. comes in a small circle enough blood (pulmonary stenosis) 2. but in a large circle through the VSD and the aorta is reset venous blood. Children behind in physical development, revealed deformation of fingers and toes as "drumsticks." Cyanosis appears in the first year of life. The boundaries of the heart is normal or slightly enlarged to the left. Along the left sternal auscultated rough systolic murmur, II tone in the pulmonary artery is weakened. Hypoxemic episodes are: stimulation occurs, increasing cyanosis, syncope, seizures usually last from a few minutes to 10-12 hours X-ray - vascular pattern of light is depleted, the heart of small size, often in the form of boots with a pronounced waist and raised tip. Birth defects from depleted systemic circulation Vices for this group is characterized by an unfavorable course of the first phase with early heart failure. Coarctation of the aorta - congenital narrowing it to a limited area. Constriction of the aorta is found. Coarctation may be isolated or combined with a PDA. Due to the increased aortic pressure on left stomach, causing it to overload. Above the constriction has hypertension, which covers the vessels of the head, shoulders, upper extremities. Vessels of lower limb get a little blood. When combined with PDA coarctation had severe pulmonary hypertension. X-rays - an increase of the left heart. Treatment of patients with congenital heart disease With a poor during the first phase of the development of heart failure, refractory to conservative treatment, surgery is necessary at an early age. The most favorable time for surgery - the second phase (3-12 years). In the terminal phase of the surgical removal does not bring healing. Conservative treatment pursues two performance objectives: 1. emergency care in a catastrophic state 2. treatment of patients with a variety of complications and comorbidities Prevention - aims to protect the health of pregnant, especially in the early stages of gestation: prevention of viral and other infectious diseases, the exclusion of bad habits, gentle respect working conditions, proper nutrition, etc. Forecast - most patients favorable for life, provided timely diagnosis and skilled surgery in optimal time. Mortality in such cases is 1-2%. Mitral Valve Prolapse Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) - deflection of one or more mitral valve in the left atrium during systole of the left ventricle. This is one of the most frequent forms of violations of the valvular heart. PMK detected in 2-18% of children and adolescents, ie significantly more frequently than in adults. In cardiac PMK record significantly higher: up to 37% with CHD, 30-70% of patients with rheumatic fever and up to 60100% of patients with inherited connective tissue disorders. Etiology and pathogenesis By origin distinguished: 1. Primary (idiopathic) 2. secondary Primary PMC associated with connective tissue dysplasia manifesting as other mikroanomaliyami valvular structure. Connective tissue dysplasia is influenced by a variety of pathological factors acting on the fetus during the period of fetal development (gestosis, SARS, adverse environmental conditions, etc.) Clinic Complaints are very diverse: fatigue, headache, dizziness, fainting, shortness of breath, pain in the heart, a sense of disruption of the heart. Characterized - reduced physical performance, psycho-emotional lability, irritability, nervousness, anxiety, depressive and Hypochondria. The boundaries of the heart is usually not extended. The most informative auscultatory data: listen more isolated clicks or a combination thereof with pozdnesistolicheskim noise. Clicks fixed in the middle or at the end of systole, usually at the top or in the fifth point of auscultation of the heart. They are not held outside of the heart, growing in intensity in the upright position and during exercise. Isolated pozdnesistolichesky noise (rough, scraping) listen at the apex of the heart, it is held in the armpit and is enhanced in the upright position. Holosystolic noise, reflecting the presence of mitral regurgitation, which occupies the entire systole, is stable. Instrumental studies On radiographs determine normal or reduced size of the heart. Often find bulging arc pulmonary artery. On ECG transient or persistent violations of ventricular repolarization (T-wave amplitude decrease, reducing the segment ST), possibly lengthening QT. Echocardiography is the most informative, identify systolic displacement of one or both of the mitral valve, the signs of mitral regurgitation. Treatment Correction of autonomic disorders. Apply tools to improve myocardial metabolism (potassium orotate, inosine, riboksin), vit. B5, B15, levocarnitine. Improve the effectiveness of the drug magnesium exchange - orotic acid, magnesium salt (magnerot). If necessary - β-blockers (propranolol), antiarrhythmic drugs. Children with MVP are subject to additional monitoring with regular examination (ECG, echocardiography, etc.) Infective endocarditis This is an acute or subacute inflammation valve and / or parietal endocarditis caused by various pathogens. Infective endocarditis - one of the known causes of death in children and adolescents. Etiology The most common cause of infectious endocarditis now - viridans streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus. Rarely - enterococci, meningo-, air-and gonorrhea, Chlamydia, Salmonella, Brucella, and mushrooms. Infective endocarditis can be: A) innate B) Acquisition Pathogenesis Infective endocarditis and complicated due to several factors: A) change in the immune response B) connective tissue dysplasia B) damaged collagen structures and parietal endocardium valve hemodynamic effects and infectious D) violation of the rheological properties and coagulation D) characteristics of the causative agent The most common infectious endocarditis occurs in patients with the morphological structures of the heart defect in which the turbulent, slow or enhanced blood flow leads to a change in the valve or atrial endocardium (tetralogy of Fallot, a small ventricular septal defect, open Botalov duct, Mitral Valve). Circulating in the blood of an infectious agent is deposited on damaged endocardium of the heart, causing inflammation, fibrin deposition and formation of thrombotic masses (vegetations), and possibly primary thrombosis. Later sprawling vegetation can break off and cause a pulmonary embolism and major vessels large and small circulation. Distinguish three phases of pathogenesis: 1) infectious-toxic 2) immunoinflammatory 3) dystrophic Classification Clinical classification of infective endocarditis (Demin AA, 1978) Etiology-cal characteristics of pathogenic-Atlantic PHASE DEGREE AKTIVNOS variants are CURRENT CLINICAL morpho-logical BODY SHAPE AND PATHOLOGY Strepto-coccus Staphylo-coccus Pneumococcus Hemophilia-tion coli Brucella Chlamydia Intestinal and sinegnoy-tion coli Klebsiela Proteus Viruses (Coxsackie) Mushrooms Rickettsiae infectious-toxic Immunovos-palitelnaya Dystrophic I degree (minimum) Grade II (moderate) Grade III (severe) acute Subacute Abortive primary Secondary Heart, heart myocardium Vessels. DIC, vasculitis, thrombosis Kidney: glomerulonephritis rit ¬ Liver - hepatitis, cirrhosis Lungs - abscesses, pneumonia Nervous system - meningoencephalitis or plegia, brain abscess Clinic Symptoms consists of three main syndromes: 1) toxicity 2) endocardial lesions 3) thromboembolic complications In the initial phase - fever, extensive toxicity, sweating. Children most often affects the aortic valve and the mitral valve in the form of their failure. In secondary bacterial endocarditis changes are noted in the lesion has endocarditis, thromboembolic complications occur - hemorrhagic rash, hematuria, heart attacks internal organs. Diagnosis An additional method for the diagnosis can serve as echocardiography - with which it is possible to detect embolic vegetation on the valves. Treatment 1) The massive and prolonged antibiotic therapy 2) Remediation of foci 3) Anticoagulants - Heparin Myocarditis In their daily work the doctor quite often the patients with myocarditis of different etiologies. Unfortunately, the diagnosis of the disease is often not installed at all or installed later. Myocarditis is often under the guise of rheumatism or tonzillokardialnogo syndrome. Etiologies of myocarditis can be a variety of infectious and non-infectious agents nature. The most common causes of myocarditis are infections - influenza, SARS, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis - ie diseases caused by streptococcal infection. One of the common causes of myocarditis is rheumatism. For rheumatic myocarditis characterized by the formation of granulomas talallaevskih ashof-and endocardial lesion. In infectious-allergic myocarditis process is localized in the parenchyma or infarction, or in the interstitial tissue. Complaints of pain in the heart, irregular, dyspnea, palpitations, growing at a voltage. To complaints of a general nature - general weakness, fatigue, low-grade fever, sweating, arthralgia, myalgia. On examination, attention is drawn to pale skin, sometimes a face pastosity. Of the heart can be noted - expanding the boundaries of the heart, muted tones, weakening, sometimes splitting the first tone, weak systolic murmur, gallop rhythm, extrasystoles. On ECG voltage reduction of electrocardiogram waves, most of the T wave voltage, often-segment ST. In the analysis of blood leukocytosis, accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Creactive protein is slightly elevated. In patients with myocarditis in the ECG, we find more pronounced diffuse myocardial changes, changes in the PCG insignificant. Infectious-allergic myocarditis is a very variable disease as the nature and the river. With weakly expressed infectious-allergic myocarditis general condition of patients varies slightly, they make usually numerous complaints (cardiac and general). In the first place there are heart pain (80-90%), there is low-grade fever, often tachycardia. Auscultation I relaxed tone, and auscultated systolic murmur at the apex, the ECG - a significant reduction of the T wave in the precordial leads. With moderate myocarditis there are elements of objectivity: shortness of breath associated with physical exertion, acrocyanosis, tachycardia, incomplete atrioventricular block, headache, enlarged heart, etc. In marked myocarditis sharply worsen the overall condition of the patient, sometimes a heart failure, shortness of breath even at rest, persistent pain in the heart, the frequency of permanent, headaches, 1 tone sharply weakened, rough systolic murmur, as if to get features organic, which is often cause of diagnostic errors. Myocarditis is usually favorable outcome, but about 20% of the inflammatory and degenerative changes in the muscle fibers and interstitial tissue gradually undergoes cicatricial transformation, resulting in growing miokardichesky cardio. As a result of sclerotic changes in the myocardium and the conduction system often observed episodes of paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, arrhythmia, which is even more tired of the myocardium and contribute to the weighting decompensated heart. Treatment of acute myocarditis known etiology should be specific. It should be remembered that for every suspected myocarditis during infection or after the diet and should be prescribed bed rest. Strict bed rest must be observed until the end vse clinical manifestations of myocarditis and less restrictive for another 15-20 days. In dplneyshem needed PHYSIOTHERAPY. From the diet excludes animal protein and is recommended only lacto-vegetarian foods rich in vitamins. Acquired heart disease - mainly found in rheumatism, rheumatic heart disease during the return. What happens in the valvular rheumatic process in evolution? Cell infiltration in the field, often through the closure of valves, is the deposition of small blood clots that are gradually turning into a dense granulation tissue. This granulation tissue, the size of a pinhead to millet grain, forms red-brown warts. Later granuloma zarubtsovyvaetsya and gradually developed fibrous tissue that shrinks and shortens, disfiguring valves. As a result, they become regidnymi not closed atrioventricular opening and developing their failure. In return, the repeated attacks of rheumatic valve further wrinkle and the mouth of the venous stenosis occurs hole. Consequently, both the insufficiency and stenosis artrioventrikulyarnogo shaped holes. In clinical practice, we encounter patients with associated heart disease with a prevalence of stenosis atrioventricular opening, the mitral valve. Thus, the evolution of rheumatic mitral can distinguish normal phase pure mitral insufficiency, then the phase of its combination with stenosis and finally phase dominance stenosis atrioventricular opening. It should, however, be very careful when making a diagnosis valvular heart on the basis of only systolic murmurs, for systolic murmur may have a functional origin. It is safe to diagnose mitral insufficiency only when there is a constant systolic murmur, weakened over the top of the first tone and emphasis of the second tone of the pulmonary artery. It should be said about the three forms or variants of mitral valve insufficiency. The first form, or option - the muscle-mild mitral regurgitation caused by functional changes in the muscular or neuro-muscular system of the heart. The second form - muscle-mitral insufficiency caused by organic changes in the myocardium of different degrees. The third form - mitral insufficiency caused by organic changes of the mitral valve. The first form is common and may be due to a variety of reasons (various degenerative and inflammatory changes of the myocardium, with common debilitating infections, anemia, nerve disorders extracardiac effects on the heart, etc.). In all such cases, the mitral valve insufficiency and occurs only ne6znachitelna unstable systolic murmur. The second form is the result of atherosclerosis and miokardicheskogo cardiosclerosis and severe degenerative changes in the myocardium. This includes failure of the mitral valve, which is observed frequently as a result of strong tonogennogo myogenic and expansion of the left ventricle in aortic insufficiency more. The third form - mitral insufficiency due to changes in the valve itself, in most cases is the result of rheumatic endocarditis. This defect is characterized by a blowing systolic murmur at the apex. Duration and sonority systolic murmur is different from relatively short to pansystolic. On ECG - there are signs of left ventricular hypertrophy, and sometimes the left atrium. When PCG-examination is recorded with a peak systolic murmur at the apex. Noise is well fixed in the middle and high frequency range, occupies most of systole, less pansystolic, usually decreasing, less band-like. The noise is closely related to the first, is often reduced tone. X-rays: in severe mitral valve heart gets mitral configuration (enlargement of the heart to the left and rounded waist). Mitral stenosis Isolated mitral stenosis in children is rare. Isolated mitral stenosis has symptoms sound pretty typical: I Flapping tone presystolic bubbling noise, mitral click. Often determined by palpation presystolic jitter (cat purring). Sooner there are complaints of shortness of breath, palpitations, signs of stagnation in the pulmonary circulation. For these patients, the characteristic may be cyanotic color, cyanosis of mucous membranes. A significant part of mitral valve stenosis in children occurs on a background of already formed mitral valve. In such cases, the initial symptoms of stenosis can be assumed from the increase in the sonority of the first tone, the appearance of the diastolic interval of noise on top. Sometimes one of the first signs of stenosis is the appearance of mitral valve opening clicks better listens along the left sternal border. On ECG mitral stenosis one of the typical signs is hypertrophy of the left atrium, and later the right heart. PCG to record an increase in the amplitude of the first tone, the lengthening of the interval PQ, first tone above 0.06 c. Usually written click opening of the mitral valve. Record the diastolic murmur. X-rays: an increase in the left atrium, and later of the right heart, signs of stagnation in the pulmonary circulation. Aortic heart defect Rheumatic endocarditis, aortic valves are affected and, although somewhat less than the mitral. Because of the comparative rarity of defeat aortic valve doctors do not pay enough attention to the issue of timely diagnosis of this type of defect. Meanwhile, the presence of noise in the projection diastolic aortic always indicates ogranicheskom defeat, whereas systolic murmur over the top can be a functional character. Aortic defect is more common in men, and mitral women. Aortic insufficiency is diagnosed by the presence of blowing systolic murmur, immediately following the second tone and is best auscultated along the sternum on the left. Heart borders extended to the left apical impulse strengthened and heard down. Peripheral symptoms include pallor, dance carotid, lower diastolic blood pressure - in children is rare. On ZHKG: signs of left ventricular hypertrophy. PCG: diastolic, ribbon-like noise, immediately following the first tone X-rays: the shadow of the heart takes the form of boots, with obvious signs of left ventricular hypertrophy. Aortic stenosis - as an isolated defect is observed mainly with congenital disease. As valvular often joins the aortic insufficiency. In the second intercostal space on the right appears quite rough systolic murmur with a maximum in the middle of systole, the noise is generally well conducted on vessels of the neck, sometimes there are heard better than on aortic valve. Other acquired defects in children are rare. Diagnosis In practice in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis, you can use the diagnostic criteria formed Kiesel-Johnson and supplemented A.I.Nesterovym. They are divided into the main "big" and additional or "small." Key: carditis, polyarthritis, chorea, erythema annulare, rheumatic subcutaneous nodules. Supplemental: A. Clinic: previous rheumatic fever or rheumatic heart disease, the evidence of effectiveness antirheumatic therapy, arthralgia, fever, fatigue, abdominal pain, epistaxis, and others. B. Laboratory: acute phase fraction (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Creactive protein, leukocytosis, increased sialic acid, etc.), increased capillary permeability, PQ interval prolongation on the ECG. The diagnosis of rheumatic fever is considered valid if two major criteria or one primary and two additional ones. In recent years, the WHO recommendations for the diagnosis of rheumatic fever is considered mandatory confirmation preceding streptococcal infection (increased levels of antistreptolysin O (ASO) or other steptokokkovyh antibodies isolated from the throat of group A streptococcus, recently transferred scarlet fever. Thus, the diagnosis of rheumatic fever is based primarily on the clinical picture. Laboratory parameters are of secondary importance, since the specific laboratory tests for the diagnosis of rheumatic fever in the present time. In clinical laboratory values are used primarily to determine the activity of the pathological process and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy. Treatment 1. In the acute phase - bed rest. Prolonged bed rest depends on the activity of the pathological process and the extent of damage to the heart. 2. Drug therapy - aimed at two main stages of pathogenesis - the infectious agent and allergic (immunologic) reaction. Maintains high sensitivity ... to many antibiotics, but preference should be given penicillin. Activity is high and significant damage to the heart to influence the allergic reaction is most commonly used combined use of glucocorticoids and non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Parallel to the main therapy is prescribed vitamins, potassium supplements, heart means. Forecast. Despite the fact that rheumatism now runs more benign than in previous years, the prognosis of this disease is serious and determined, above all, the outcome of heart disease. After the first attack in 10-15% of children formed a heart defect, after repeated attacks - 30%. Proper treatment of streptococcal infections, which began no later than the 30th day from the beginning, virtually guarantees the child from diseases rheumatism. Under the primary prevention refers to a set of measures that reduce the possibility of strep infection. Clinical supervision. After the end of the stationary and sanatorium treatment of patients with rheumatism comes under the supervision of a pediatrician - cardiology clinic. Particularly important in the prevention of recurrent attacks of rheumatic fever is attached properly conducted secondary prevention of rheumatic fever. Patients who have had rheumatic fever without evidence of primary, acute and subacute bitsillinoprofilaktika carried round of three years. Children with rheumatic heart disease undergoing primary valve lesion prevention held for five years. Preschool children bitsillin one dose of 600,000 IU every other week, school-age children at a dose of 1.2 million units every month. Bicillin-5 is used at a dose of 750 000 IU, the students - 1.5 million units, the dose frequency is the same as that of the bitsillina-1. In subsequent years, in parallel with bitsillinom ekstentsillin started using (this is also bicillin 5), which is kept longer in the blood, it is technically better prepared to be five times more expensive than bitsillin.